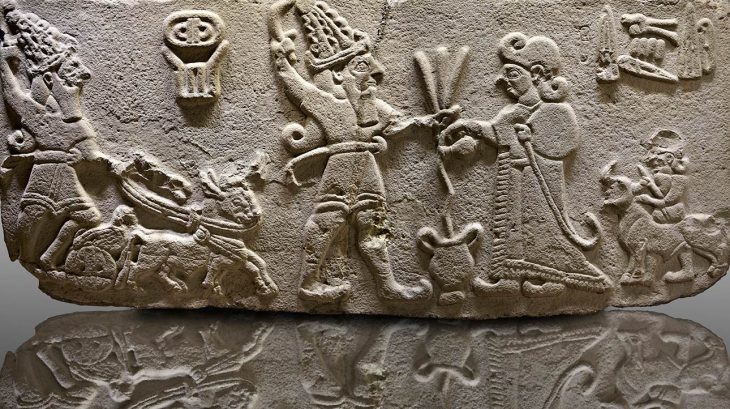
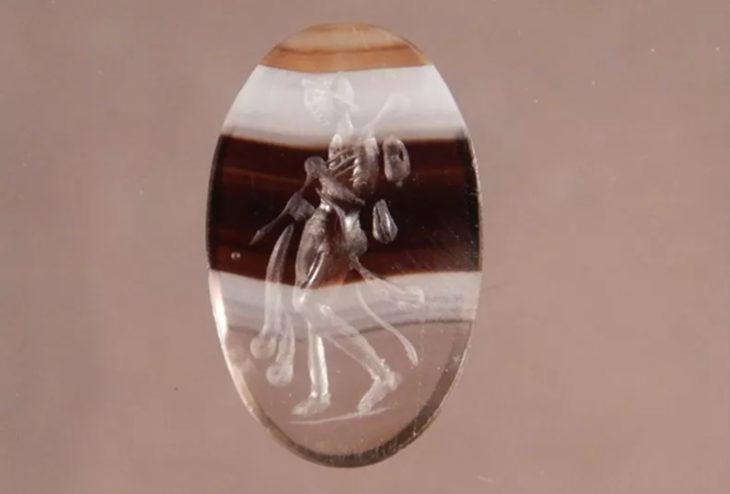
Burial includes ornate belt, ram-headed buckle, bronze mirror, and horse harness elements, revealing the elite status of the Scythian Noble Warrior.
Archaeologists in Siberia have uncovered the burial of a Scythian noble warrior dating back to the 6th century BCE, shedding new light on the martial traditions and cultural complexity of the Scytho-Siberian world.
The discovery, made on the banks of the Kem River in the Krasnoyarsk region by researchers from Siberian Federal University, has already been hailed as one of the most significant archaeological finds in recent years.

