New Neolithic-era discoveries at Çayönü in southeastern Türkiye, dating back to approximately 10,200–6,500 BCE, include four grid-plan buildings and a Bronze Age (c. 3100–1100 BCE) water channel. Excavations reveal rich cultural layers spanning over millennia and early evidence of urban planning, metallurgy, and copper craftsmanship.
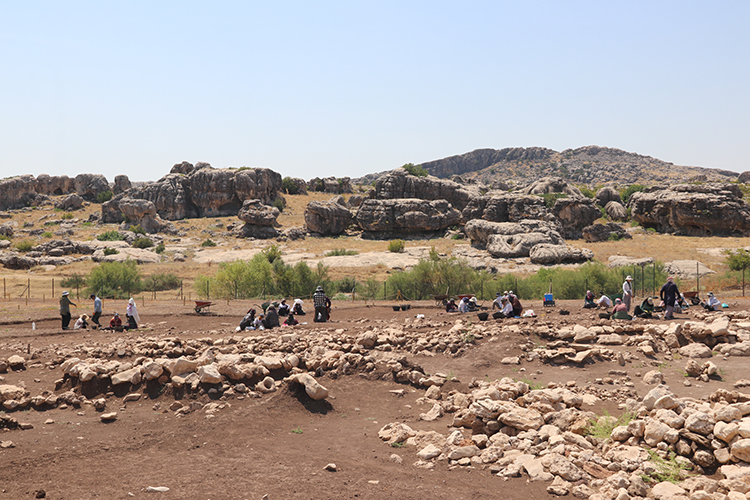
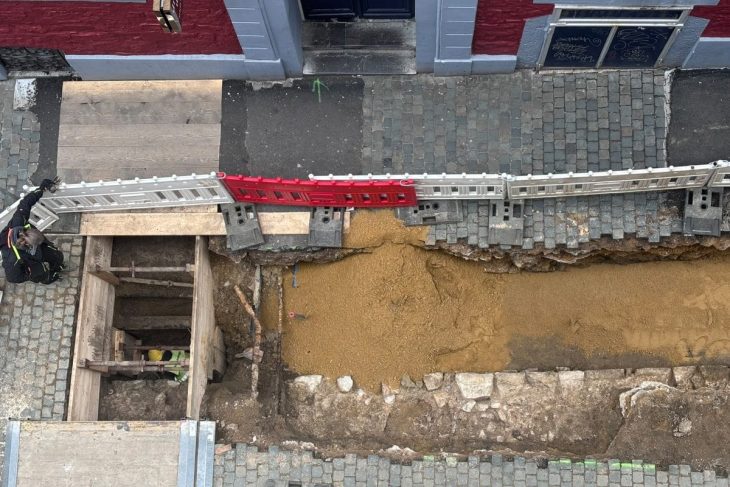
Excavations at the 12,000-year-old Neolithic site of Çayönü Mound, located in southeastern Turkey’s Ergani district, have unearthed four grid-plan structures and a Bronze Age water channel, shedding new light on the region’s prehistoric urban planning and craft production.
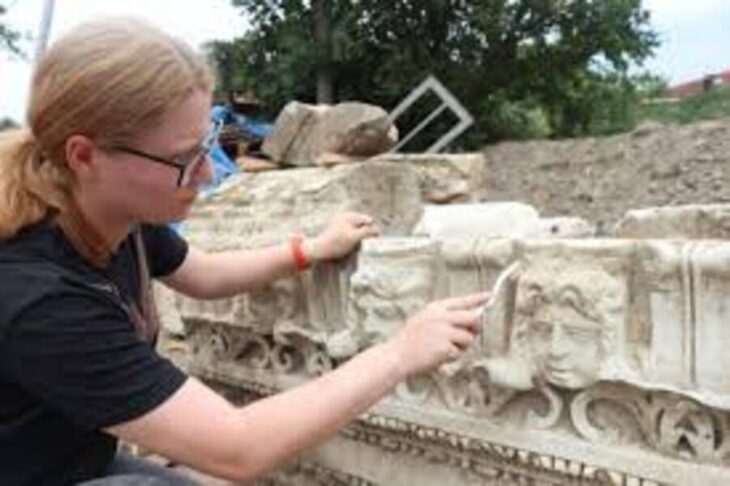
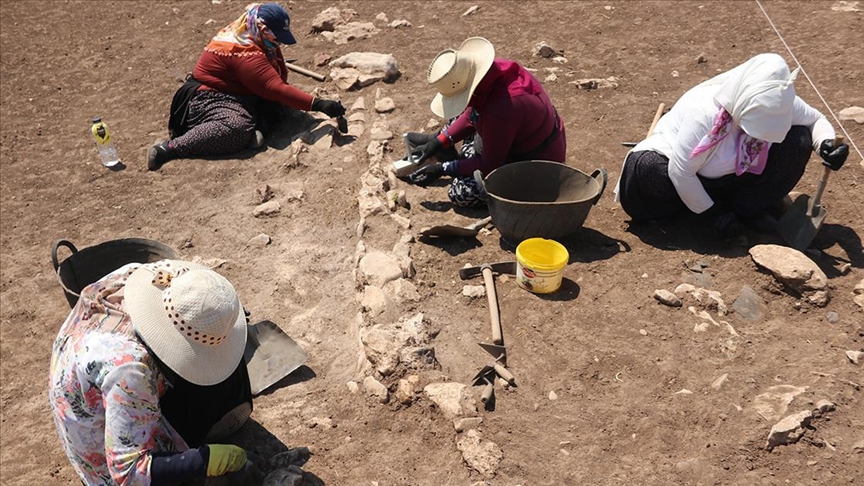
The latest findings were revealed during the 2025 excavation season led by Associate Professor Dr. Savaş Sarıaltun from Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University. According to a report by Anadolu Agency (AA), the discoveries come from the eastern part of the mound—an area never previously excavated.
