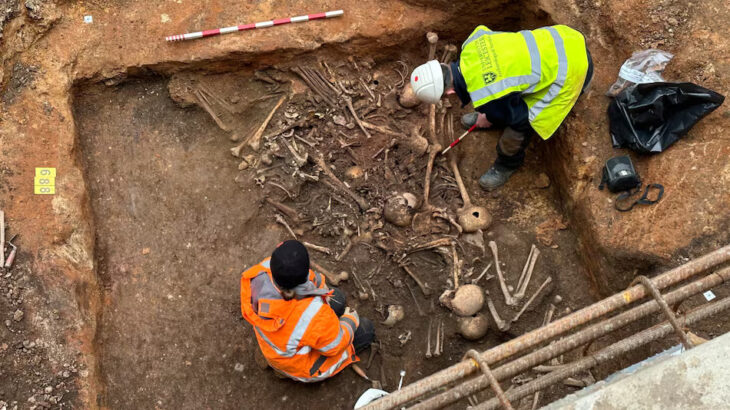
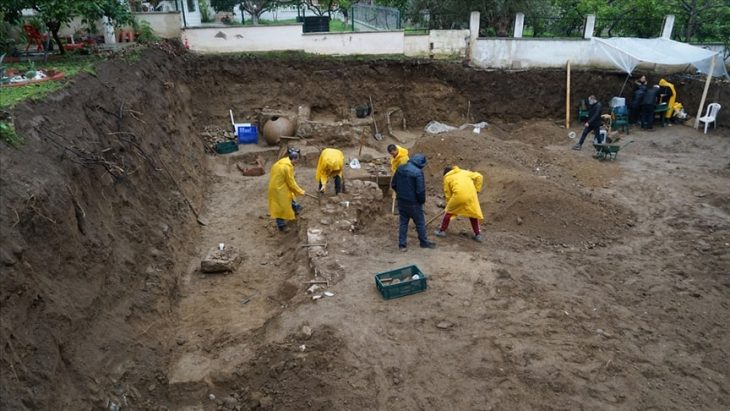
Archaeologists discovered 15 new sculptures during recent digs around the Yesemek Open Air Museum and Sculpture Workshop in the Islahiye region of southern Gaziantep province.
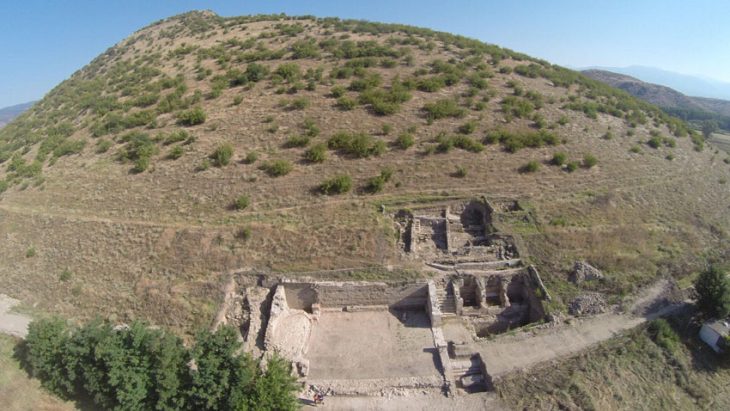
The Yesemek Open-Air Museum and Sculpture Workshop, which spans 100 decares (24.7 acres) and was inscribed on UNESCO’s Tentative World Heritage List in 2012, exhibits how the sculpture workshop was managed, as well as the techniques and materials utilized in the sculpture-making process.
