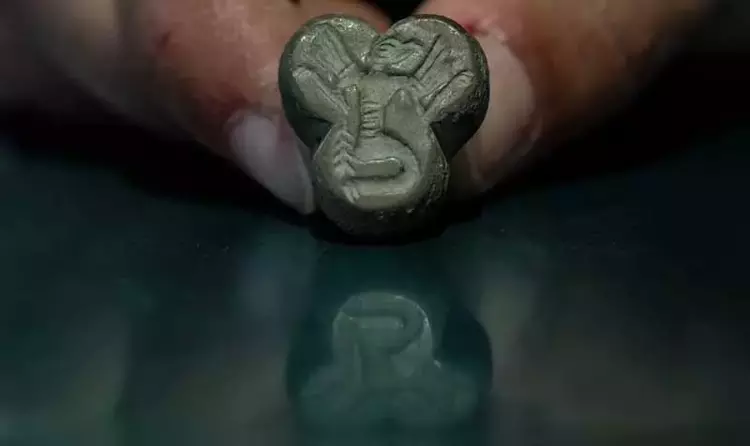
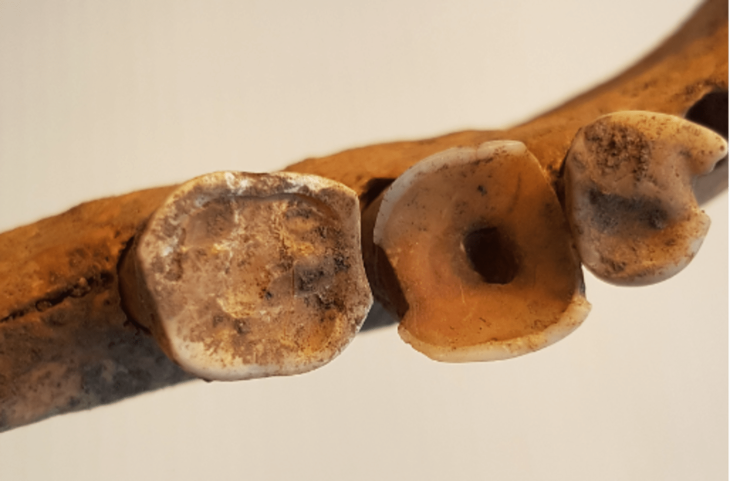
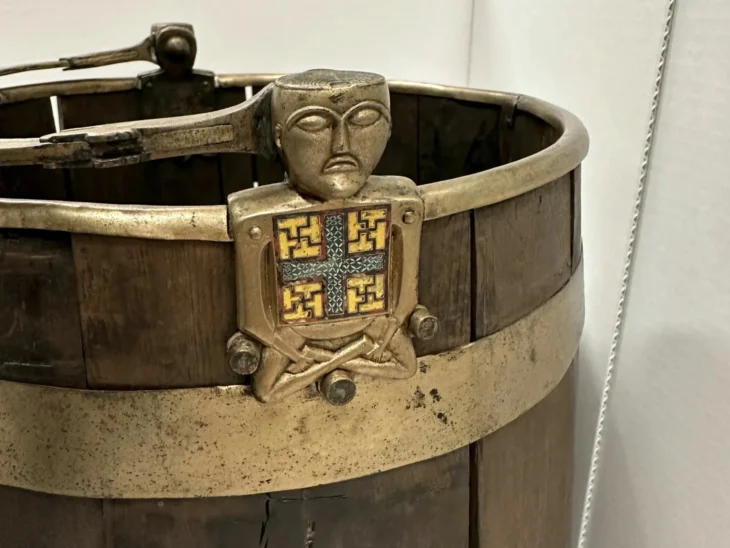
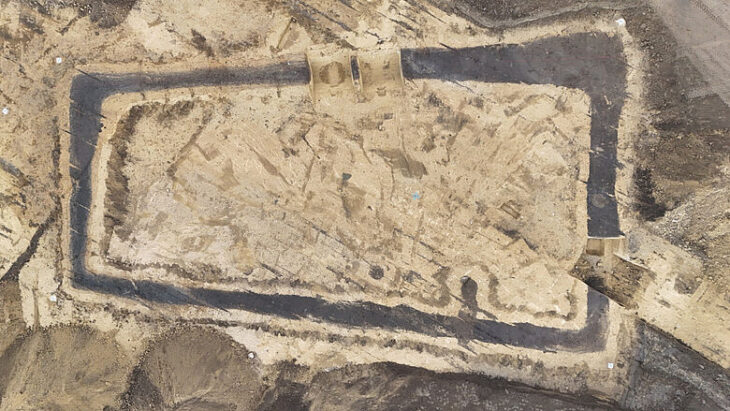
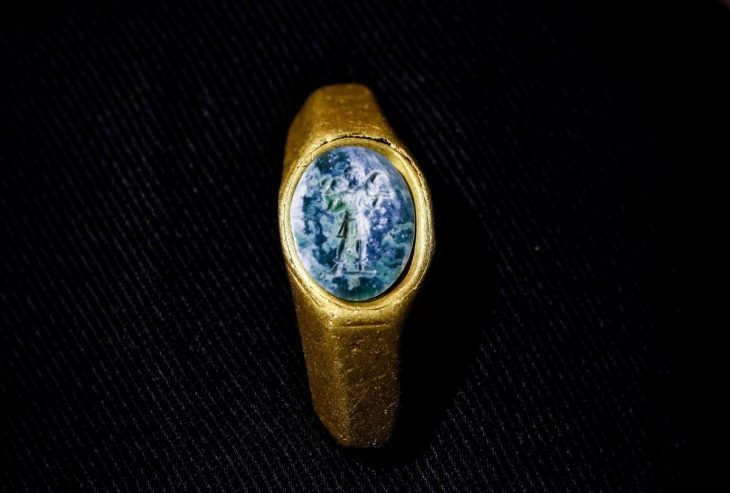
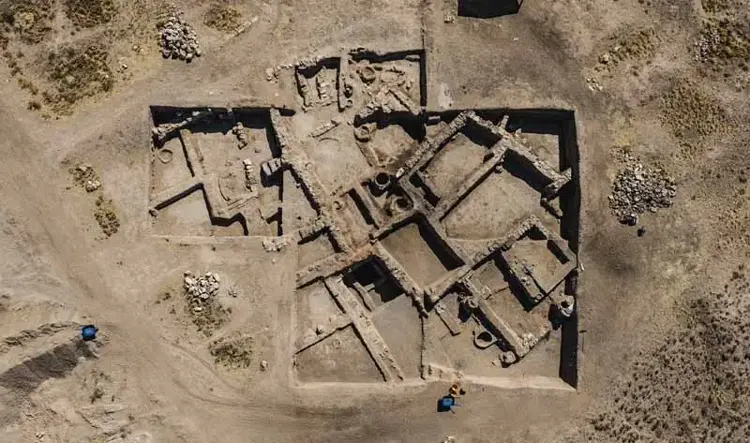
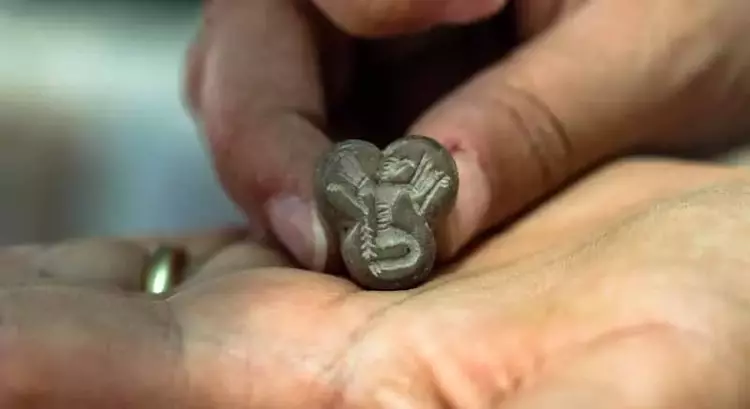
Archaeological excavations at Karahöyük in central Türkiye have led to a remarkable discovery: a 3,500-year-old human-headed, eagle-bodied seal. According to Assoc. Prof. Gonca Dardeniz Arıkan of Istanbul University, who leads the excavation, this rare artifact provides valuable insights into the religious beliefs and symbolic practices of ancient Anatolian societies, highlighting the interplay between daily life and spiritual traditions during the Bronze Age.
