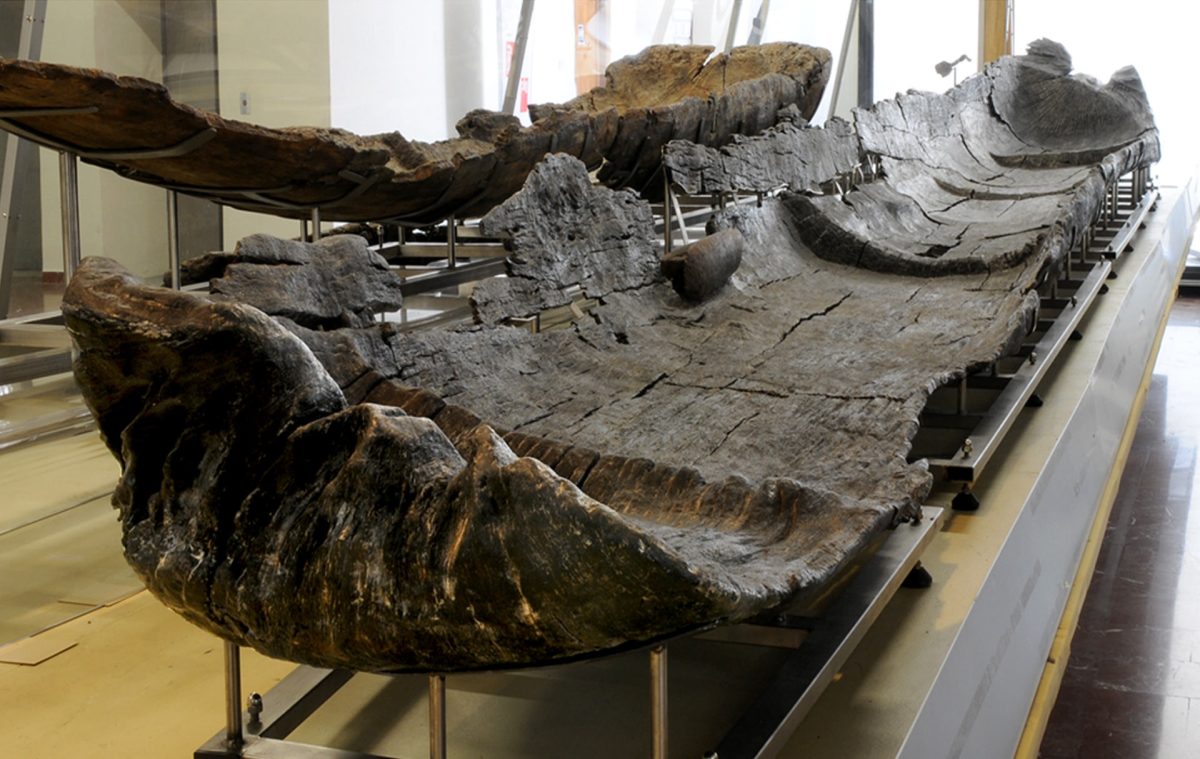
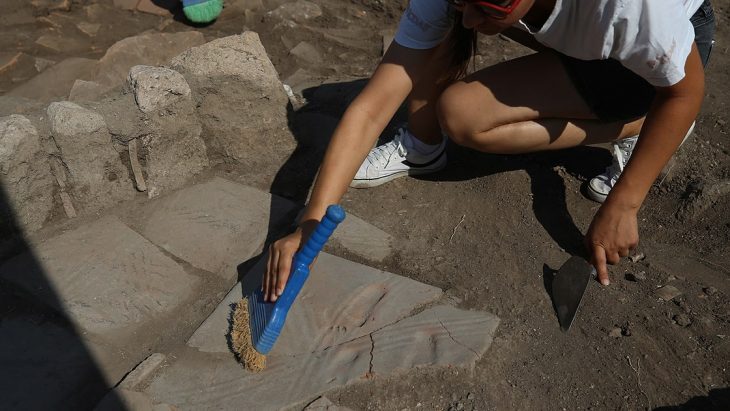
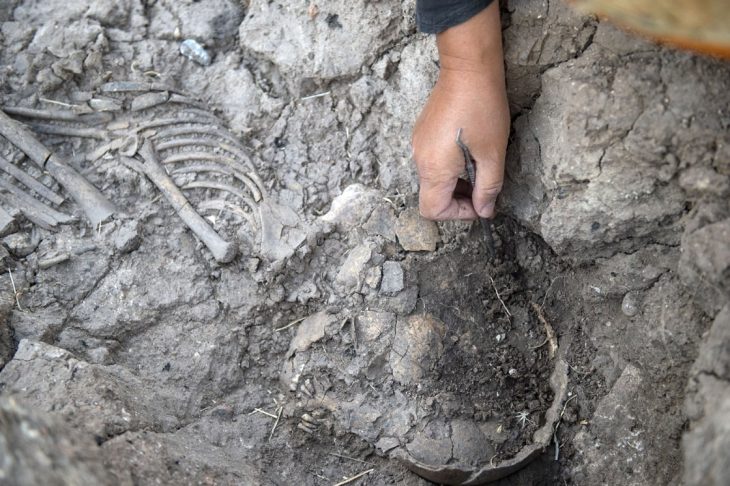
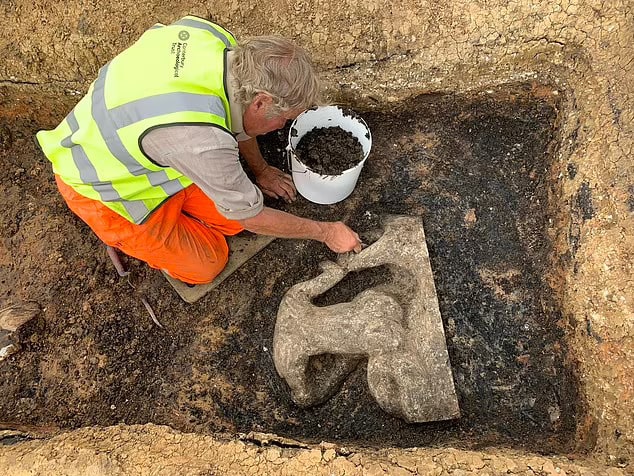
The discovery of five “technologically sophisticated” canoes in Italy has revealed that Neolithic people were navigating the Mediterranean more than 7,000 years ago. The canoes date from between 5700 BC and 5100 BC and are the oldest in the region.
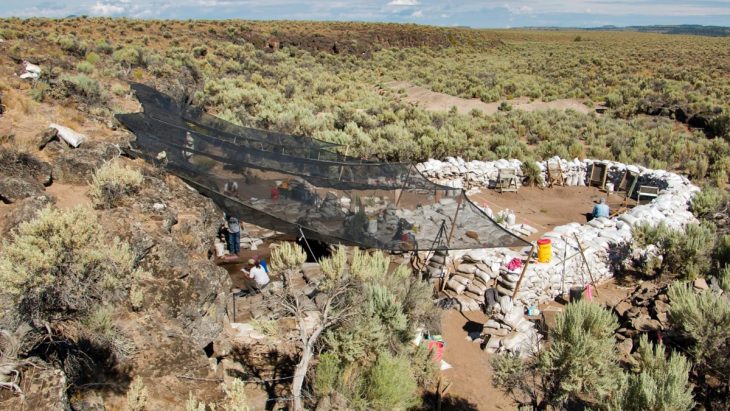
In research published in the journal PLOS ONE, archaeologists describe the discovery, at the Neolithic (Late Stone Age) lakeshore village of La Marmotta, about 30 km northwest of central Rome.
The quality and complexity of these prehistoric vessels suggest that several significant advances in sailing occurred during the late Stone Age, paving the way for the spread of the ancient world’s most important civilizations.
The authors note that the spread of Neolithic culture through Europe was chiefly carried out along the shores of the Mediterranean.
