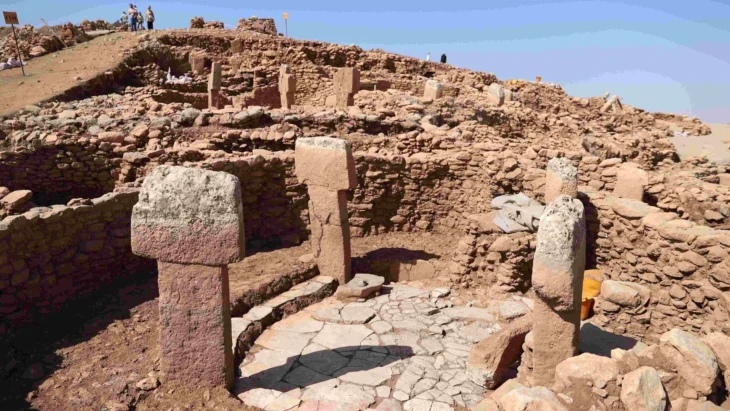
Archaeologists have uncovered one of the earliest known Christian buildings in the Arabian Gulf, located in Samahij, Bahrain, and providing the first physical evidence of a long-lost Christian community in the region.
Christianity today is not something usually associated with the Gulf, but the Church of the East, sometimes referred to as the Nestorian Church, thrived there until large-scale conversion to Islam began to occur after the religion was established in 610 CE.
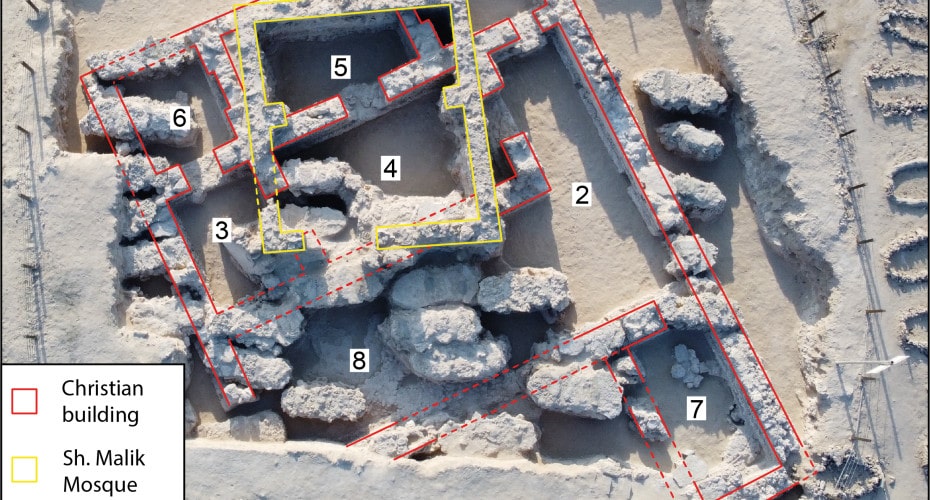
Located in Samahij, Bahrain, the radiocarbon dating of the building indicates that it was occupied between the mid-4th and the mid-8th centuries AD. The site was abandoned after the population converted to Islam.
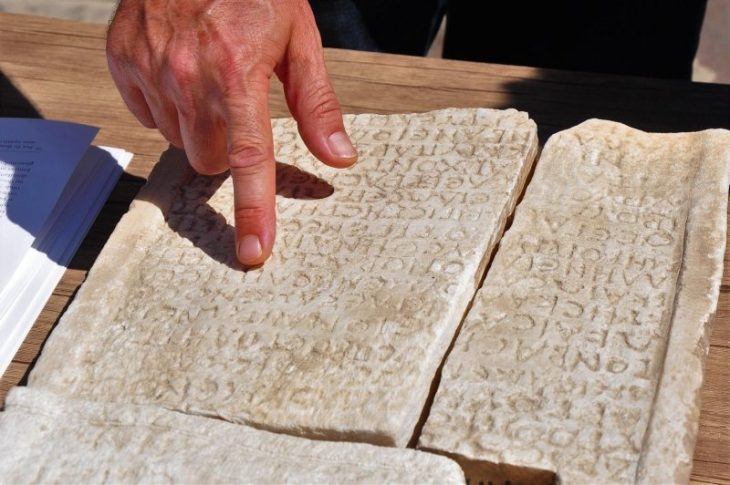
Its identity as a Christian site is shown by three plaster crosses found, two of which decorated the building and another which looks as if it had been carried or kept as a personal memento. Another indicator is a piece of graffiti scratched into the plaster of a Chi-Rho and a fish, early Christian symbols.
