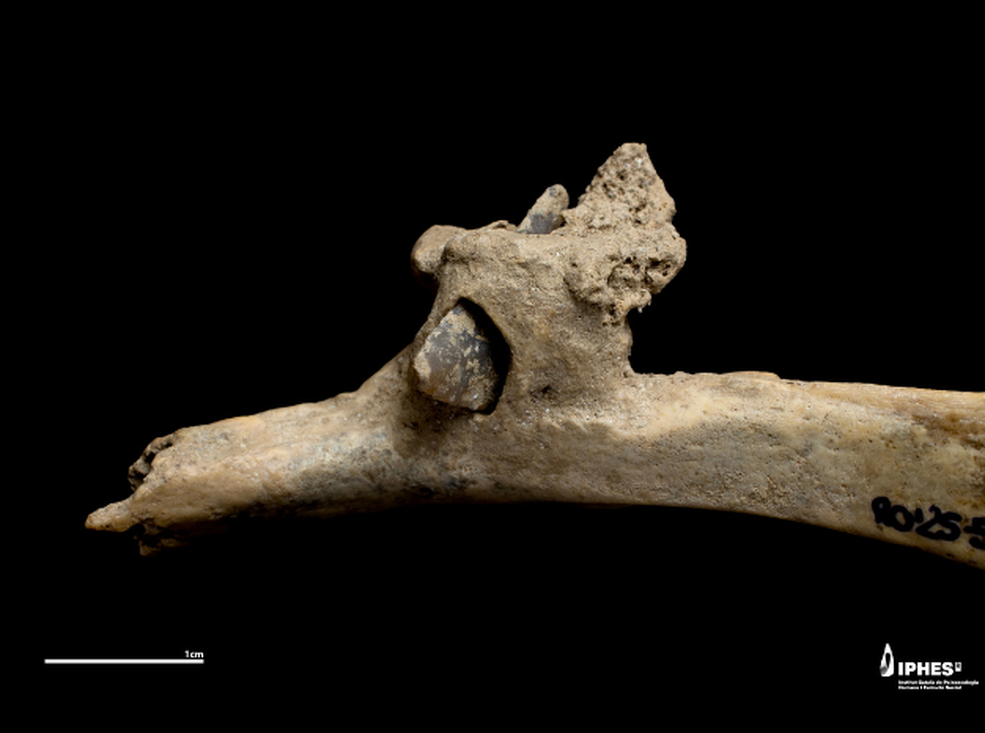
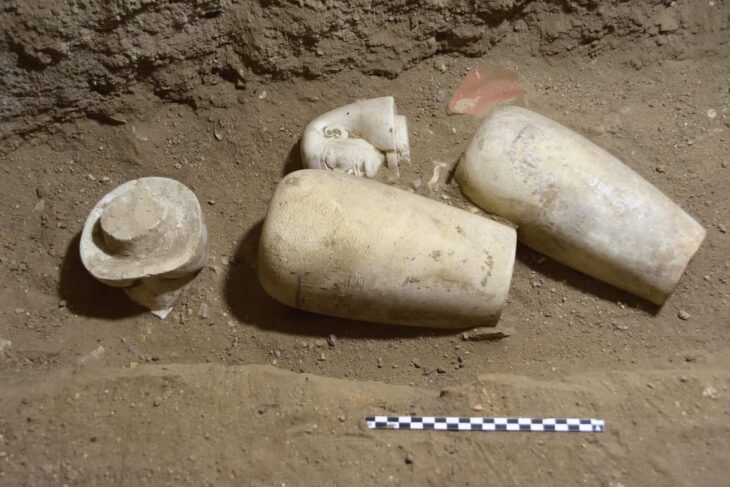
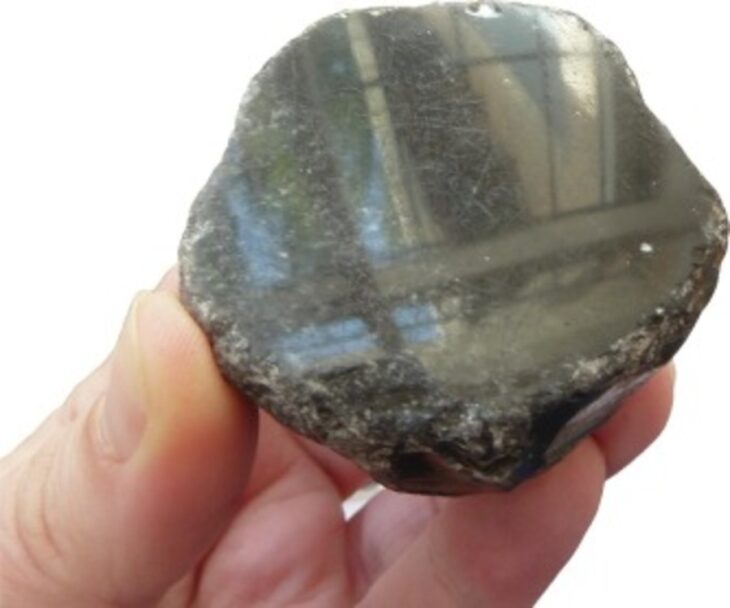
In a discovery shedding light on prehistoric human conflict, archaeologists have found a flint arrowhead embedded in a human rib dating back more than 4,000 years. The remains were unearthed at Roc de les Orenetes, a high-altitude collective burial site in the Catalan Pyrenees (northeast Spain), situated over 1,800 meters above sea level.
