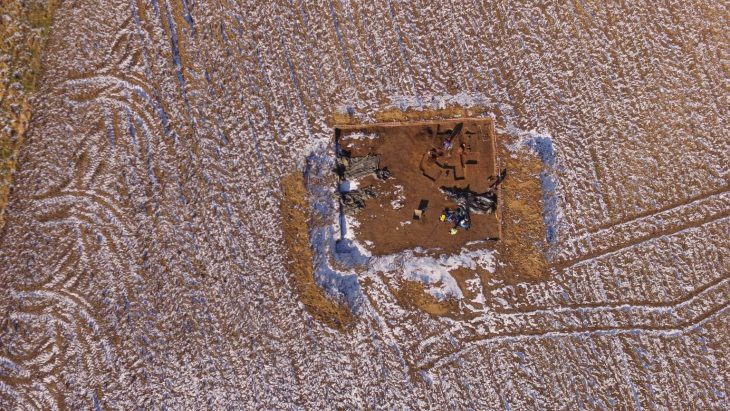
Archaeologists in France unearthed the remains of a series of wooden buildings within a defensive enclosure that were built at the same time as the first stone monuments were being erected.
People in west-central France built a variety of megalithic monuments during the Neolithic period, including mound-like barrows and “dolmens” — a type of single-chamber tomb supported by two or more upright megaliths. While these stone monuments are visible and have withstood the test of time, traces of their homes have been more difficult to find — until now.
Now, Dr. Vincent Ard from the French National Center for Scientific Research. and a team of researchers working in the Charente department has identified the first known residential site belonging to some of Europe’s first megalithic builders.
“It has been known for a long time that the oldest European megaliths appeared on the Atlantic coast, but the habitats of their builders remained unknown,” said Dr. Vincent Ard.
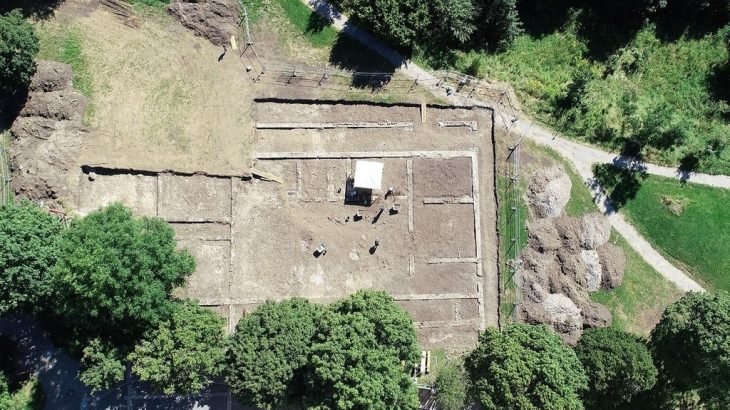
Since it was first found during an aerial survey back in 2011, the enclosure at Le Peu, in the commune of Charmé, has been the focus of an intense investigation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The results of this work, published in the journal Antiquity, revealed a palisade encircling several timber buildings built during the fifth millennium BC.
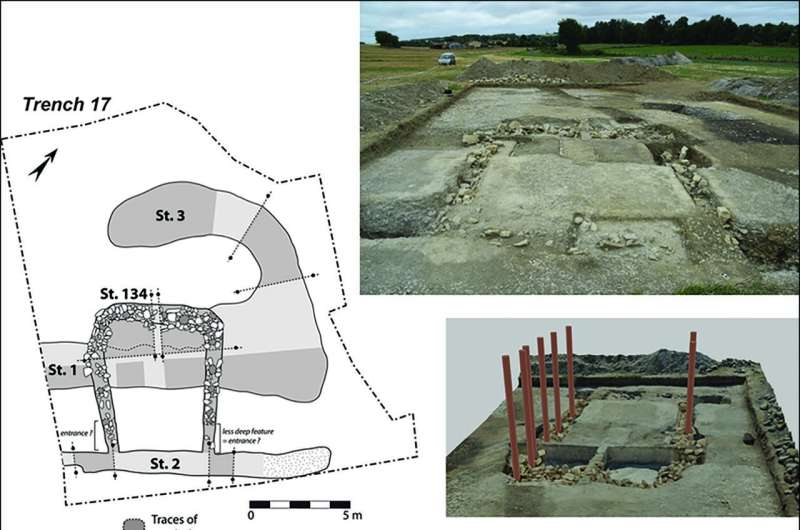
This makes them the oldest wooden structures in the region and the first residential site contemporary with the Neolithic monument makers. At least three homes were found, each around 13 meters long, clustered together near the top of a small hill enclosed by the palisade.
The structures at Le Peu, the researchers said, represent both the oldest-known wooden structures in the region as well as the first known residential site that existed at the same time that the Neolithic monuments were being built.
To test this, the archaeologists carried out radiocarbon dating that revealed these monuments are contemporary with Le Peu, suggesting the two sites are linked.
While the people of Le Peu may have built monuments to the dead, they also invested a lot of time and effort in protecting the living. Analysis of the paleosol recovered from the site revealed it was located on a promontory bordered by a marsh. These natural defenses were enhanced by a ditch palisade wall that extended around the site.

The entrance had particularly heavy defenses, guarded by two monumental structures. These appear to have been later additions, requiring part of the defensive ditch to be filled in.
“The site reveals the existence of unique monumental architectures, probably defensive. This demonstrates a rise in Neolithic social tensions,” said Dr. Ard.
However, these impressive defenses may have proved insufficient as all the buildings at Le Peu appear to have been burnt down around 4400 BC. However, such destruction helped preserve the site.
As a result, Dr. Ard and the team are hopeful that future studies at Le Peu will continue to provide insight into the lives of people whose only known contributions to human history are memorials. Already, it demonstrates the monumental scale of their residential sites, which was unprecedented in prehistoric Atlantic society.
Cover Photo: Photo: Ard et al. / Antiquity / Archeovision Production
















