Unique tombs wrapped in high-quality fabrics and painted bodies were discovered at the monumental temple in Peru.
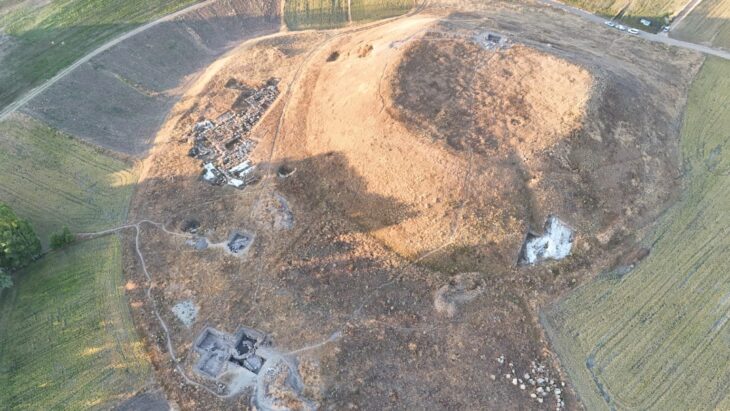
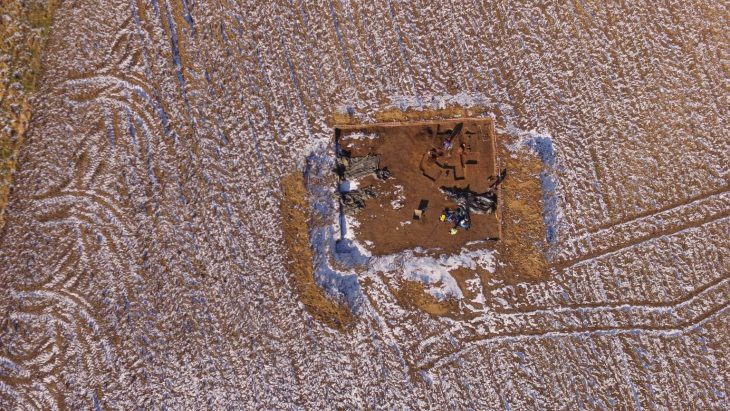
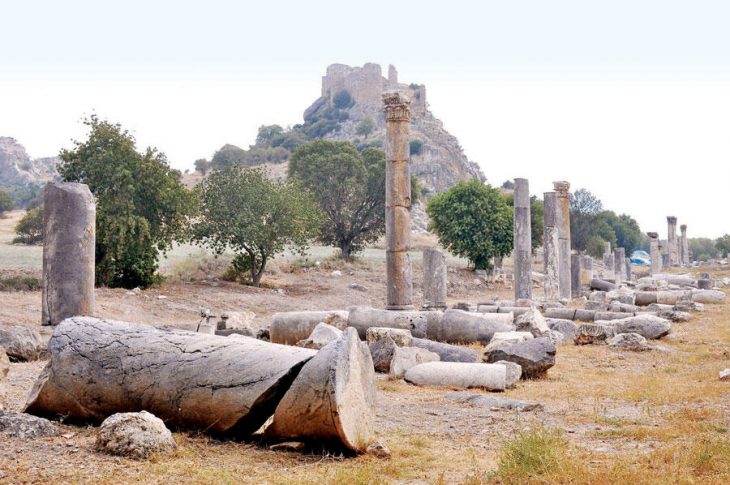
Located on the Cerro Colorado hill near the city of Barranca, Peru, four mysterious mounds were identified as spots with potential archaeological significance. The mounds were later revealed to contain human remains and the remain of a temple structure.
Excavations are being carried out by archaeologists from the Jagiellonian University and St Mark’s University as part of the Programa de Investigacion “Los valles de Barranca” project.
The project to investigate the area began in 2022, and the results were announced in February of this year, according to Nauka W Polsce.
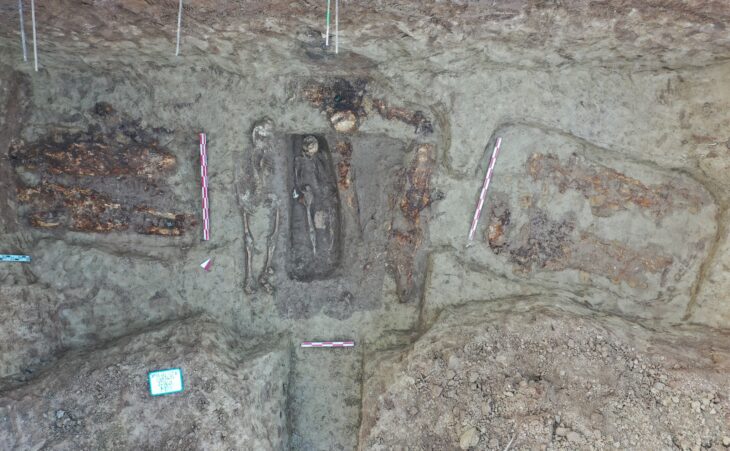
Human burials and monumental architecture made of dried bricks and stone blocks were discovered during research on two of the mounds. This has resulted in a large-scale excavation of the site, where the project has discovered destroyed burials in the form of burial bundles, which were placed within the ruins of a temple complex made of dried brick.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

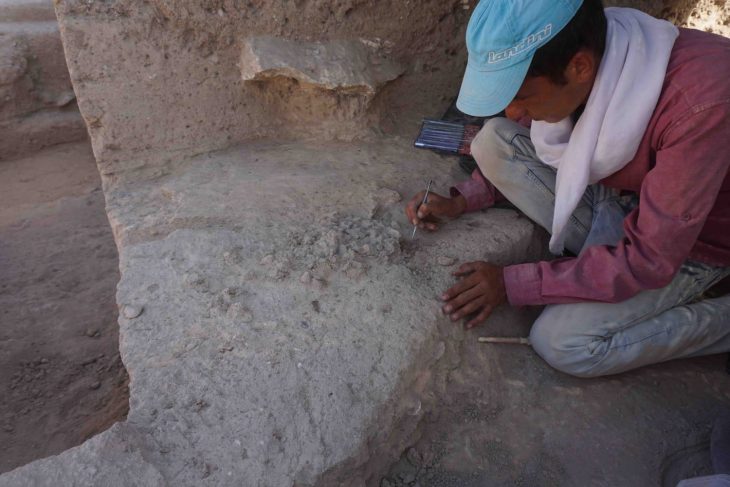
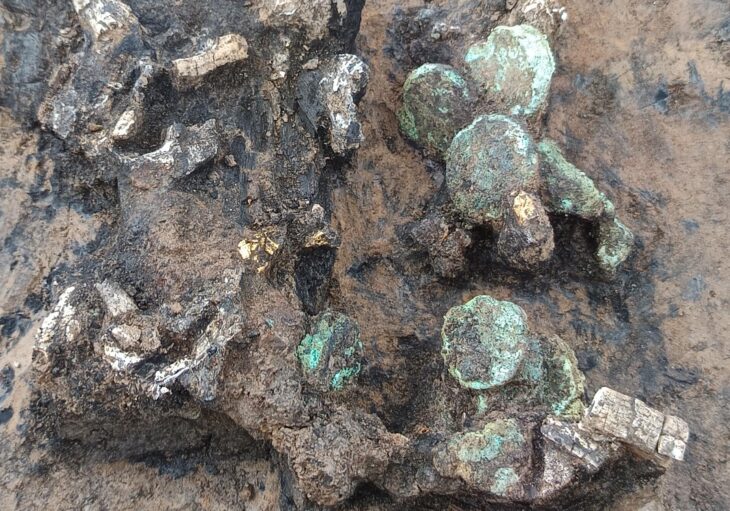
