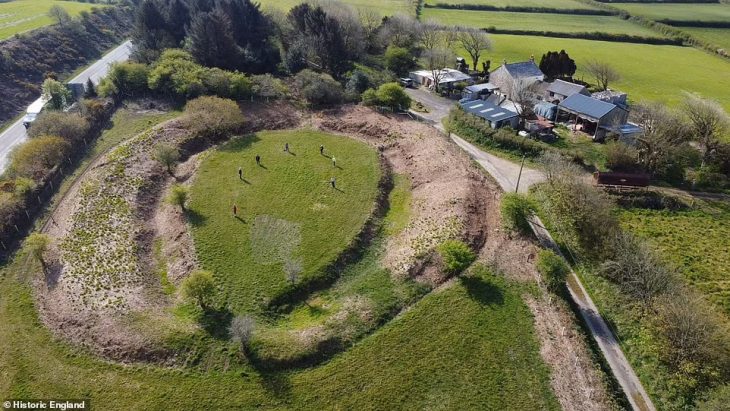
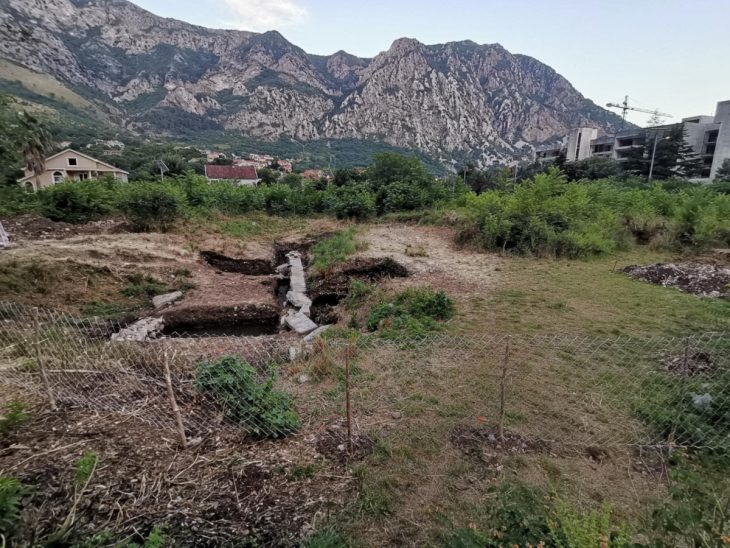
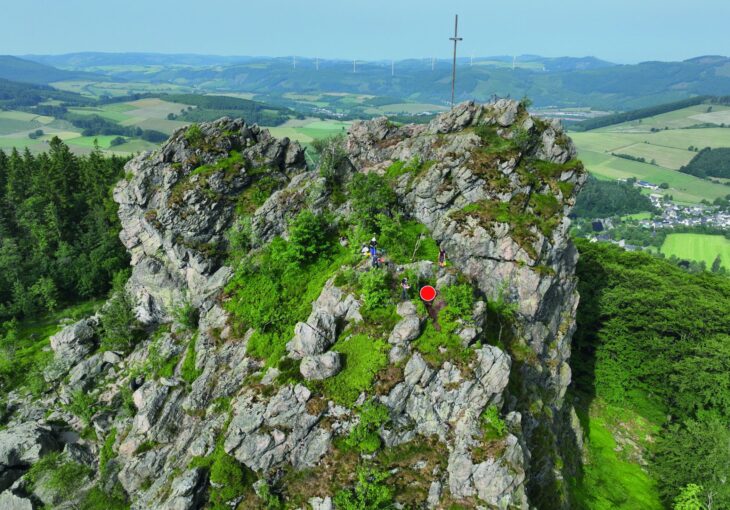
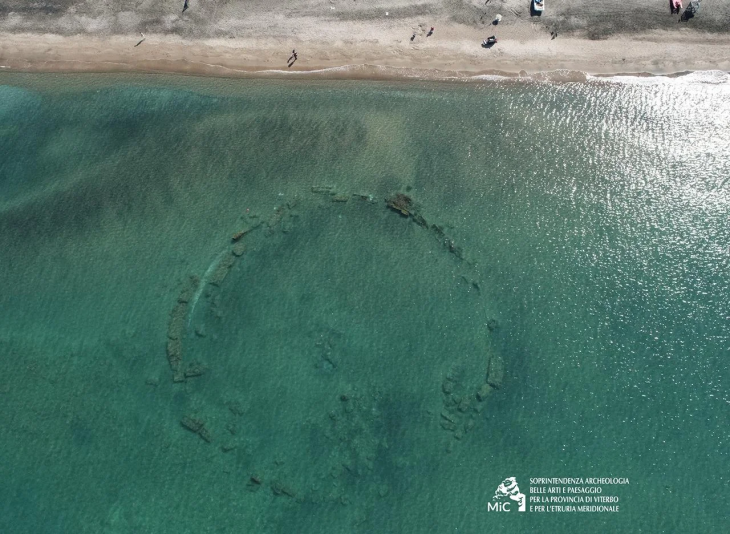
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has unearthed a significant number of megalithic structures near the Malampuzha dam in Palakkad, Kerala. The excavation revealed over 110 megaliths spread across 45 hectares of land, primarily constructed from massive granite slabs and boulders, with some structures incorporating laterite stones.