“Many of the most important civilisations in Europe originated on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea,” they write. “Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans and Carthaginians plied that practically enclosed sea to move rapidly along its coasts and between its islands.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The writers say Neolithic communities occupied the whole Mediterranean between 9,500 and 9,000 years ago. They reached the Atlantic coast of Portugal by about 5400 BCE.
“It is clear that the Mediterranean Sea must have often been used for travel, as boats allowed rapid movements of population, contacts and exchange of goods,” the authors say.
It’s well known that maritime trade links existed in the Mediterranean during the Neolithic, although until now it was unclear how adept these early mariners were at handling the waves.
Navigating through this uncertainty, the authors of a new study have analyzed five dug-out canoes that were discovered at a 7,000-year-old settlement that now lies at the bottom of an Italian lake.
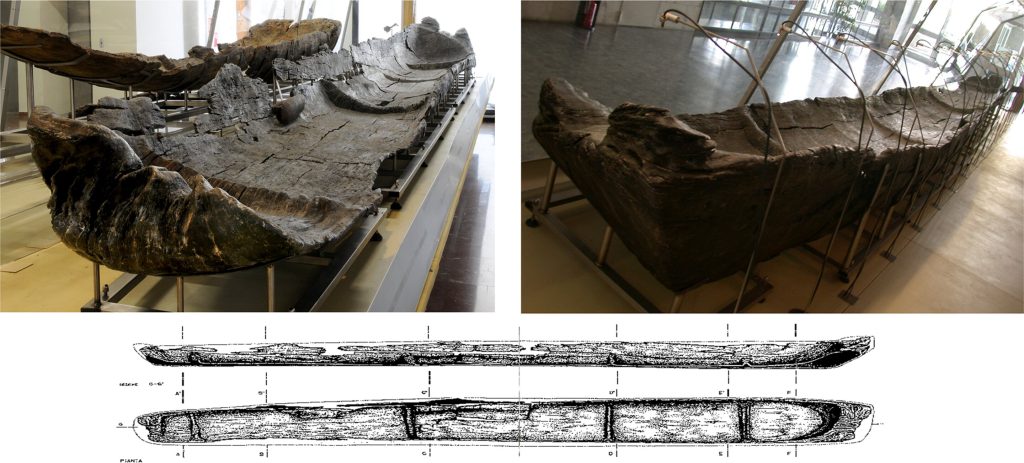

In this study, Juan F. Gibaja and colleagues provide new insights into the history of seafaring technology through analysis of canoes at the Neolithic lakeshore village of La Marmotta, near Rome, Italy.
Excavation at this site has recovered five canoes built from hollowed-out trees (dugout canoes) dating between 5700 and 5100 BC. Analysis of these boats reveals that they are built from four different types of wood, unusual among similar sites, and that they include advanced construction techniques such as transverse reinforcements.
One canoe is also associated with three T-shaped wooden objects, each with a series of holes that were likely used to fasten ropes tied to sails or other nautical elements.
These features, along with previous reconstruction experiments, indicate these were seaworthy vessels, a conclusion supported by the presence at the site of stone tools linked to nearby islands.
“These canoes are exceptional examples of prehistoric boats whose construction required a detailed understanding of structural design and wood properties in addition to well-organized specialized labor,” the researchers said.
Recent nautical technologies and these canoes share similarities, bolstering the theory that the early Neolithic saw many significant advancements in sailing. The authors suggest there may be more boats preserved near La Marmotta, a potential avenue for future research.
“Direct dating of Neolithic canoes from La Marmotta reveals them to be the oldest in the Mediterranean, offering invaluable insights into Neolithic navigation,” the authors add.
The study was published online in the journal PLoS ONE.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299765
Cover Photo: The 7,300-year-old canoe Marmotta 1 on display in the Museo delle Civiltà in Rome. It is a huge dugout canoe made from an oak trunk about 10.43 m long, 1.15 m wide at the stern, and 0.85 m wide at the bow. It is 65 to 44cm high, depending on the part of the canoe. Image credit: Gibaja et al., doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299765.