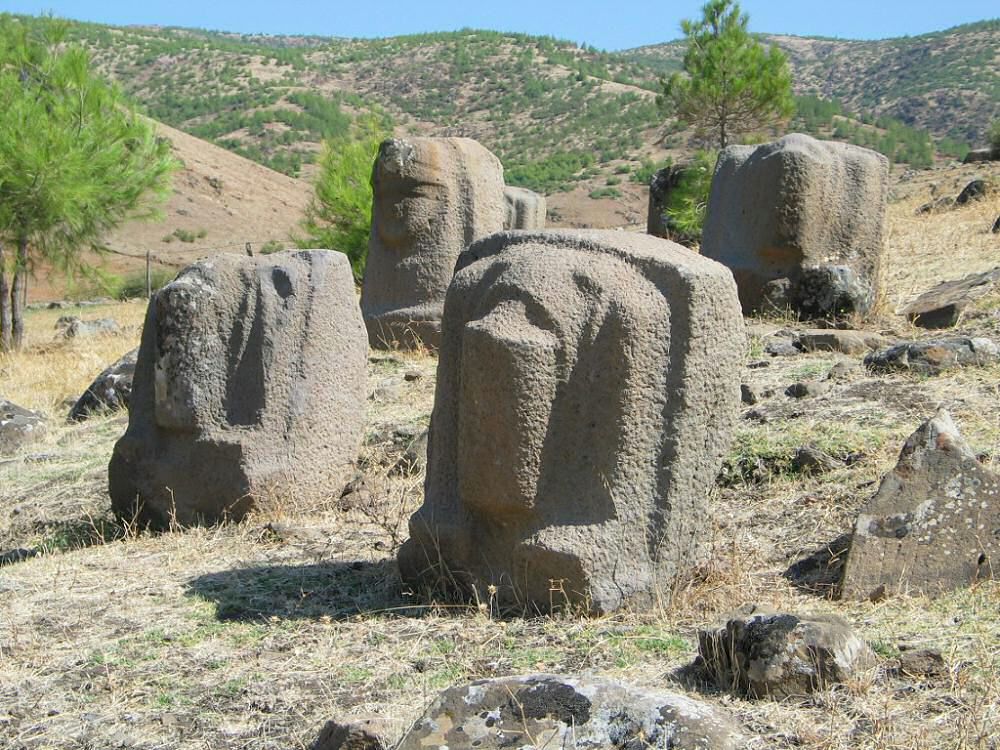
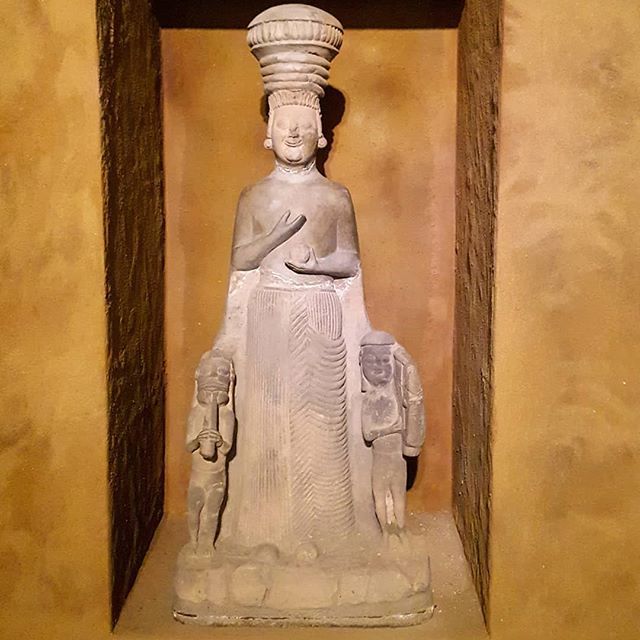
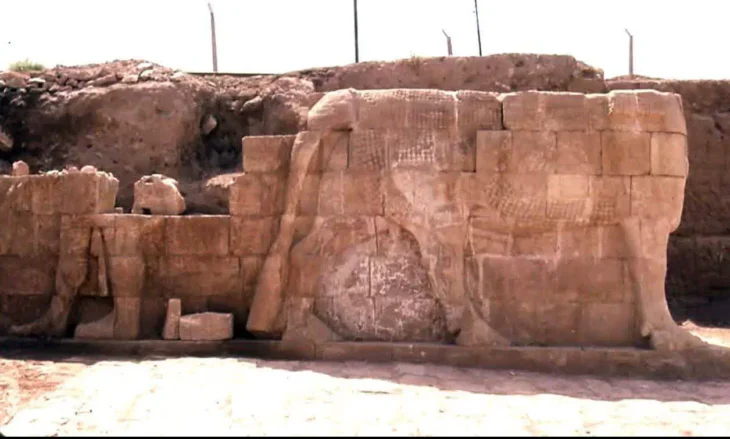
The significance of Yesemek Stone Quarry and Sculptural Workshop is rooted in its basalt quarry and stone sculptures found at the site.
