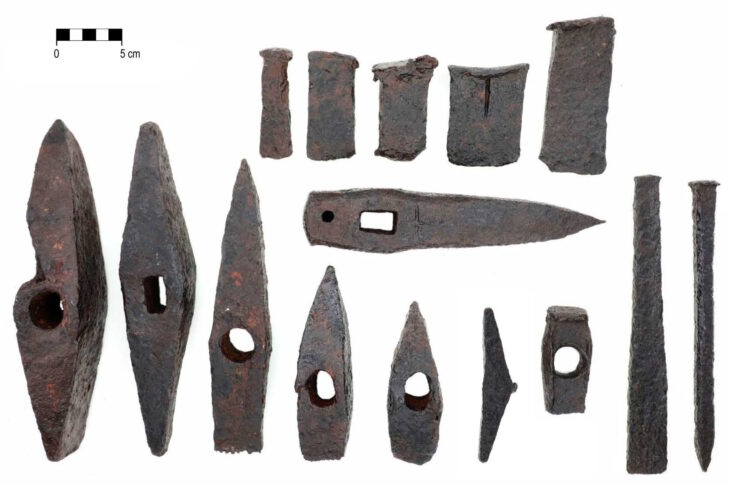
Archaeologists have discovered the first Etruscan domestic structure, dating to the 6th to 4th centuries BC, off the east coast of Corsica, the fourth largest island in the Mediterranean.
As part of a project to construct a single-family home in the municipality of Ghisonaccia in Upper Corsica, archaeologists from Inrap, the French National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research, have identified, excavated, and studied a single residential building, the first discovered in Corsica aside from public structures.
Until now, in Corsica, Etruscan tombs had been found, but not the homes. In the municipality of Aleria, in the Lamajone area (seventy kilometers from Bastia), a team of French researchers from Inrap