“These grid-plan buildings and the channel system show that Çayönü still holds many undiscovered layers and stories,” said Dr. Sarıaltun.

A Legacy of Firsts: Çayönü’s Historical Significance
Discovered during surface surveys in 1963 and first excavated in 1964 by Dr. Halet Çambel and Prof. Dr. Robert J. Braidwood, Çayönü is one of the earliest known Neolithic settlements in the world. Situated just north of Hilar village, the site is often cited as one of the birthplaces of agriculture, settled life, and early metallurgy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeological evidence shows that Çayönü hosted continuous habitation from 10,000 BCE, transitioning from hunter-gatherer lifestyles to farming and settled communities. Its discoveries have contributed to understanding early human societal structures, rituals, and technological innovations.
2025 Discoveries: Architecture, Tools, and Water Engineering
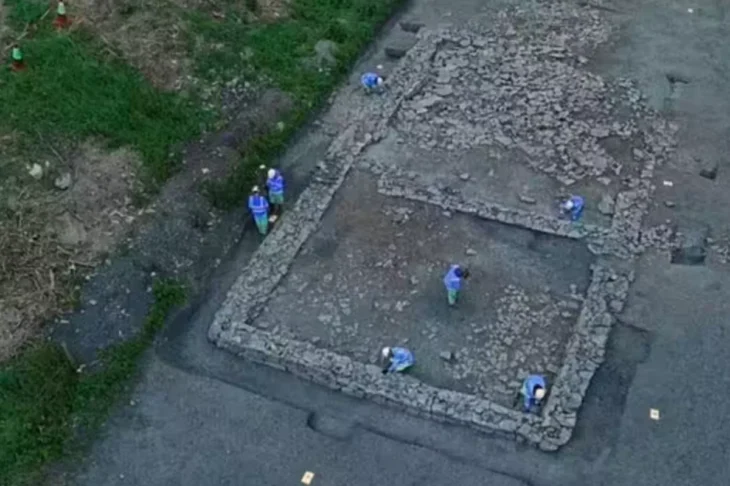
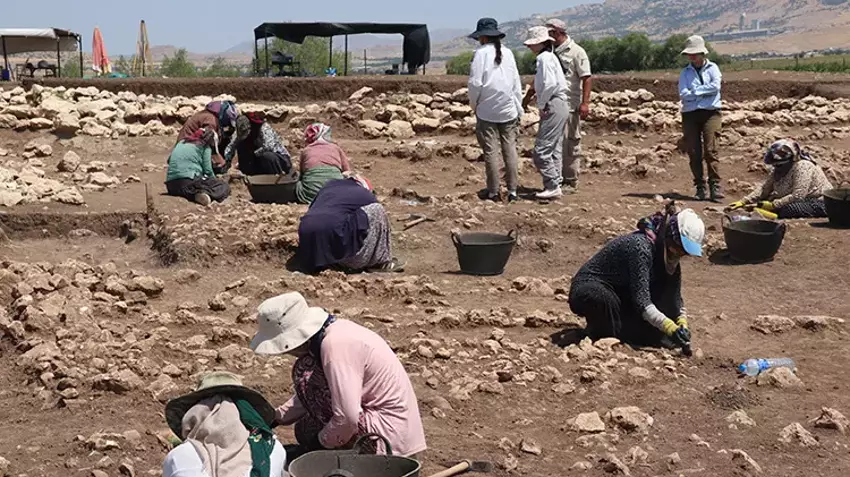
The current excavation team, consisting of 60 members including scientists, students, and local workers, has focused on both Neolithic and Early Bronze Age layers. In the eastern zone, archaeologists unearthed:
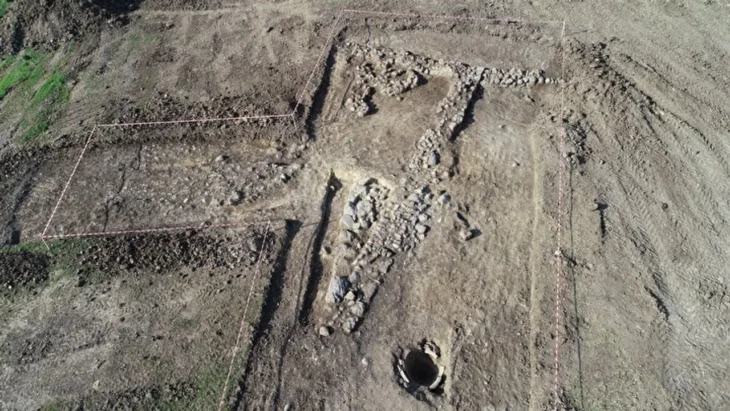
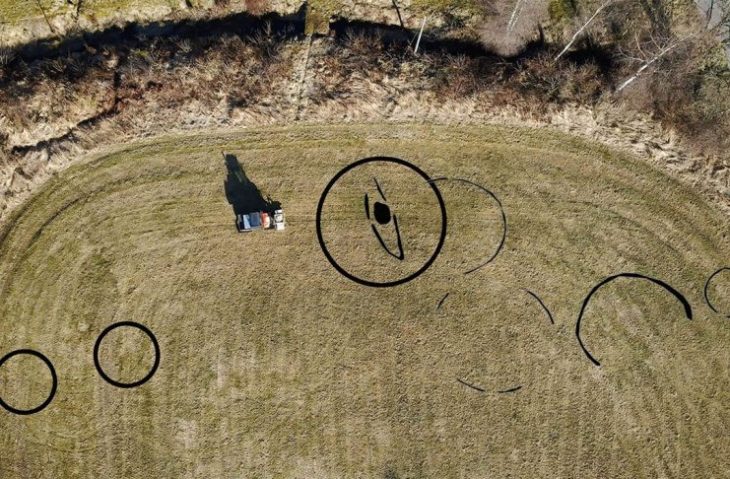
Four Neolithic grid-plan buildings, offering new insights into early urban planning and community organization.
A carefully constructed water channel made of terracotta “küng” pipes and stone walls, possibly used for waste or clean water—still under analysis.
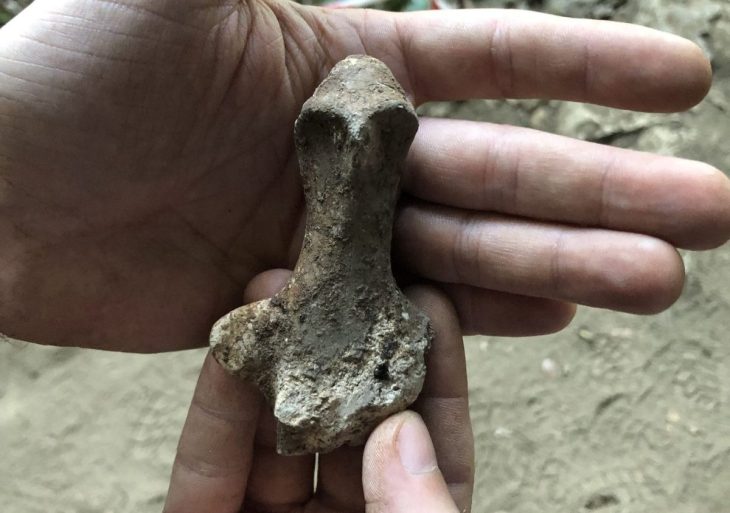
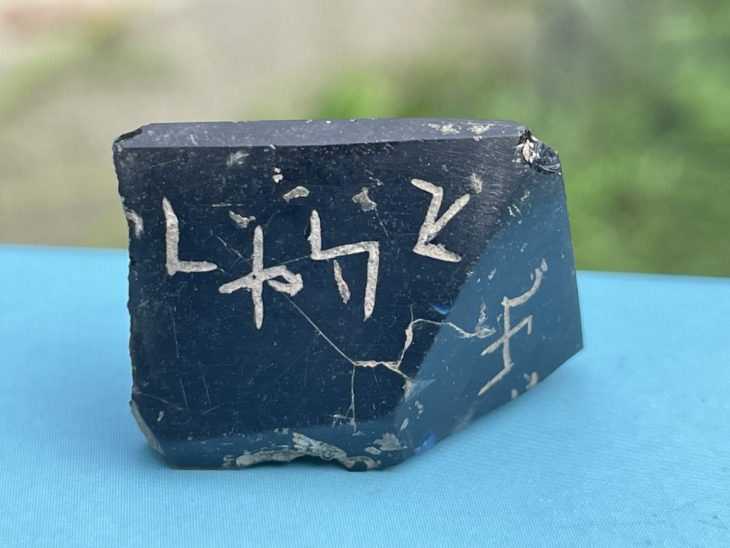
A range of obsidian tools, including a unique artifact dubbed the “Çayönü Tool.”