Yesemek was first discovered by Felix Von Luschan in 1890 while he was excavating Zincirli (Sam’al). Between 1958 and 1961, the site was excavated by a team under the leadership of Prof. Dr. Bahadır Alkım. The site-hosted excavations were carried out in the area by İlhan Temizsoy in the 1990s. The excavations at the site yielded approximately three hundred finished or unfinished lion, sphinx, and mountain god sculptures.
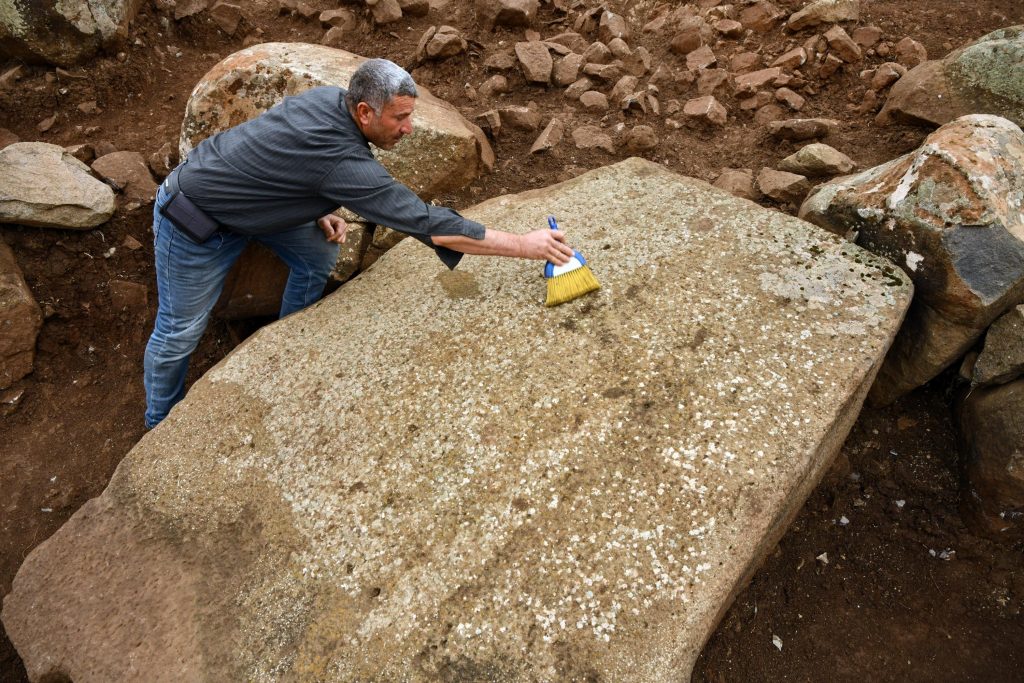

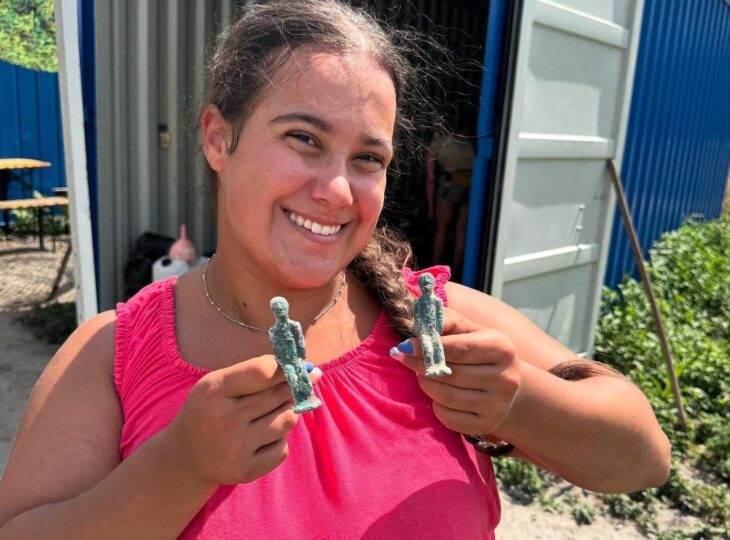
The latest archaeological excavation of the site’s researchers added 15 additional new sculptures to Yesemek’s collection, chiefly of lions and sphinxes. The open-air museum’s director, Özgür Çomak, told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the relics were unearthed during excavations under the presidency of Professor Atilla Engin.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Stating that they uncovered important findings in the excavations that started after about 31 years, Çomak said: “It was known that there were approximately 520 sculptures in the Yesemek Open Air Museum and Sculpture Workshop. However, our recent works proved there are more artworks hidden under the site. We will continue our archaeological studies and hopefully will uncover more sculptures.”
