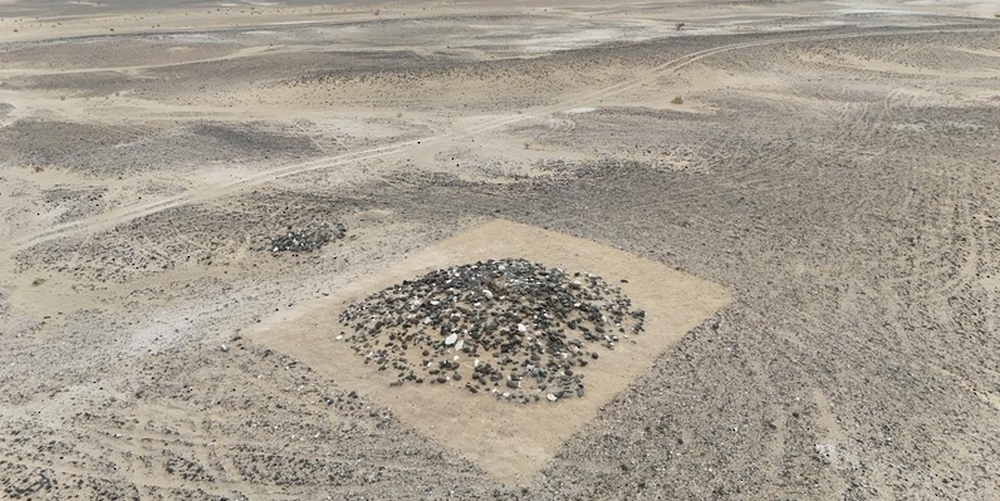
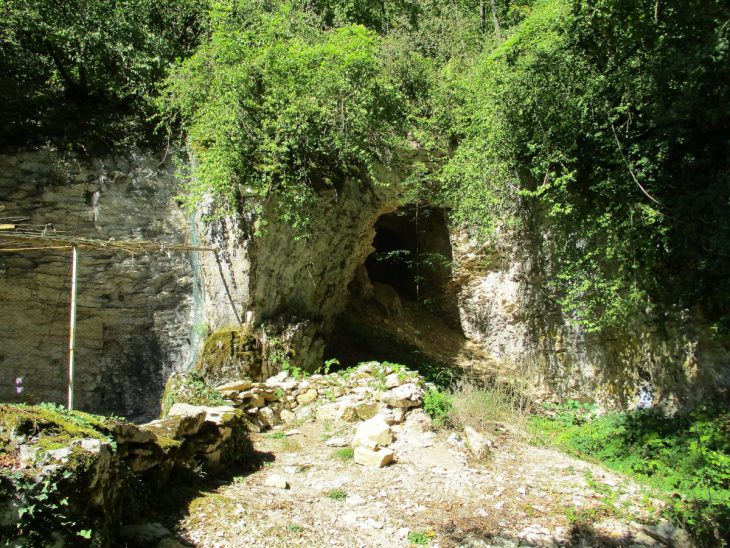
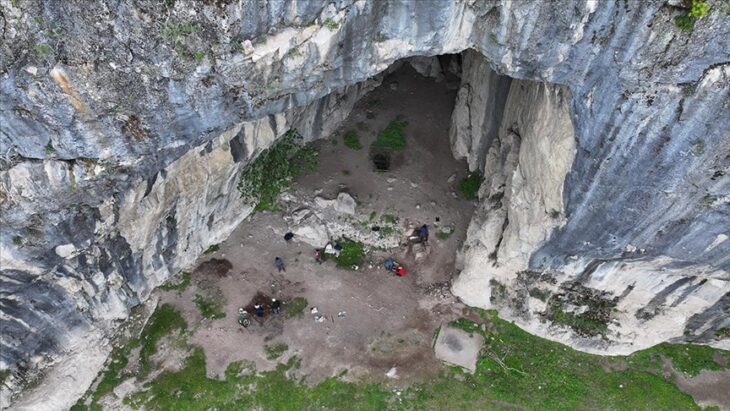
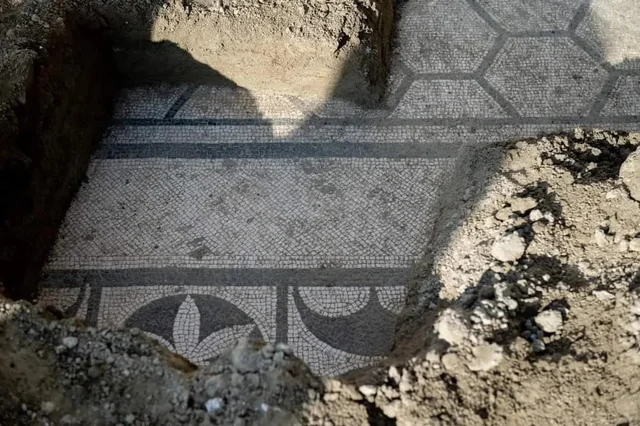
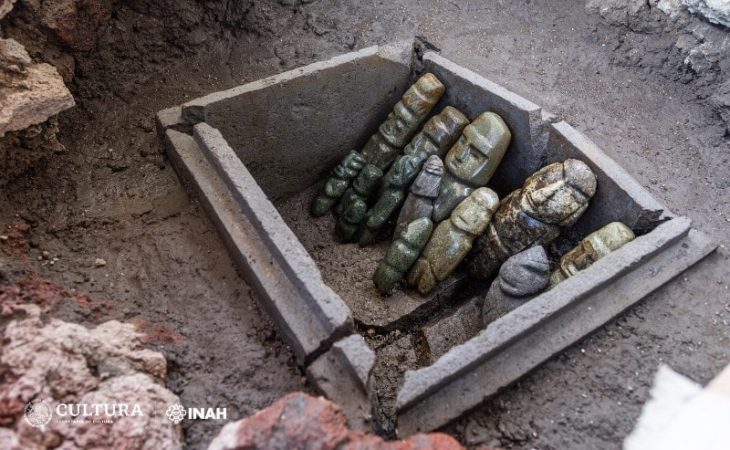
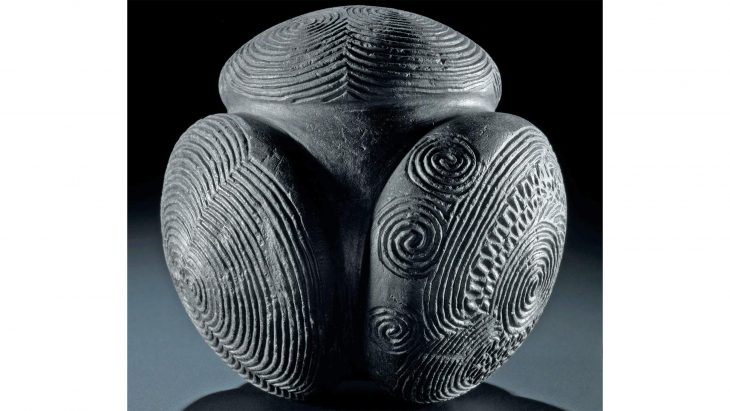
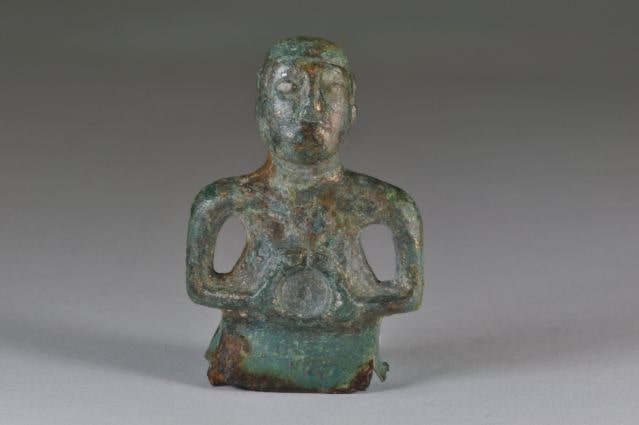
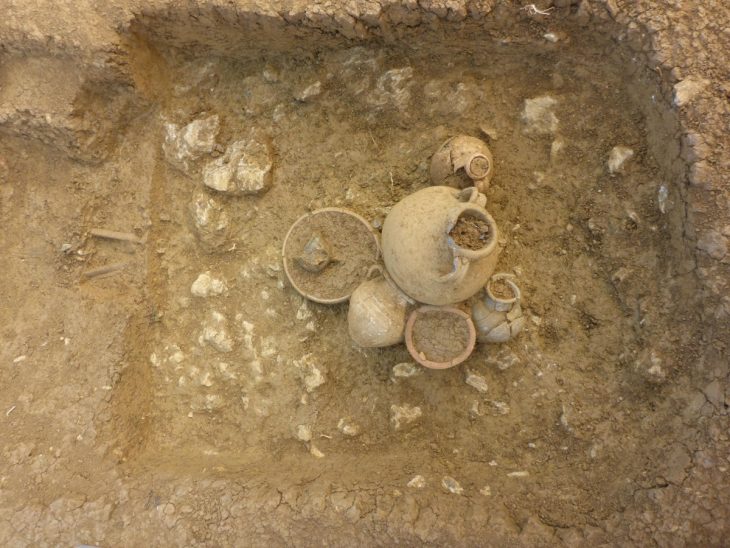
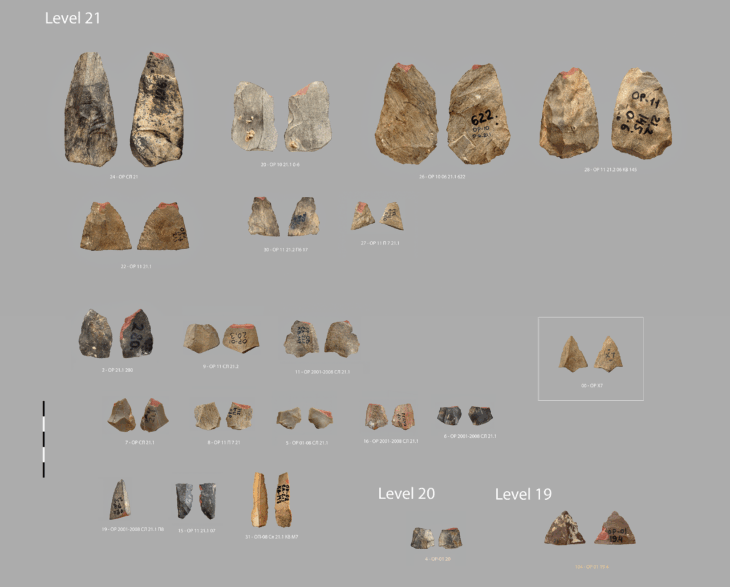
Oman’s Ministry of Heritage and Tourism has announced a remarkable discovery in the Al-Sabikhi area of the Wilayat of Ibri, within the A’Dhahirah Governorate. A rescue excavation carried out by its Department of Heritage and Tourism has uncovered 25 tombs dating back to the third millennium BC, offering new insight into Oman’s ancient connections with Mesopotamia.