In a statement to Demirören News Agency (DHA), Arıkan said, “This season, we uncovered a seal showing a human-bodied, single-headed eagle. It is one of the most significant finds of this year and provides us with deeper insights into the spiritual and cultural life of the period.”

Ancient Burial Practices: Babies at Home, Adults Cremated
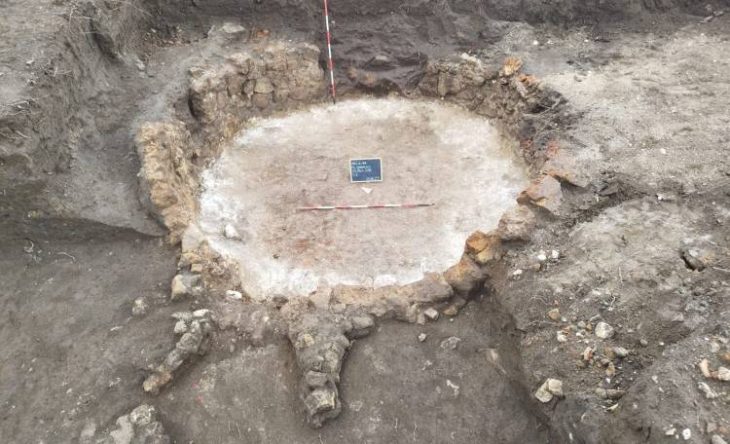
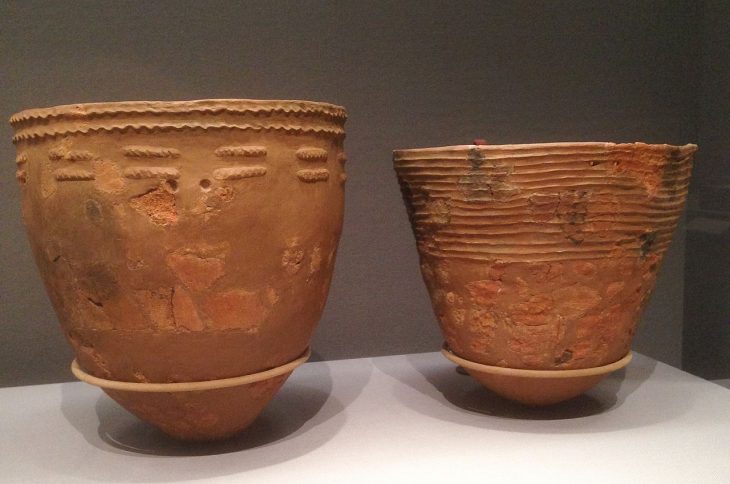
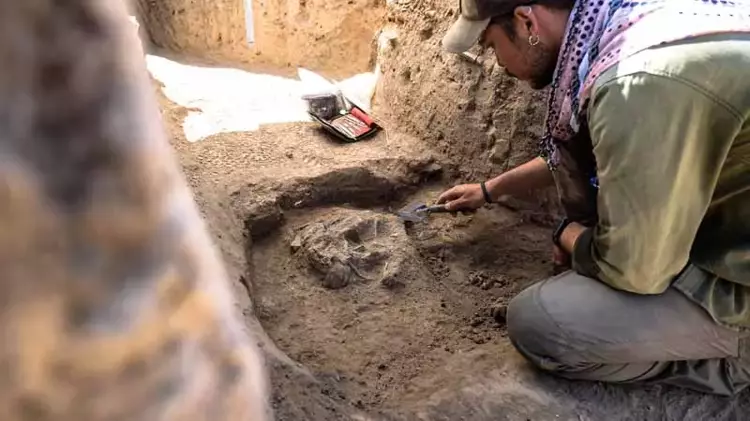
The excavations revealed fascinating details about burial rituals practiced in Karahöyük around 1500 BCE. While adult burials were carried out through cremation, archaeologists discovered that infants were often buried inside domestic living spaces.
