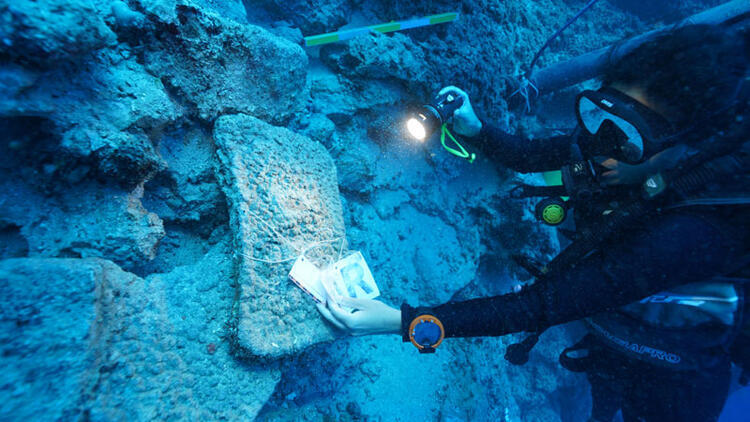
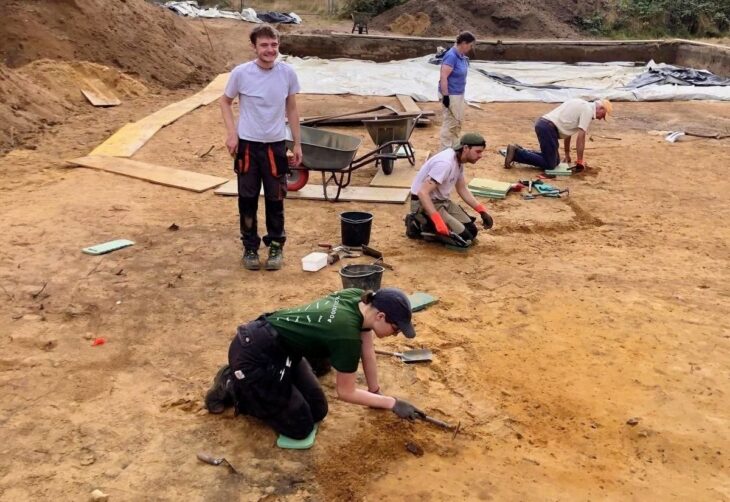
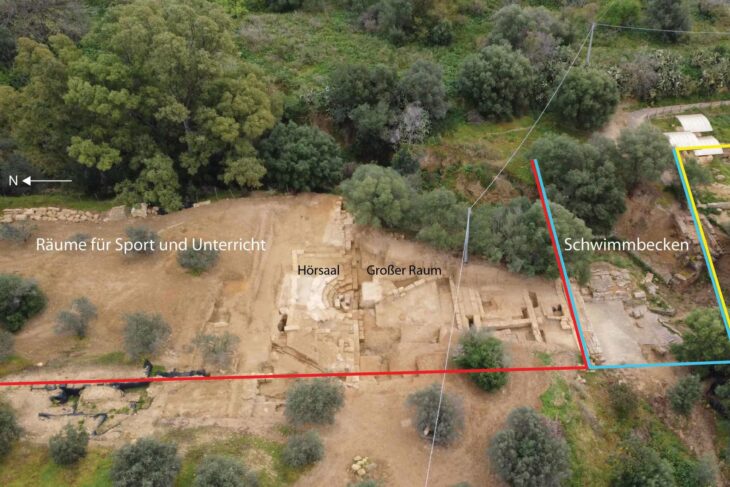
Underwater archaeological work continues in the Bronze Age shipwreck off Antalya Kumluca, one of the oldest shipwrecks in the world.
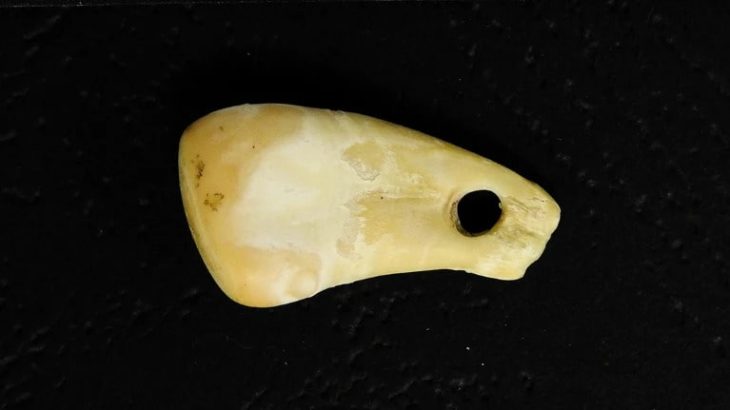
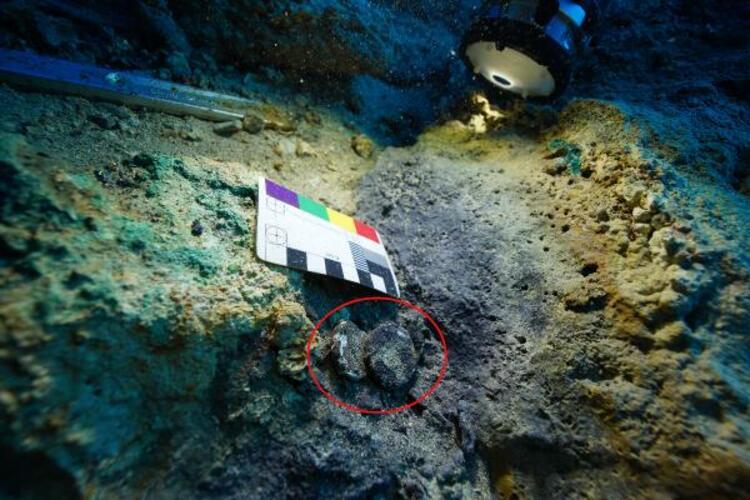
During the underwater archaeological excavations carried out in the Bronze Age shipwreck dated to the 16th century BC, 2 lead weights weighing 22 and 44 gr were found.
