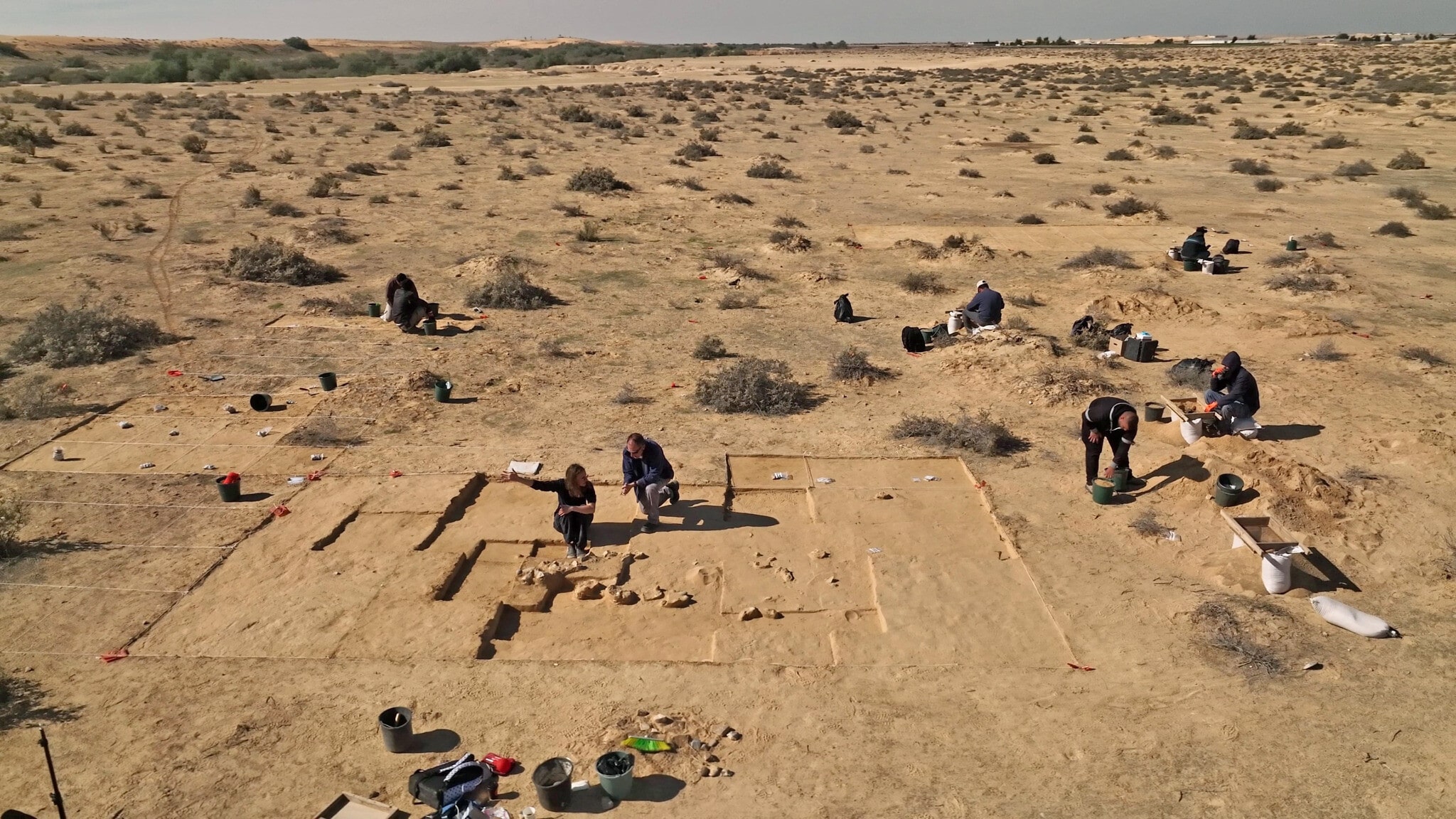
Eight ostrich eggs dating between 4,000 and 7,500 years ago have been found during excavations next to a fire pit in Israel at a Negev campsite that has been used by desert nomads since prehistoric times.
The eggs were discovered during an archaeological dig by the Israel Antiquities Authority in the Moshav Be’er Milka farmland.
Excavation director Lauren Davis said: “We found a campsite, which extends over about 200 square meters, that was used by the desert nomads since prehistoric times. At the site, we found burnt stones, flint, and stone tools as well as pottery sherds, but the truly special find is this collection of ostrich eggs,”.
In addition to the ostrich eggs, the excavations uncovered burnt stones, flint and stone tools, and pottery shards.
Ostriches were common in the area from prehistoric times until they became extinct in the wild during the nineteenth century. Their eggs have been discovered in archaeological sites for several periods, indicating the importance of ostrich eggs as a raw material.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“We find ostrich eggs in archaeological sites in funerary contexts, and as luxury items and water canteens. Naturally, they were used as a source of food: one ostrich egg has the nutritional value of about 25 normal chicken eggs!” said IAA researcher Dr. Amir Gorzalczany.
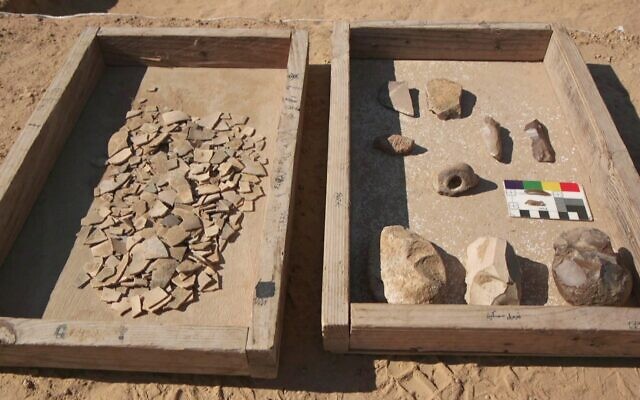

“There is sometimes even evidence of decorating and incising on ostrich eggs, showing their use as decorative items. It is interesting that whilst ostrich eggs are not uncommon in excavations, the bones of the large bird are not found. This may indicate that in the ancient world, people avoided tackling the ostrich and were content with collecting their eggs,” he added.
For her part, Davis noted that the proximity of the group of eggs to the fire pit indicated that they were collected and thus likely used as food.
“After the excavation we will reconstruct the eggs, just like a puzzle. The whole egg may tell us the species, and exactly what they were used for. As far as I’m concerned, every eggshell is worth its weight in gold! I am really looking forward to the research in the labs. The best is yet ahead!” said Davis.
“Although the nomads did not build permanent structures at this site, the finds allow us to feel their presence in the desert,” Davis continued. “These campsites were quickly covered over by the dunes and were re-exposed with the sand movement over hundreds and thousands of years. This fact explains the exceptional preservation of the eggs, allowing us a glimpse into the lives of the nomads who roamed the desert in ancient times.”
Cover Photo: Ostrich eggs found in the Nitzana dunes excavations, southern Israel. Emil Aladjem/Israel Antiquities Authority