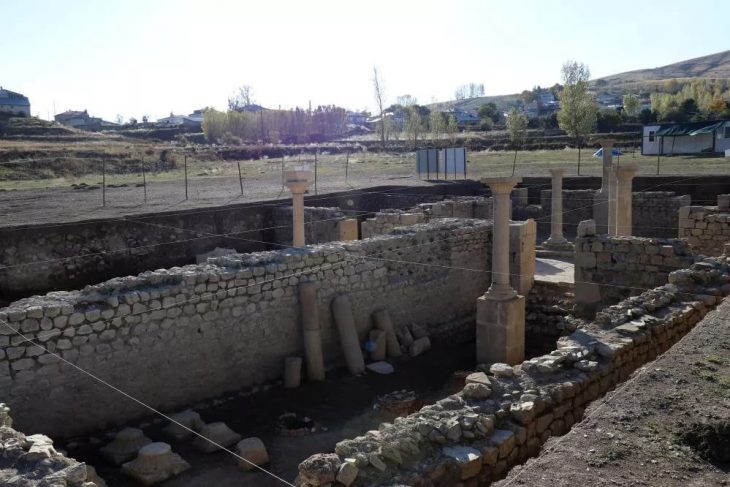
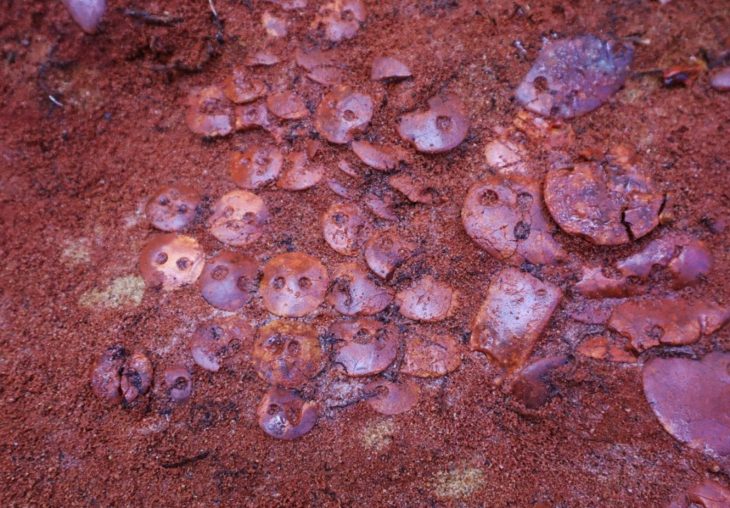
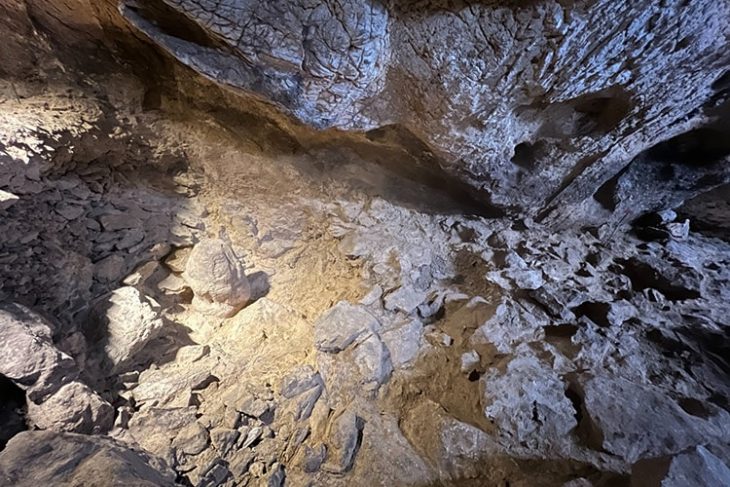
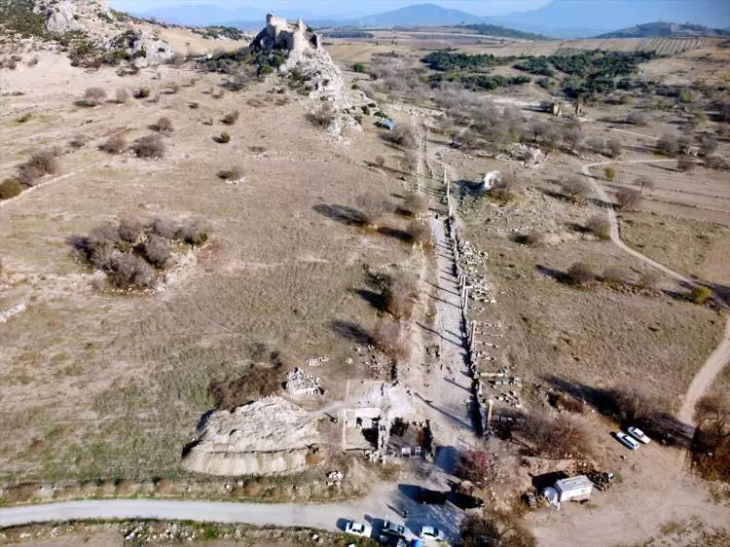
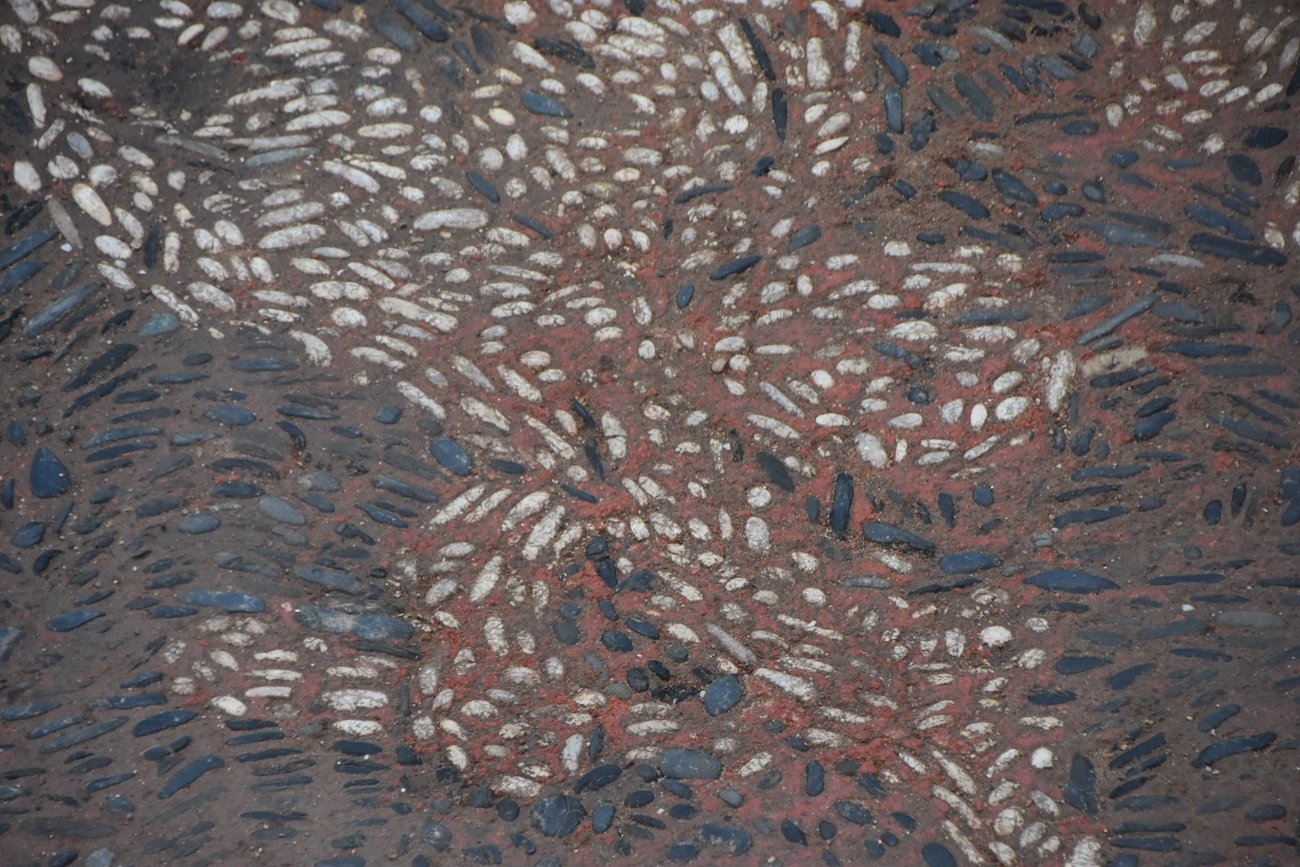
The pebble mosaics unearthed during the excavation of a building complex in the province of Sinop on Turkey’s Black Sea coast turned out to belong to the dining room of a wealthy family from the Hellenistic period.