Ancient Tombs and Remarkable Artefacts
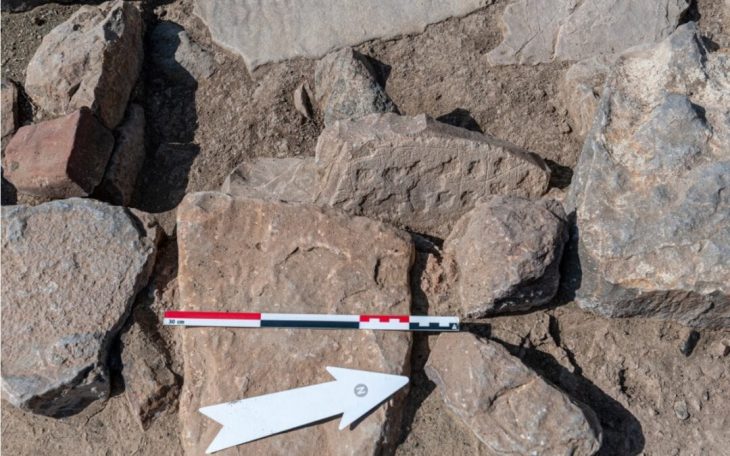
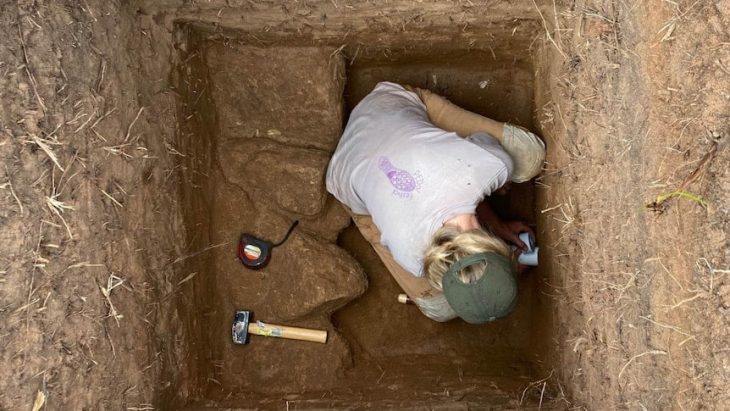
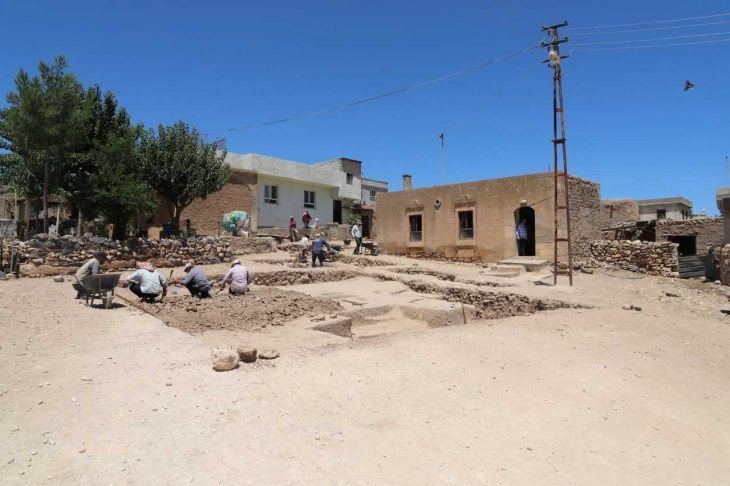
The excavation, led by archaeologists from the Department of Heritage and Tourism, revealed skeletal remains alongside complete pottery vessels carefully placed inside the burial chambers. Remarkably, some of these vessels were identified as imports from the Jemdet Nasr civilization of Mesopotamia, a culture that thrived in present-day Iraq around 3100–2900 BC.
In addition to pottery, researchers unearthed Bronze Age beads made of stone and shells, reflecting the craftsmanship and symbolic practices of early societies