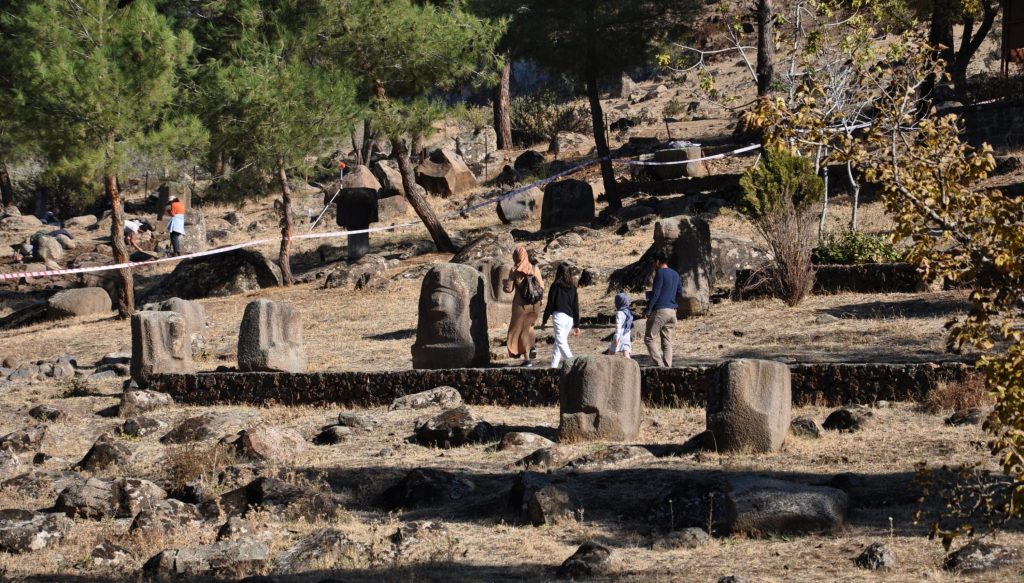

Reiterating that Yesemek is in a UNESCO process, Çomak said that they need more information and documents about the history of the site for its inclusion to the UNESCO World Heritage List. Noting that they have been sustaining their excavations for this purpose, the director continued: “Hittites produced sculptures using local stone from the slopes outside the quarry here. Yesemek is the largest and oldest sculpture workshop in the region. This place has a universal cultural value and we have to introduce this value to the world.”
Yesemek was the largest stone quarry and statue-processing worksite of Near East between the fourth quarter of the 2nd thousand B.C. and 8th century B.C.
The region was ruled by Hittite between 1375-1335 BC. in this period in the Emperor of Suppilluma I the administration of the workshop was started where local people were working. In the worksite where activities are slowed down for a while, studies again gained speed during the late Hittite Kingdoms Period. During the new period especially Hittite, Syrian, Aromi, and Assyrian Art Elements gained importance.