New findings of importance for the scientific world continue to emerge during the excavations in the Balatlar Building Complex in the city center of Sinop.
Excavations continue under the leadership of Professor Gülgün Köroğlu, one of the distinguished faculty members of Mimar Sinan Fine Arts University.
The structure was recently determined that the artifact belonged to the “dining room of a wealthy family from the 4th century B.C.”
“Dating back to the 4th century B.C. in the Hellenistic era, the mosaics are believed to have adorned the dining room of a wealthy family. These intricate mosaics serve as a testament to Sinop’s prominence as a flourishing hub for trade, religion, and settlement at that time. The mosaic designs exhibit a diverse range of motifs, including religious symbolism, depictions of everyday life, and unique patterns have also been found in various sections of the mosaic,” Köroğlu said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
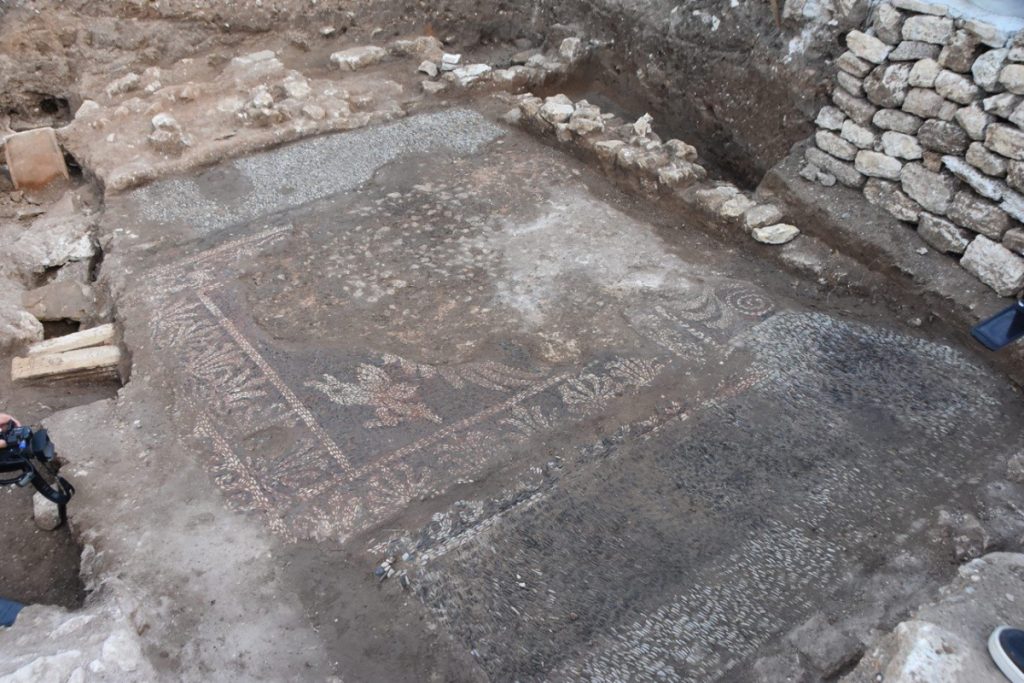

Sinop Provincial Culture and Tourism Director Metin Süren said, “Pebble stone mosaics that are rarely seen in the remains of buildings dating back to the classical period and the Hellenistic period in the 4th century B.C. have been unearthed in the Balatlar excavations that have been carried out for 11 years.”
Stating that Sinop may be among the most important ancient cities in the world after Rome, Süren said, “Sinop, which has hosted many civilizations from the prehistoric period to the present, is one of the most important ancient cities in the world.”
“We found these mosaics during the recent excavations. There is also a claim that these pebble mosaics are unique in our country and may be rare in the world, perhaps they are found only in ancient cities in Greece or Rome. There are those who claim that Sinop is such an important ancient city that it may be one of the most important ancient cities in the world after Rome, but unfortunately, there are no scientific excavations to confirm these claims except for Balatlar, although nearly 150-200 mounds have been identified and registered so far,” he added.
According to legend, Sinope was founded by the Amazons, who named it after their queen, Sinova. The city’s ancient inhabitants ascribed its foundation to Autolycus, a companion of Hercules. Destroyed by the equestrian nomadic Cimmerians, it was refounded toward the end of the 7th century bce by a colony of Milesians.