in Oman. These findings not only point to the burial customs of ancient communities but also indicate vibrant cultural exchanges and long-distance trade routes that once connected the Arabian Peninsula to Mesopotamia and beyond.
Expert Preservation and International Collaboration
Walid Awad Al Ghafri, an archaeology specialist at the Department of Heritage and Tourism in A’Dhahirah, emphasized that the discoveries are being carefully documented, studied, and preserved in line with international standards. A joint team of Omani and international experts is currently handling the artifacts to ensure their protection for future research.
“The excavation highlights the civilizational expanse of Oman and its role in cultural communication with neighboring societies,” said Al Ghafri. “These results enrich our understanding of the Arabian Peninsula’s ancient heritage and enhance the global significance of Oman as a center for archaeological research.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
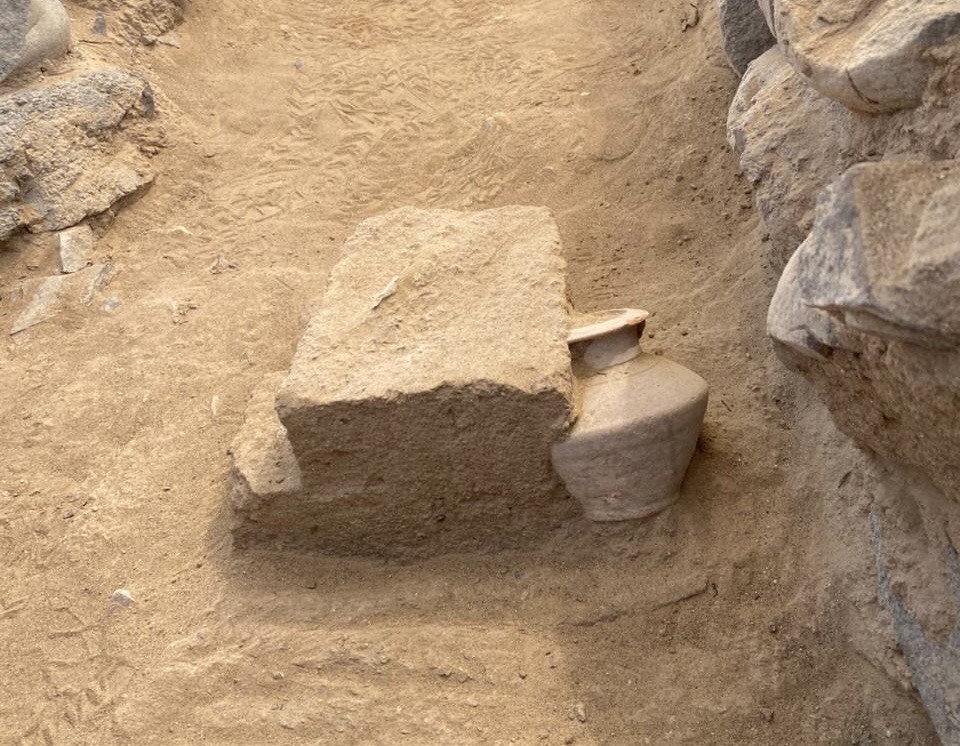

Ibri: A Crossroads of History and Culture
The Wilayat of Ibri, located about 230 kilometers west of Muscat, serves as the administrative center of A’Dhahirah Governorate. Nestled near Oman’s border with the United Arab Emirates, Ibri lies at the crossroads of mountain ranges and desert plains, a position that historically made it a vital stop for trade caravans.
