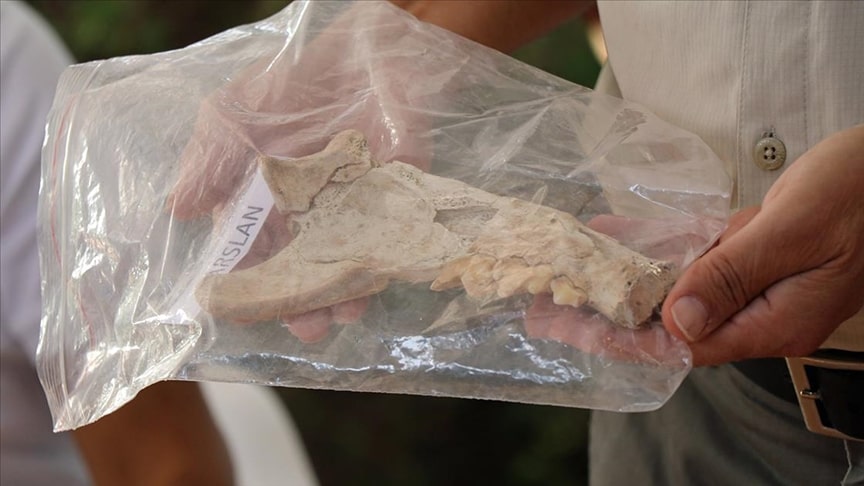
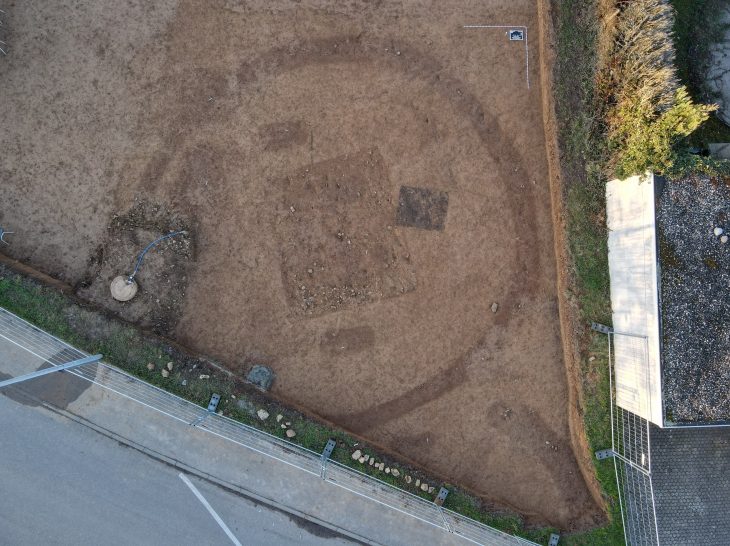
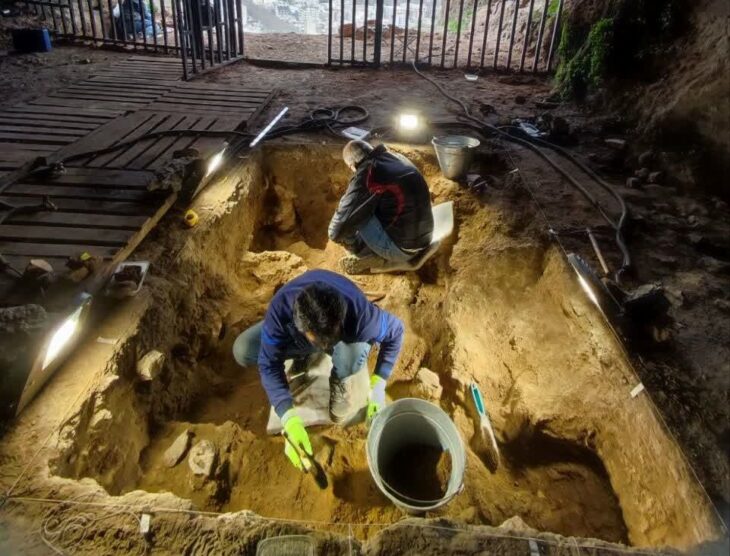
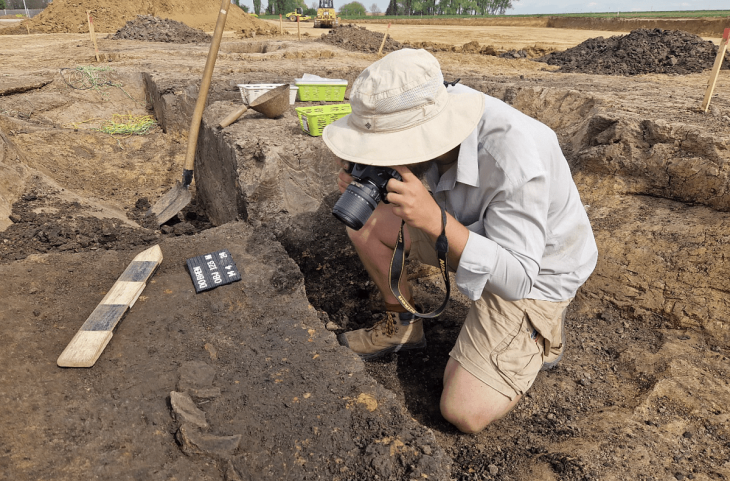
Excavations continue in Kültepe, the starting point of Anatolian written history. During the excavations, a 4,000-year-old lion jawbone was unearthed.