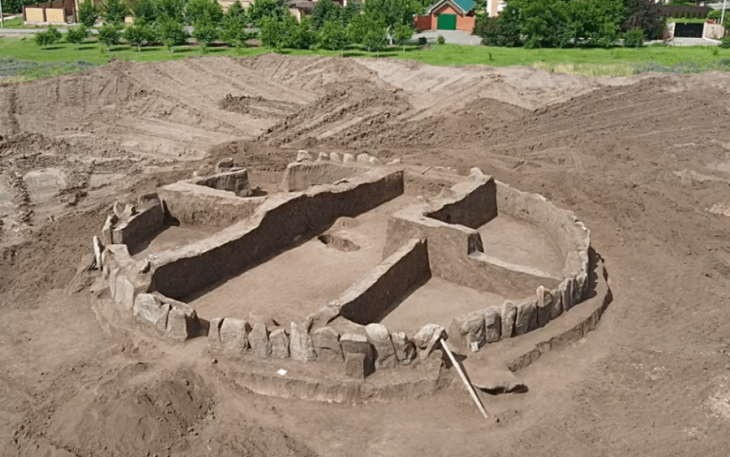
The excavations, by British and Bahraini archaeologists, under a mound in a village cemetery revealed a large building with eight rooms surviving. These included a kitchen, a refectory or dining room, a possible work room, and three living rooms. It had survived as it had a later mosque built on top of it.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
It is believed that the building might have been the bishop’s palace for the diocese that included Samahij, historically referred to as Meshmahig or Mašmahig. Records indicate a tumultuous relationship between Meshmahig and the central church authorities, with a bishop excommunicated in 410 and another condemned in the seventh century for challenging church unity.
Previously, the few Christian buildings—churches, monasteries, residences—discovered in the Gulf were found in remote areas of Iran, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, and eastern Saudi Arabia, mostly dating to later periods. Samahij is unique because it is situated in a modern settlement.