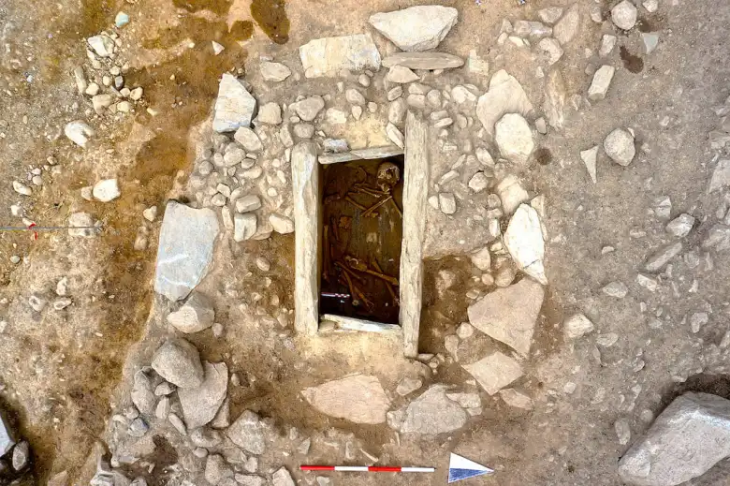
Most of the burials are of Cists variety – both single and multiple chambered-Stone Circles, Urns, Dolmens, and Dolmenoid Cists,” ASI wrote while sharing the images of the megaliths.
Among these ancient structures, dolmens are particularly noteworthy. Dolmens are a type of megalithic tomb consisting of two or more vertical stones supporting a large horizontal stone slab, often used for burial purposes. These structures provide valuable insights into the burial practices and belief systems of early societies.
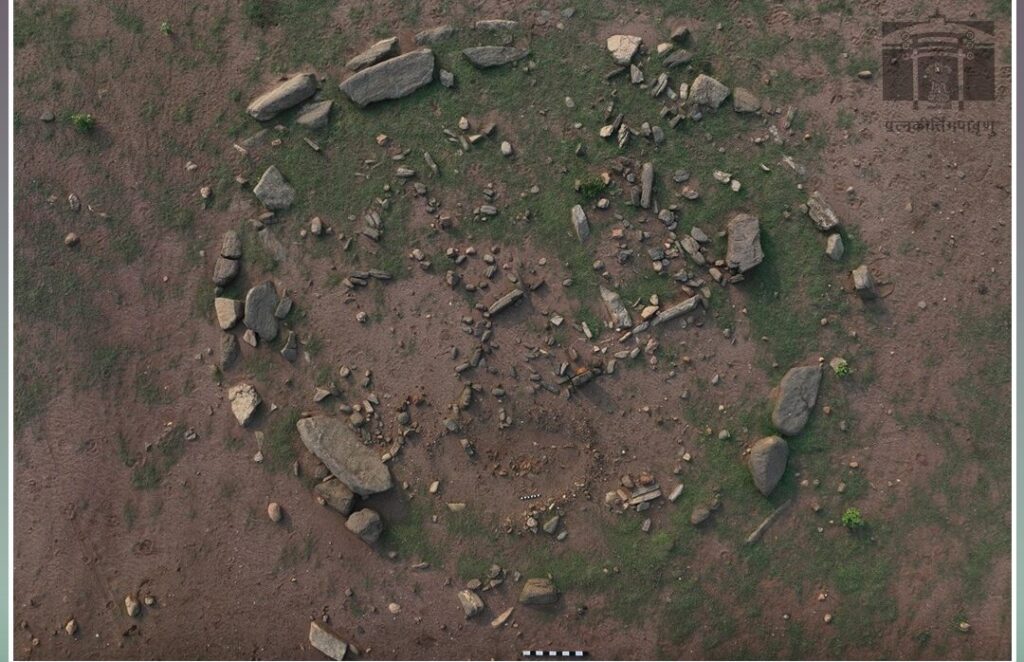

The ASI noted that the clustering of these megalithic burials is expected to enhance our understanding of early Iron Age society in Kerala. As researchers continue to analyze the findings, more information is anticipated to shed light on the historical significance of these structures.