“People buried their babies within the rooms they used daily. We believe this was closely tied to their religious beliefs,” said Arıkan. “Perhaps they wanted to keep the memory of their children alive within their households, unlike adults, who were cremated and taken away.”
Excavators also identified altars, ritual areas, symbolic objects, and grave goods connected to these practices, highlighting the close relationship between everyday life and spiritual traditions in ancient Konya.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Unexpected Discovery: Ancient Konya Residents Ate Squid
One of the most surprising findings was evidence of seafood consumption—including squid—in landlocked Konya 3,500 years ago.
“We found large storage vessels containing not only agricultural products but also freshwater and marine species. Freshwater fish likely came from Beyşehir Lake and nearby rivers, while marine products such as squid were probably brought from Alanya on the Mediterranean coast,” Arıkan noted.
Alongside seafood, remains of red deer, fallow deer, rabbits, hyenas, and even cave bears were discovered, painting a picture of a far richer and more diverse ecosystem than today.

A Window Into Ancient Belief Systems
The eagle-headed human seal is now considered a symbolic artifact that reflects the spiritual worldview of Karahöyük’s inhabitants.
“Seals were personal signatures, representing both identity and belief. Through these images, we can understand how people of the era expressed themselves and their connection to their gods and rituals,” Arıkan emphasized.
This discovery positions Karahöyük as one of Anatolia’s most significant Bronze Age settlements, offering rare glimpses into the intersection of daily life, religious practice, and cultural identity.

About Karahöyük
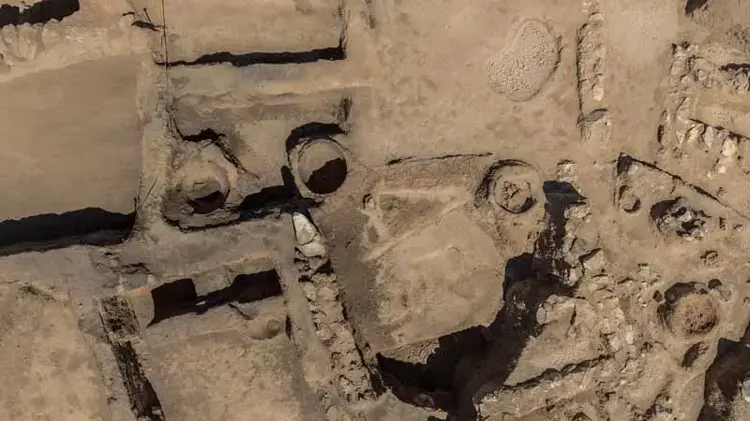
Karahöyük, located in the Meram district of Konya, Türkiye, is a significant Bronze Age settlement with a history dating back over 4,000 years. Excavations at the site have revealed complex urban planning, domestic architecture, storage facilities, and ritual areas, providing valuable insights into the social, economic, and religious life of ancient Anatolian communities. Artifacts such as seals, pottery, and burial goods indicate that Karahöyük was a hub for both local production and long-distance trade, connecting inland populations with the Mediterranean coast.
📌 Related Reading: Just last week, archaeologists also uncovered a 3,500-Year-Old Dining Set at Konya Karahöyük in Türkiye, offering further insights into the daily life of its ancient inhabitants.
Cover Image Credit: DHA