had discovered, under a Roman necropolis, an extraordinary hypogeal Etruscan tomb dating back to the 4th century BC containing a skeleton and dozens of artifacts.
“This discovery constitutes privileged evidence of the presence of this pre-Roman civilization on the island through the richness of its ceramic furniture and because it is the first domestic settlement excavated in Corsica linked to the Etruscan culture” commented the archaeologists of the Inrap.
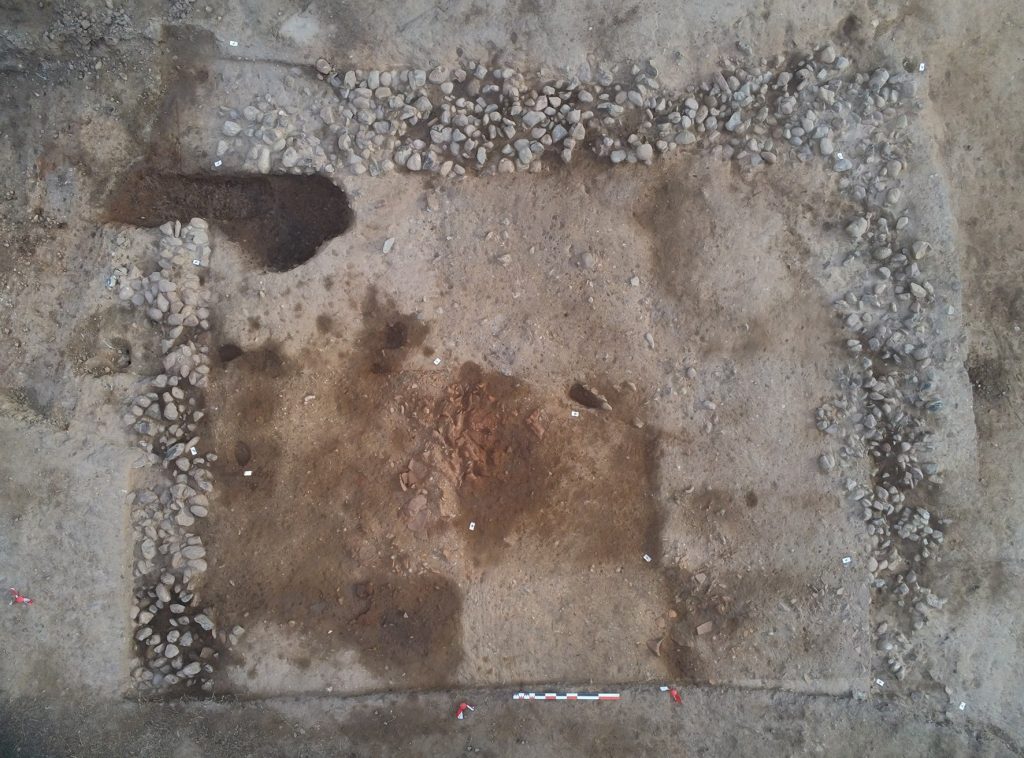

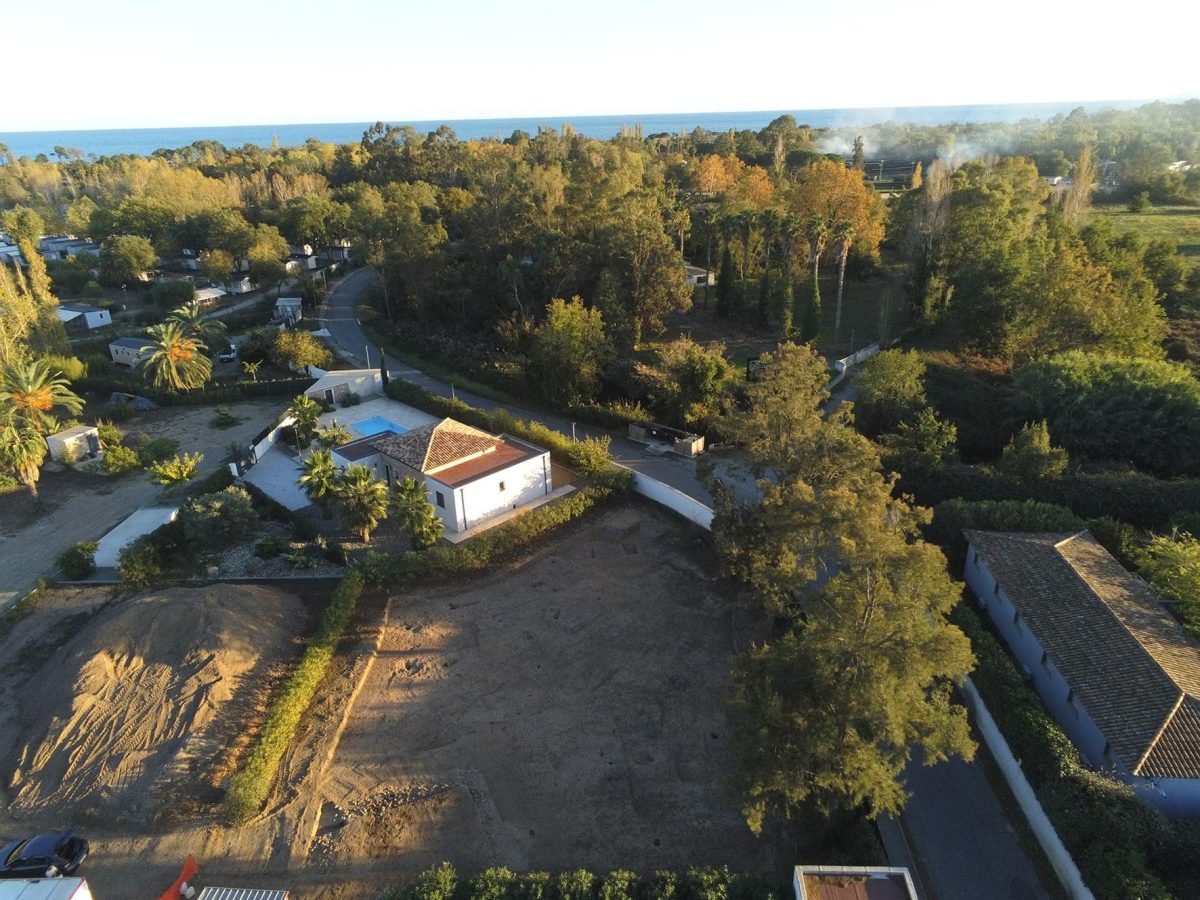
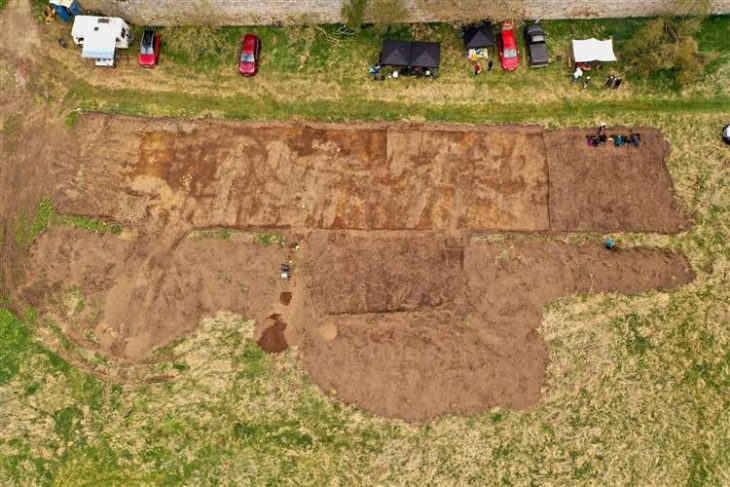
The discovery occurred during a single-house construction project on a 605 m² plot in the Chiusevia neighborhood, located 800 meters from the Tyrrhenian Sea and 3.5 km east of Ghisonaccia. The project ran from mid-October to early December 2023.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
