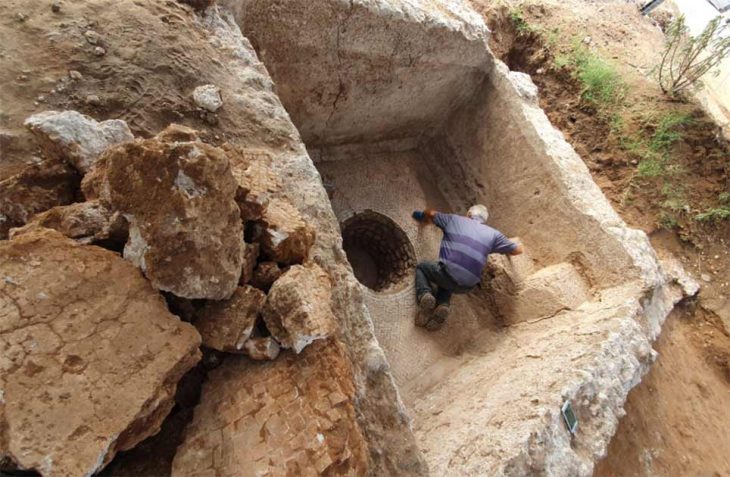
The Parthian Battery is believed to be about 2000 years old (from the Parthian period, roughly 250 BCE to CE 250).
History there have been several eureka moments and breakthrough inventions that have shaped our modern lives. Electricity is one of the most revolutionary discoveries in history, among many other amazing discoveries.
Over the centuries, several scientists and inventors have stood out for their contributions to the field of electricity. However, there are also impressive discoveries whose inventor is unknown and are almost 2000 thousand years old.
In 1936, while constructing a railway near Baghdad (once part of Iran’s mighty Parthian Empire, roughly 250 BCE to CE 250), workers stumbled upon what appeared to be an ancient battery, now famously known as the Parthian Battery.
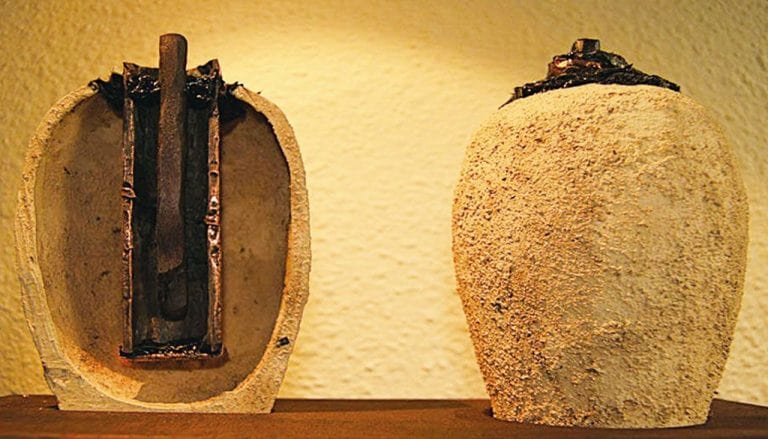
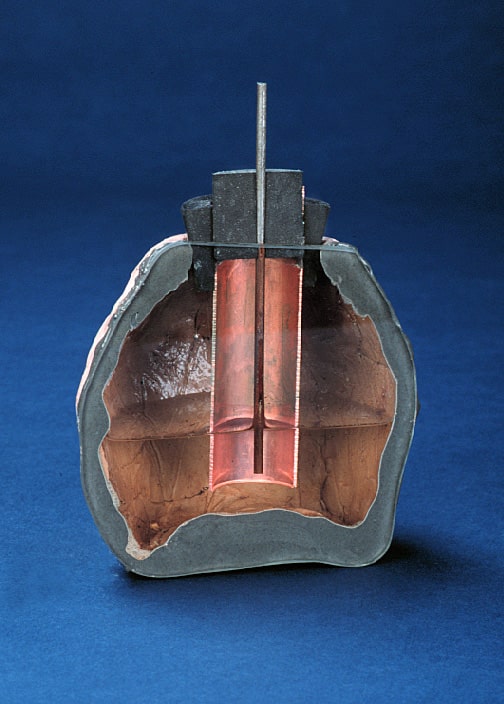
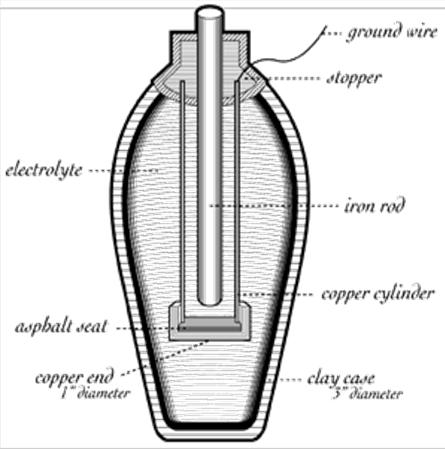
The jar was found in Khujut Rabu just outside Baghdad, estimated to be around 2,000 years old, and consists of a clay jar filled with a vinegar solution, housing an iron rod encased by a copper cylinder. Remarkably, this configuration generates approximately 1.1 to 2.0 volts of electricity.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
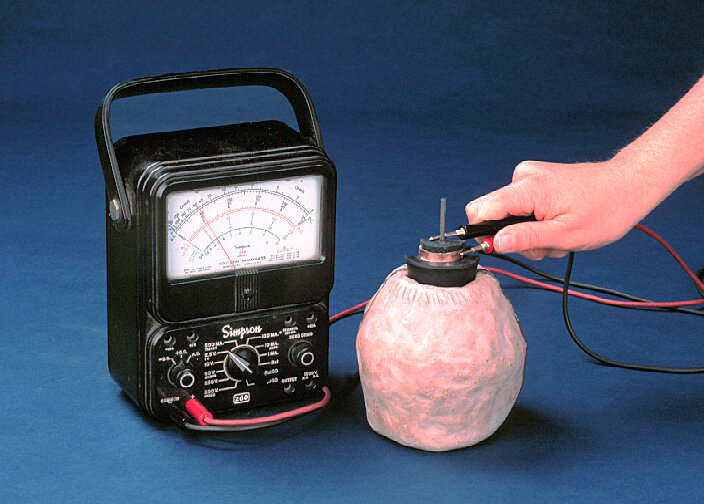

In 1938, German archaeologist Wilhelm Konig gave the jar’s first description, pointing out that it resembled an electric battery. American scientist Willard F. M. Gray later replicated the device, confirming its electrochemical capabilities when filled with an electrolyte such as grape juice, despite World War II impeding further exploration.
Scholars continue to debate the true function of these jars. While some argue for their use as batteries, others are skeptical, prompting questions about their origins and intended use. If they were batteries, though, who made them and what were they used for?