A Burial Rich in Symbols of Power
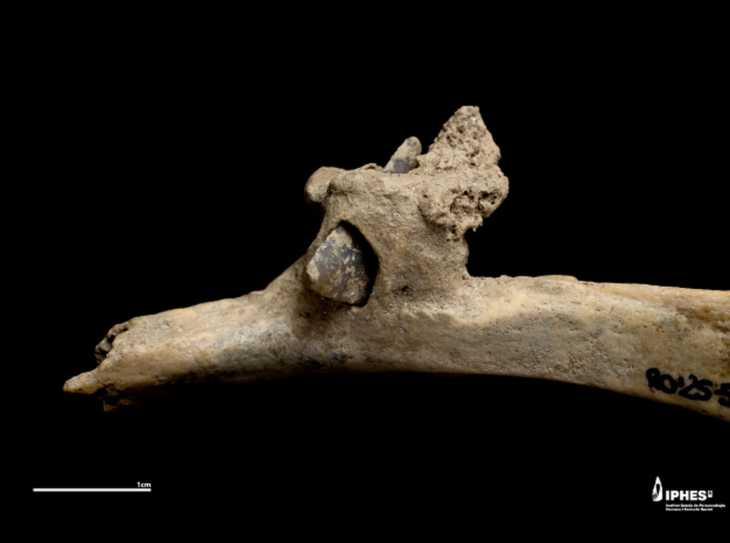
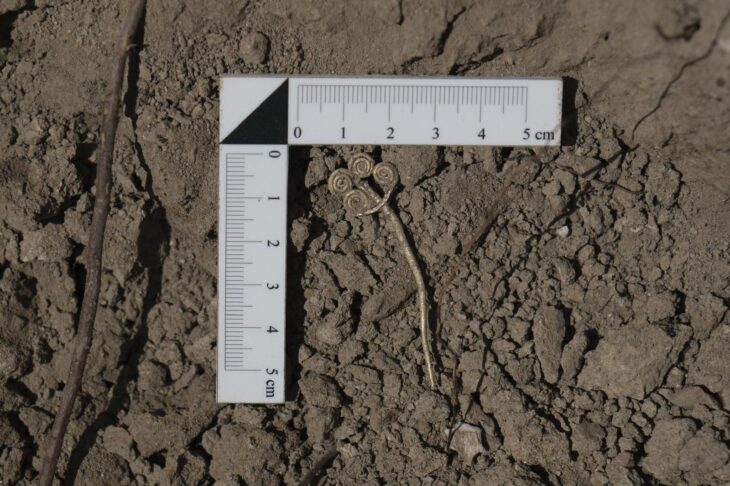
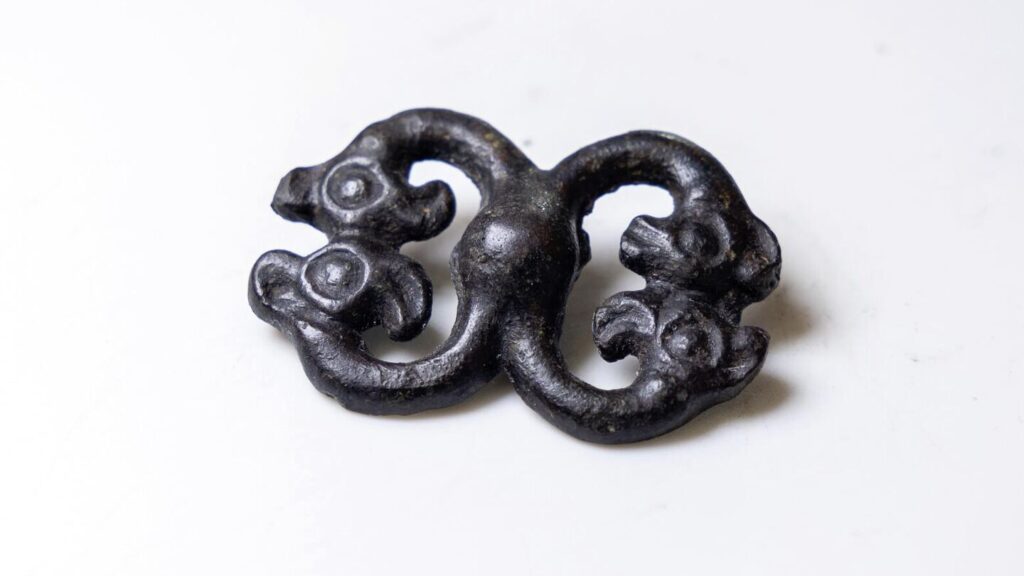
The burial chamber revealed a warrior interred with a remarkable array of possessions: a decorated belt adorned with bronze plaques, a buckle shaped like the head of a mountain ram, ornate jewelry, a polished bronze mirror, weaponry, and elements of a horse’s harness. Each object was not only a personal belonging but also a marker of status, wealth, and spiritual identity.