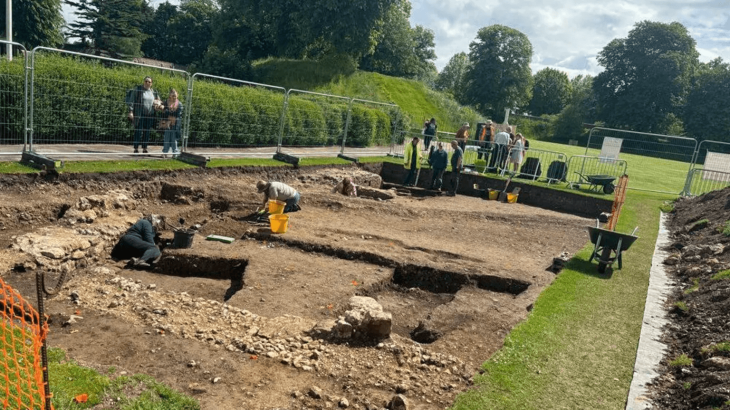
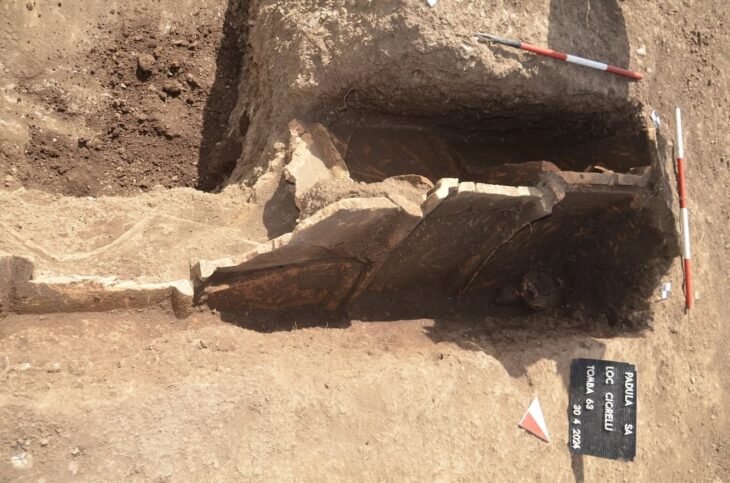
The excavation, conducted under the supervision of the Regional Archaeology Service (DRAC of Corsica), identified a building with pebble foundations on a slightly sloping alluvial terrace. The house was built on a plateau. This building, situated on a natural level area north of the site, extends on a northwest-southeast axis and has an internal space of at least 34 m², defined by three pebble floors. The surface of the building is at least 50 m².
Outside the house, there were traces of poles which suggest the use of constructions made of wood or perishable materials, such as reeds.