This exceptional find—revealing direct evidence of interpersonal violence—was made during recent excavations led by Dr. Carlos Tornero from the IPHES-CERCA and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
This discovery provides a rare, tangible glimpse into the social tensions within early highland communities of the third millennium BCE. It stands as direct, almost forensic proof of interpersonal conflict—highlighting the critical value of archaeological research in uncovering not just how these people lived, but how they responded to violence and adversity.
A Violent Encounter in Prehistoric Times
The arrow, shot from behind, struck a rib but didn’t kill the individual immediately. Instead, the bone showed signs of healing, suggesting the person survived the attack, at least temporarily. According to osteoarchaeologist Dr. Miguel Ángel Moreno (University of Edinburgh), this opens new possibilities for studying trauma, weapon types, and even the attacker’s position relative to the victim.
Further analysis is underway using X-ray microtomography and advanced biochemical techniques to learn more about the impact and healing processes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

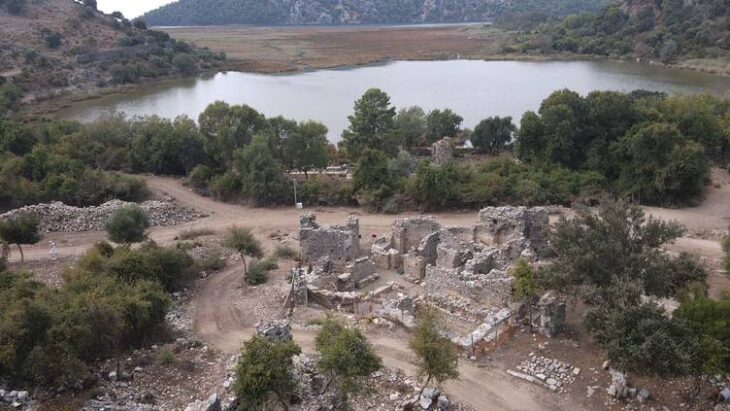
A Burial Cave Tied to a Close-Knit Mountain Community
Roc de les Orenetes served as a burial site for over 60 individuals between 2200–2000 BCE, likely members of the same community. Excavations since 2019 have recovered more than 6,000 human bone fragments. The skeletal remains suggest a population of robust, physically active herders, deeply adapted to life in the mountains.
Earlier studies had already identified cut marks, fractures, and weapon-related injuries, but until now, it wasn’t clear whether the weapons had actually struck people or were simply grave goods. This embedded arrowhead offers the first unambiguous evidence of a violent encounter.
A Site of Ongoing Discovery
First discovered in the 1960s, the cave has a long archaeological history. It was recently revitalized as part of the ARRELS/RAÍCES Prehistoric Roots Project, supported by the Catalan government, the town of Queralbs, and the Ripoll Ethnographic Museum.

The site is now considered one of the most important prehistoric high-mountain cemeteries in southern Europe—providing an unprecedented window into the lives, struggles, and resilience of early Pyrenean societies.
Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES-CERCA)
Cover Image Credit: Flint arrowhead embedded in a human rib, discovered at the Roc de les Orenetes prehistoric burial site in Queralbs (Ripollès, Catalonia). Image credit: Maria D. Guillén / IPHES-CERCA