For the first time, a lion’s jawbone was found in Kültepe.
Prof. Dr. Fikri Kulakoğlu of Ankara University’s Faculty of Language, History-Geography, and Archeology Department said that in 2021, they discovered many animal bones and large storage logs in the basement of a large edifice in the region.
Providing information about the lion bone found in the Kültepe excavation site to journalists, Kulakoğlu said, “For the first time, a lion’s jawbone has been found in Kültepe.”
According to the news in Anadolu Agency (AA), Kulakoğlu said:
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
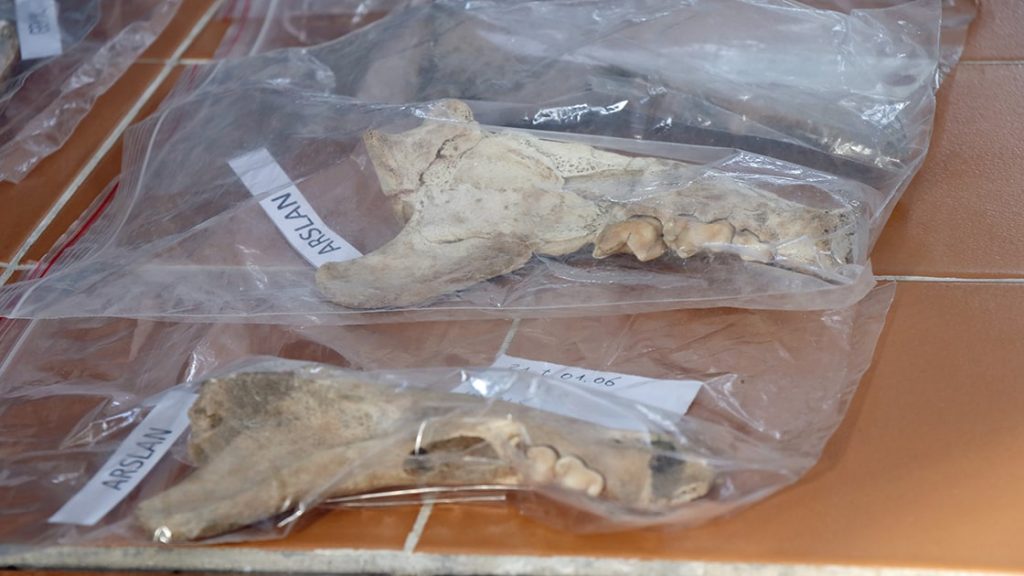
“During the excavations, we made this year, we found a group of bones of two lions, bears, mountain sheep, deer, and wild pigs in a trench. These bones were found in bulk. All of these animal bones belong to large, large, and wild animals. For the first time, we found two separate jawbones from two different lions, a very large bear, and bones from a large deer in this period in Anatolia. It is necessary to evaluate them as follows, these are the animals that we will accept to be raised in this region. Animals living around Erciyes or in mountainous areas or up to Sivas. There are no lion bones unearthed in other regions dating back 4,000 years. Of course, there are bones from several million years ago. But these are two of the earliest examples of human settlement. We date these bones to 4,000 years ago. These are wild animals, they must be hunted and brought to Kültepe..”
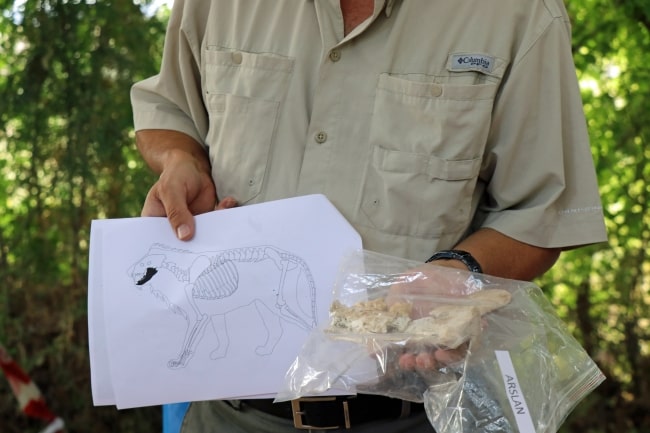

Animal bones might be linked to mythos
Kulakoğlu stated that the animal bones discovered at Kültepe may be connected to a myth:
“There is a tablet found in Boğazköy, its name is the Anitta tablet. According to this tablet, the king named Anitta captured Nesha with his father, and they did not touch anyone. They even built palaces and temples. These bones were found in the area of these temples and palaces. In the inscription allegedly written by this king, it is written that he went hunting. ‘I hunted and brought back more than 100 animals, including two lions, leopards, panthers, bears, deer, and wild animals.’ he writes. This is the area right next to the temple. Of course, we don’t think for sure that these bones are related to this story, but there is a high probability that they are. Because there are traces of injury among the animal bones we found, so these were brought by hunting. This must have a historical significance and a relationship with a subject in Kültepe..”
On the lion’s jawbone and bone finds of other animals, a member of the Kültepe Excavation Committee, zooarchaeologist Prof. Dr. Claudia Minniti does scientific studies.
Cover Photo:4,000-year-old lion jawbone Photo: Esma Küçükşahin – Anadolu Agency
