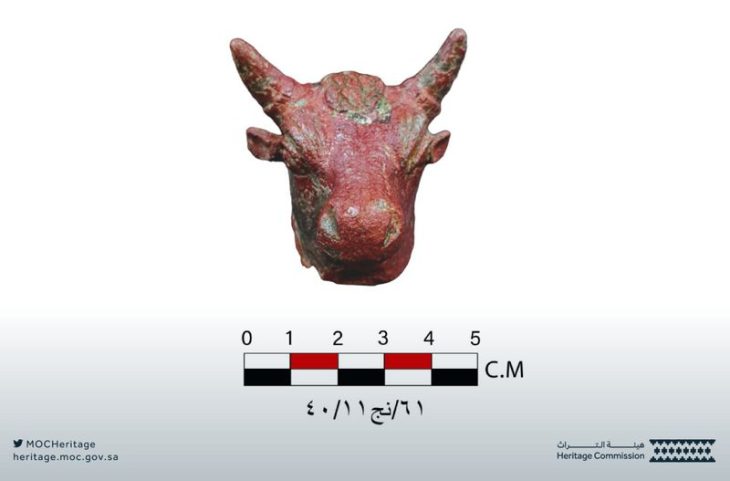
Numerous malachite samples, copper objects, and ornamental beads, indicating advanced metalworking and decorative arts.
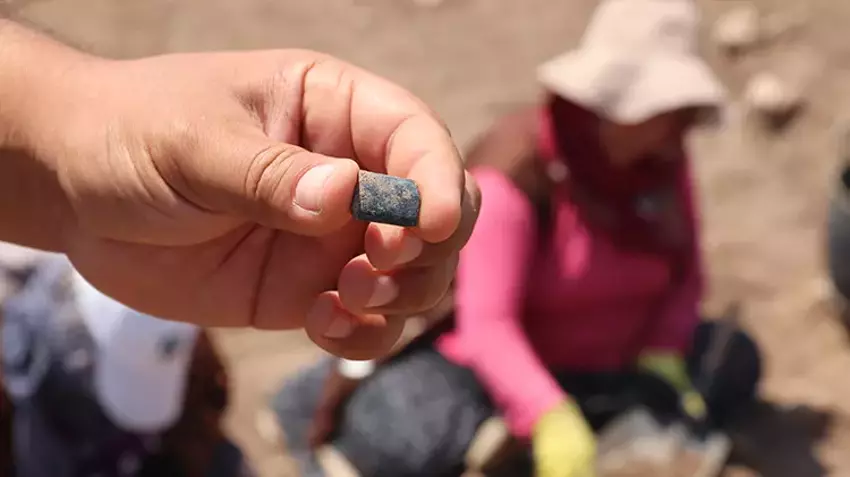

These finds help clarify the architectural and social strategies of Çayönü’s ancient inhabitants.
“This year alone, we’ve already discovered twice as many artifacts as last year,” noted Sarıaltun, underlining the productivity of the 2025 season.
Early Metallurgy and Ornamentation
The presence of malachite and worked copper objects points to early metallurgical expertise in the region. Among the notable finds are:
Beads in various forms: single-holed, two-holed square, four-holed square, and almond-shaped varieties
14 confirmed copper artifacts, with expectations for more as excavations continue
Evidence of localized production zones, highlighting specialization and craft diversity
These elements support the theory that Çayönü was a center for both utilitarian and decorative production during the Neolithic.
Interpreting Social Structure Through Space and Objects
The newly identified grid-plan structures—especially those dated between 9100–9000 BCE—offer a rare glimpse into the spatial planning and social organization of prehistoric communities. Comparing the eastern and western building zones, archaeologists suggest that different functional areas may have existed for habitation, production, or possibly governance.
“These structures help us understand settlement strategies, group behavior, and the range of tools and ornaments produced. Each layer tells a new story about life 12,000 years ago,” said Sarıaltun.

Looking Ahead: Çayönü’s Unfinished Story
With excavation areas set to expand from 750 to 1,500 square meters by the end of 2025, archaeologists believe Çayönü still holds many secrets about the earliest chapters of human civilization. The site continues to serve as a focal point for understanding humanity’s transformation from nomadic to settled life, with implications for agriculture, architecture, and social evolution.
“Each season at Çayönü brings a new discovery. There are still many chapters left to uncover,” concluded Sarıaltun.
Cover Image Credit: Anadolu Agency (AA),