For centuries, Ibri was a gateway linking Oman’s interior with neighboring regions, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural traditions. Today, it remains renowned for its traditional souqs, historic forts, and archaeological landscapes. The imposing Ibri Fort and nearby Bronze Age necropolises are key attractions that continue to draw researchers and visitors alike.
This unique blend of geographical advantage and cultural heritage underscores why discoveries in Ibri, such as the Al-Sabikhi tombs, are of global archaeological importance. They highlight Oman’s role as a bridge between civilizations—a role it has maintained for thousands of years.
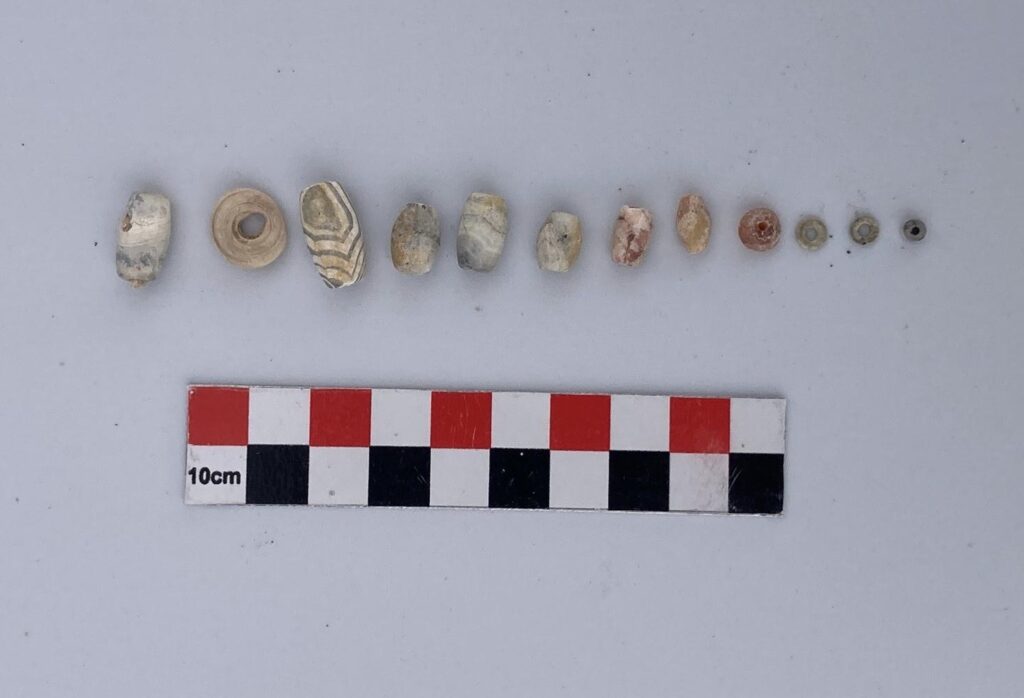

Enriching Oman’s Cultural Heritage
For Oman, the preservation and study of these archaeological remains carry significance beyond academia. They strengthen the country’s efforts to highlight its rich heritage, attract cultural tourism, and raise awareness of its role in the development of early human civilization. Sites like Al-Sabikhi contribute to the growing narrative that Oman was not isolated but deeply interconnected with the world’s earliest advanced societies.
As rescue excavations continue, the Ministry of Heritage and Tourism underscores its commitment to safeguarding Oman’s past. Each discovery, such as the Al-Sabikhi tombs, adds new chapters to the story of human civilization in the Arabian Peninsula, positioning Oman as a vital center for historical research and cultural dialogue.
Cover Image Credit: Oman News Agency