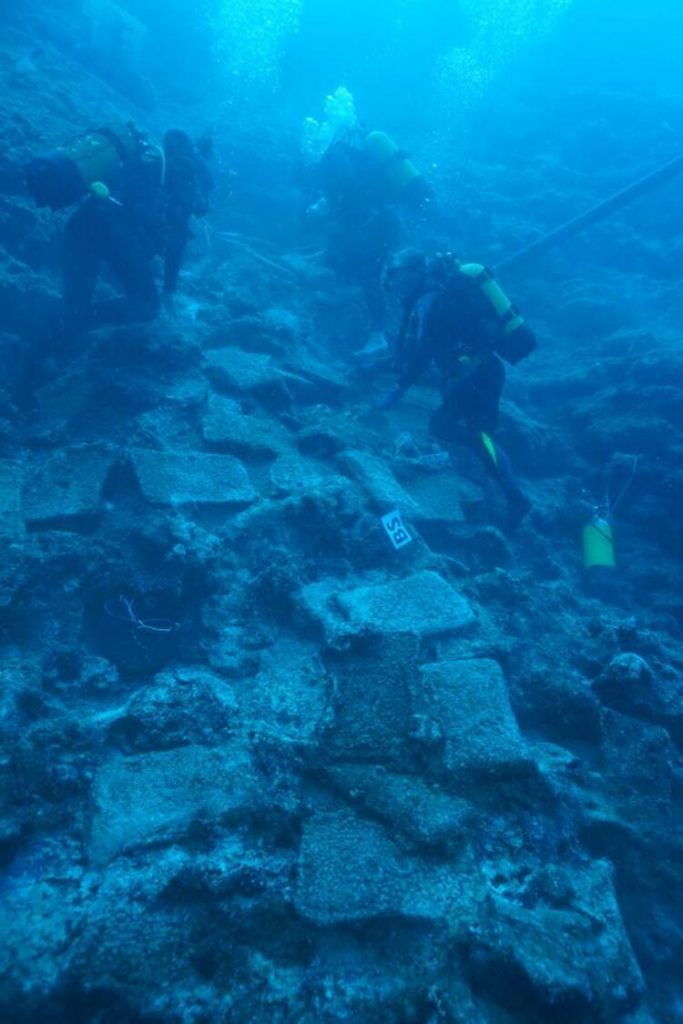
The shipwreck, estimated to date back to 1600 B.C., was discovered off the western shores of southern Turkey’s Antalya province, in 2018, by Antalya University’s Underwater Research Department.
About the lead weights used in commercial life 3600 years ago, the head of the excavation, Associate Professor Hakan Öniz said, “We found lead weights that we have never seen among the 350 shipwrecks we have identified so far.”
The 14-meter-long (46-foot) shipwreck was found in a 50-meter depth, with 1.5 tons of copper bullion inside of it.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The researchers used sonar surveys, photo scans, and photographic mosaics to create three-dimensional scans of the bullion on the ship. They were able to determine that the bullion were taken from mines in Cyprus, and then molded in the 15th or 16th centuries B.C.

Akdeniz University (AU) Underwater Cultural Heritage Conservation and Restoration Department Head Associate Professor Hakan Öniz, “It was probably caught in the middle of a storm while traveling to the Aegean region from Cyprus. It was carrying a cargo of copper bullion and type of that bullion helped us date the ship. This may well be world’s earliest vessel carrying industrial goods,”.
Öniz said, “These copper ingots have an important feature. “If the Egyptians were the dominant power in the region in those days, other states in the region, such as Cyprus or the Minoan palaces or Assyrians, pay their taxes to the Egyptians with these copper ingots,” he said.
Noting that they encountered every form of copper ingot in the shipwreck, Associate Professor Hakan Öniz said: “We have also found clues about how it was made in the 16th century, Mediterranean trade.”

Noting that the lead weights, one of which is 22 grams and the other 44 grams, indicate that there was probably a Syrian merchant on the sinking ship, Öniz said, “Probably, the traders go everywhere with their own weights. Therefore, the merchant on this ship travels with lead weights of 22 grams and 44 grams. The merchant, who owns these weights, probably went to different copper mines in Cyprus and collected copper from one mine, for example, 10 ingots, and 20 ingots from another mine, and loaded them onto the ship. What we understand from this is that the business was not only about maritime trade, but that the merchant went around the mines one by one and bought them, perhaps using his own weight units to measure something else.”
Öniz added that they have identified approximately 350 shipwrecks within the borders of Antalya and Mersin during the underwater archaeological excavations they have carried out since 1999.
Cover Photo: DHA