Ancient Inscriptions and Rock Art in Kadapa
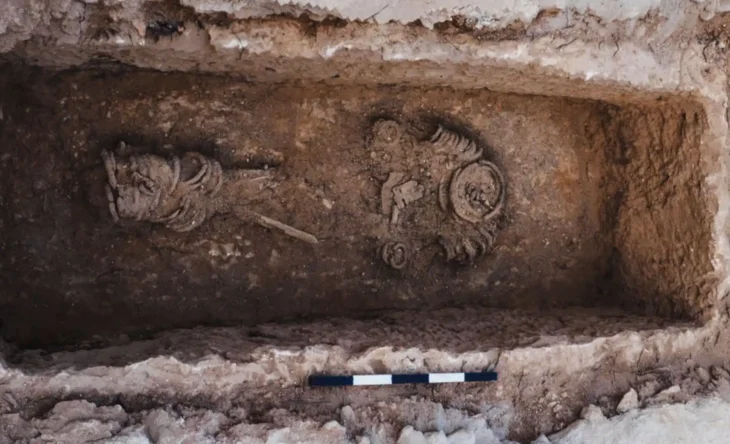
In a separate but equally significant discovery, ancient inscriptions have been uncovered at the Lankkamala Reserve Forest in Kadapa, Andhra Pradesh. The ASI’s survey revealed three rock shelters, one of which contained stunning prehistoric paintings depicting animals, geometric patterns, and human figures. These artworks, dating back to the Megalithic period and early historic periods (2500 BCE- 2nd century CE), were created using natural materials such as red ochre, kaolin, animal fat, and crushed bones.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
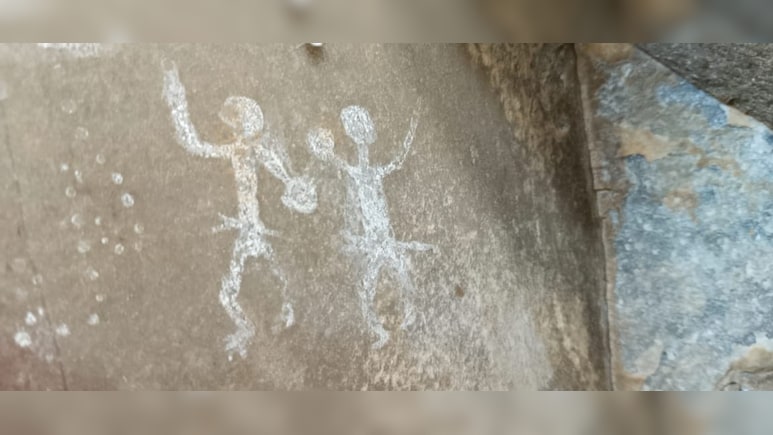
The inscriptions found in Lankkamala, dating from the 4th to the 16th Century CE, suggest that the area was a major Shaivite pilgrimage center frequented by devotees from northern India. The survey, conducted in the rugged terrain of Nityapujakona, Akkadevatala Konda, and Bandigani Chella, examined nearly 30 inscriptions, revealing scripts in Brahmi, Shell, Nagari (Sanskrit), and Telugu characters.
K. Munirathnam, the leader of the survey, described these findings as a landmark discovery in the ASI’s history, emphasizing their importance in understanding the pilgrimage routes that connected various regions. He noted that the shift of the Shaivite pilgrimage center from Lankkamala to Srisailam began in the 4th Century, highlighting the evolving religious landscape of the area.
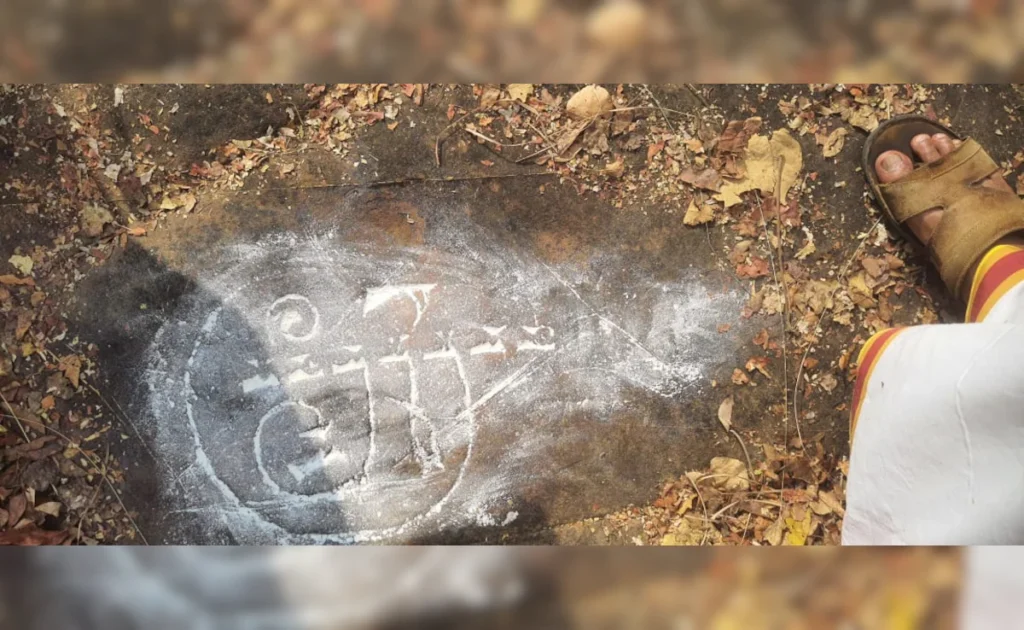
Together, these discoveries in Kerala and Andhra Pradesh not only enhance our understanding of ancient societies but also underscore the rich cultural heritage of India. As further research unfolds, these findings are expected to provide valuable insights into the history, culture, and traditions of the regions involved.
Cover Image Credit: Megalithic structures found in Malampuzha Dam in Palakkad, Kerala. ASI
