Unfortunately, there is no written record as to the exact function of the jar, due to the destruction of Iranian literary sources and libraries by Arabs upon the invasion of Iranian territories in the 7th century CE.
There is no written record as to the exact function of the jar, but the best guess is that it was a type of battery. Scientists believe the batteries (if that is their correct function) were used to electroplate items such as putting a layer of one metal (gold) onto the surface of another (silver), a method still practiced in Iran today.
The discovery casts doubt on accepted theories by implying that the idea for a battery may have existed long before the invention of the famous scientist Alessandro Volta.
To recall some of the defining moments in the development of electricity and power, the first of these moments was undoubtedly when the ancient Egyptians (2750 BC) electricity first recorded in the form of electric fish.
The ancient Egyptians called electric catfish the ‘thunderers of the Nile’. It sparked nearly millennia of wonder and intrigue, including the conduct and documentation of crude experiments like touching the fish with an iron rod to induce electric shocks.
Thales of Miletus discovered in the year 500 BC that rubbing lightweight materials like fur or feathers against amber could produce static electricity. Up to William Gilbert’s serious discovery of static electricity in 1600 AD, this static effect was unknown for nearly 2,000 years.
Who knows! If such jars were indeed “batteries” in the modern sense, then Count Alessandro Volta’s invention of the modern battery may have been predated by 1,600 years or more.
Cover Photo: An ancient Parthian battery displayed by the Iraqi Civil Society Photo: Mohamed Al-Taher, Iraqi Civil Society. Source: Dr. Kaveh Farrokh