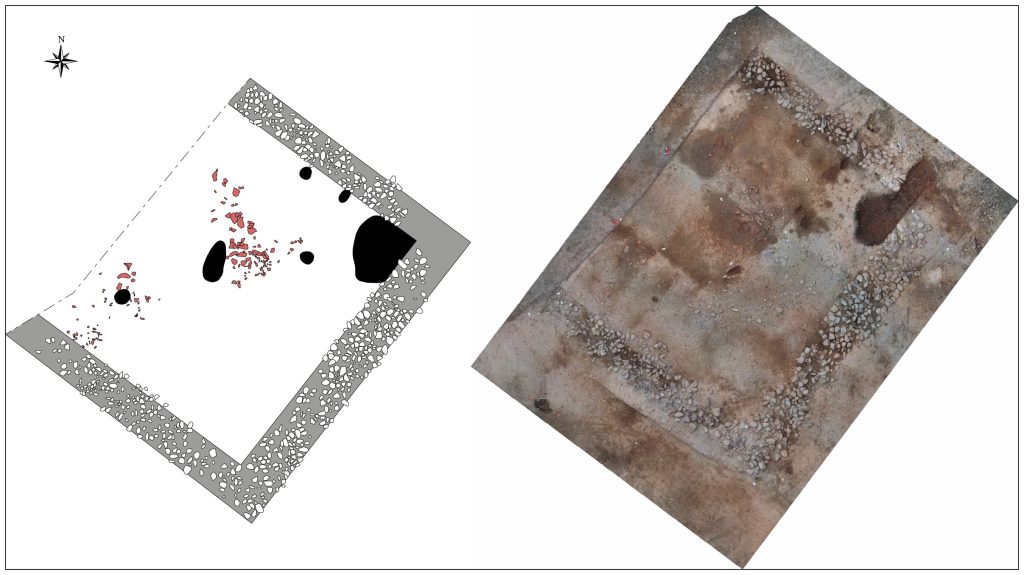
The uneven arrangement and slanted walls of the wall foundations, which are composed of pebbles of different sizes bound by silty sediment, suggest a simple yet efficient building method.
In total, archaeologists found about 45 kg of pottery fragments. These fragments were homogeneous and largely from undecorated storage containers. The artifacts were described as common Etruscan ceramics, reflecting an occupation between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE.
The homogeneous corpus is particularly characterized by the absence of locally modeled ceramics and the lack of refined Etruscan productions, suggesting a specific and differentiated use of these containers, the French National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research said in a July 9 news release.
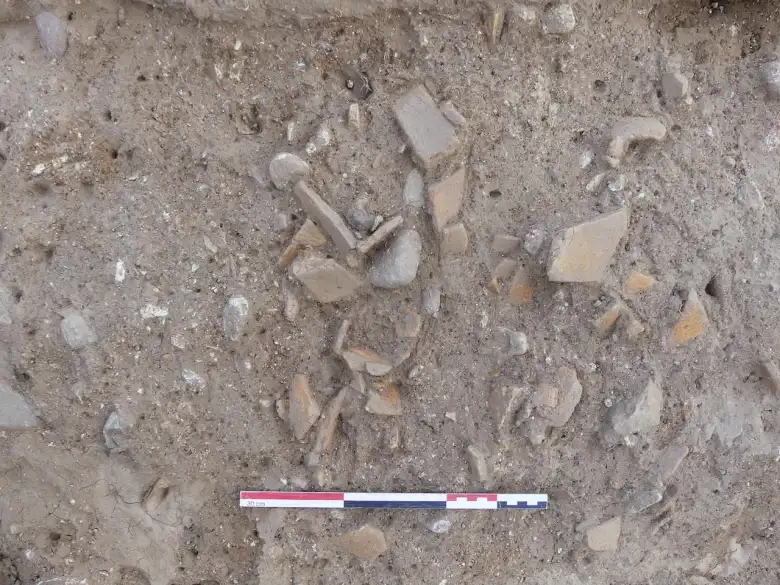

They added that the combination of typochronological studies, organic marker analysis, and petrographic studies will allow for a more precise definition of the chronology and characteristics of this Etruscan settlement in Corsica, placing it within the broader context of cultural and commercial interactions in the Mediterranean.
A sizable ditch that is 1.70 meters wide and 15 meters long has been found about twenty meters south of the structure. This ditch may have been used to collect water from the Alzetta stream and add to the settlement’s water supply. The ditch could have also been used to define the limits and layout of the site.
The ancient Etruscan home found in Corsica is a first-of-its-kind find for the island, the institute said.
Cover Photo: Aerial view of the Ghisonaccia site with the Alzetta River in the background, flowing towards the Tyrrhenian Sea. Photo: B. Chevaux, Inrap
