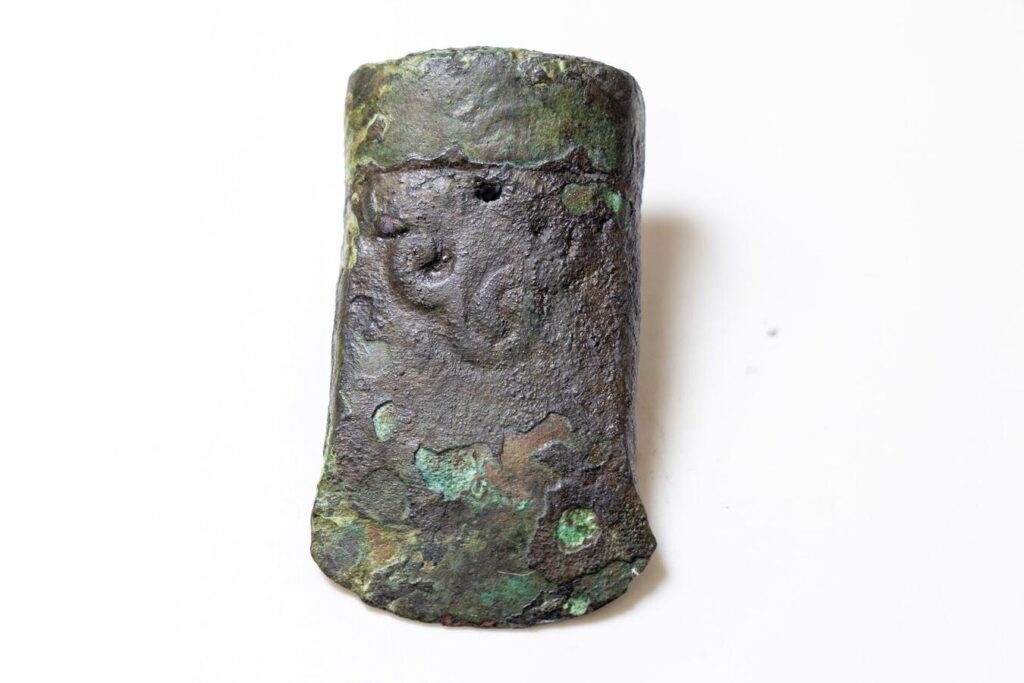
Among the finds, one object stands out as extraordinary: an iron battle axe known as a chekan. According to Pavel Mandryka, head of the Laboratory of Archaeology of Yenisei Siberia, this weapon was particularly rare for its time. “The chekan had a sharp point designed to pierce armor. Such an item highlights the high status of the warrior,” Mandryka explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
What makes the axe exceptional is its material. In Siberia, widespread use of iron would not become common until five centuries later. The presence of such an advanced weapon strongly suggests that the warrior either belonged to a privileged elite with access to distant trade networks or had migrated into the region from the southwest, bypassing the forest-steppe zones of modern Krasnoyarsk.

Weapons and Warfare of the Scythians
The Scythians were legendary across the ancient world as master horsemen and archers. Their short composite bows allowed for precision shooting from horseback, while their iron swords and bronze-tipped arrows struck fear into enemies. Yet the chekan adds a new dimension to our understanding of their arsenal. Unlike swords, which cut, or arrows, which pierced lightly armored foes, the battle axe was designed for brute force. With its pointed head, it could shatter helmets and puncture armor, making it both a practical and symbolic tool of authority.
Other items from the burial reinforce this interpretation. The belt, decorated with bronze plates, would have been a visible marker of rank. The ram-headed buckle evoked strength and virility, while the horse harness elements emphasized the inseparable bond between Scythian warriors and their steeds. Horses were not merely transportation; they were companions in battle and often buried alongside their riders to accompany them into the afterlife.

Mirrors and Rituals
Equally intriguing is the presence of a polished bronze mirror. Archaeologists believe it carried more than a decorative purpose. In Scythian culture, mirrors could serve ritual functions, acting as protective talismans or instruments in shamanic practices.
While warriors could be male or female in Scythian society—and even adolescents sometimes took on martial roles—the combination of weaponry, harness fittings, and belt ornaments in this case strongly indicates the burial of a man.

A Glimpse into the Scytho-Siberian World
This discovery is part of a broader pattern of archaeological revelations across Siberia. From frozen tombs in the Altai Mountains preserving tattooed bodies to golden treasures unearthed along the Yenisei River, the Scythians emerge not simply as raiders of the steppe but as a complex society with rich symbolism, far-reaching connections, and advanced martial traditions.
The Krasnoyarsk warrior’s grave highlights the interplay between local traditions and external influences. The use of iron, centuries ahead of its widespread adoption in Siberia, points to a flow of technology, trade, and ideas across the Eurasian steppe. At the same time, the burial’s wealth and ritual items underscore the deeply spiritual dimension of Scythian warfare, where every object—from a mirror to a horse harness—carried layers of meaning.
As excavations continue, archaeologists believe more secrets of the Scythians will surface from Siberia’s frozen ground. For now, the iron axe of the Kem River warrior stands as a silent witness to a world of power, prestige, and the enduring mystery of nomads who once ruled the steppe.
Cover Image Credit: Press Service of Siberian Federal University / Evgeny Puzin