The occupants enjoyed a high standard of living, consuming pork—evidence of which disappeared after the Islamic conversion—fish, seafood, and various crops still under analysis.
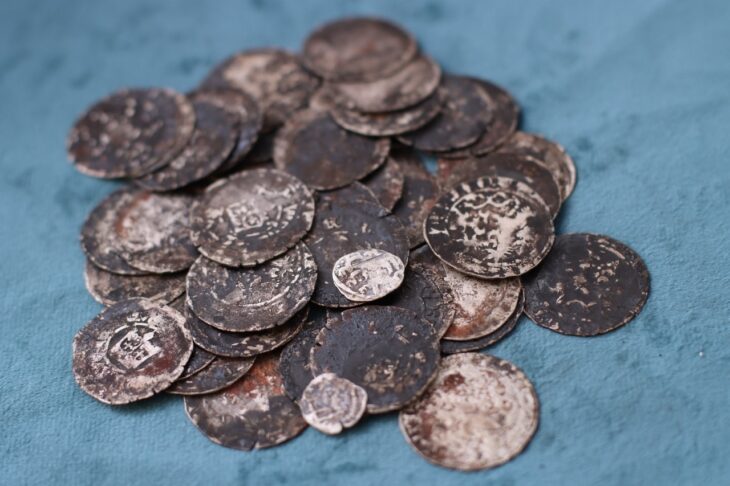
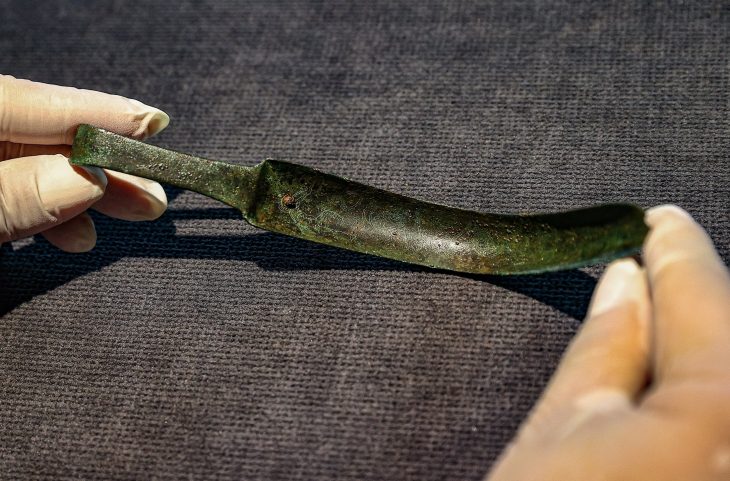
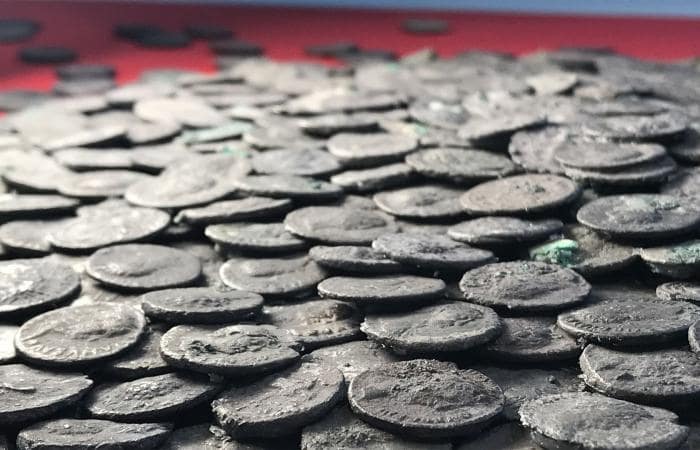
Additional discoveries include carnelian semi-precious stones beads and broken sherds of pottery of Indian origin, indicating trade. Also found were small wine glasses and copper coins minted in the Sasanian Empire. Spindle whorls and copper needles found in the building suggests textiles being produced, likely used in worship.
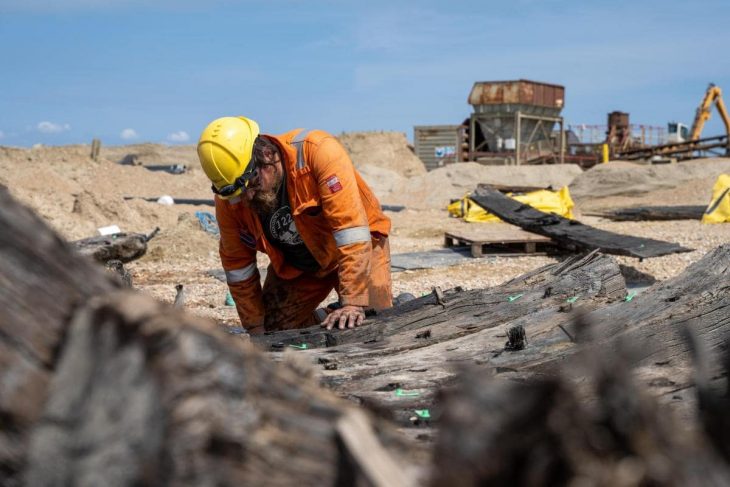
The building was excavated between 2019 and 2023 as part of a joint project led by Professor Timothy Insoll from the University of Exeter and Dr. Salman Almahari from the Bahrain Authority for Culture and Antiquities.
Professor Insoll noted that this is the first physical evidence of the Nestorian Church in Bahrain and offers a fascinating insight into how people lived, worked, and worshiped.
A museum is now being developed at the site to preserve and present this remarkable survival and is planned to open in 2025.
Cover Photo: University of Exeter