The remains of a young boy whose skull was intentionally deformed are found in one of the destroyed burials. He was originally buried with decorated textiles, indicating that he came from a high-status family. The fabric was three meters long and decorated with totally unique zoomorphic representations.
Bioarchaeologist, Łukasz Majchrzak, said “One of them (fabrics), 3 meters long, was decorated with zoomorphic representations and is unique – similar fabrics have not been found in the entire Andes so far,”
The construction of the temple complex was dated by physicochemical analysis and carbon dating of organic remains to between 2500 and 2200 BC, whereas the same method used to date the burials indicates that they were interred between AD 772 and 989.
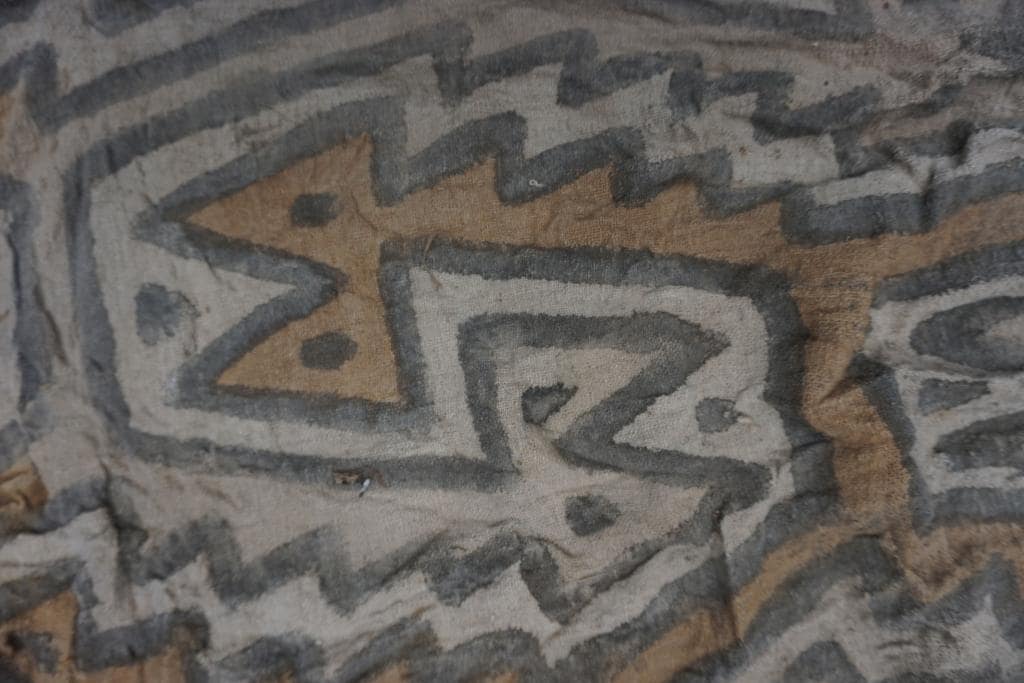

“Andeans used to set up necropolises in abandoned places of worship. This was also the case here because the graves were dug into structures that were several thousand years older,” added Majchrzak.
The grass and mortar mixture that was used to bind the blocks that made up the small pyramid was sampled for the structure’s dating. Settlements with imposing architecture were built in the Andes during the third millennium BC, and agriculture spread as a result of interactions with communities residing in the Amazon.
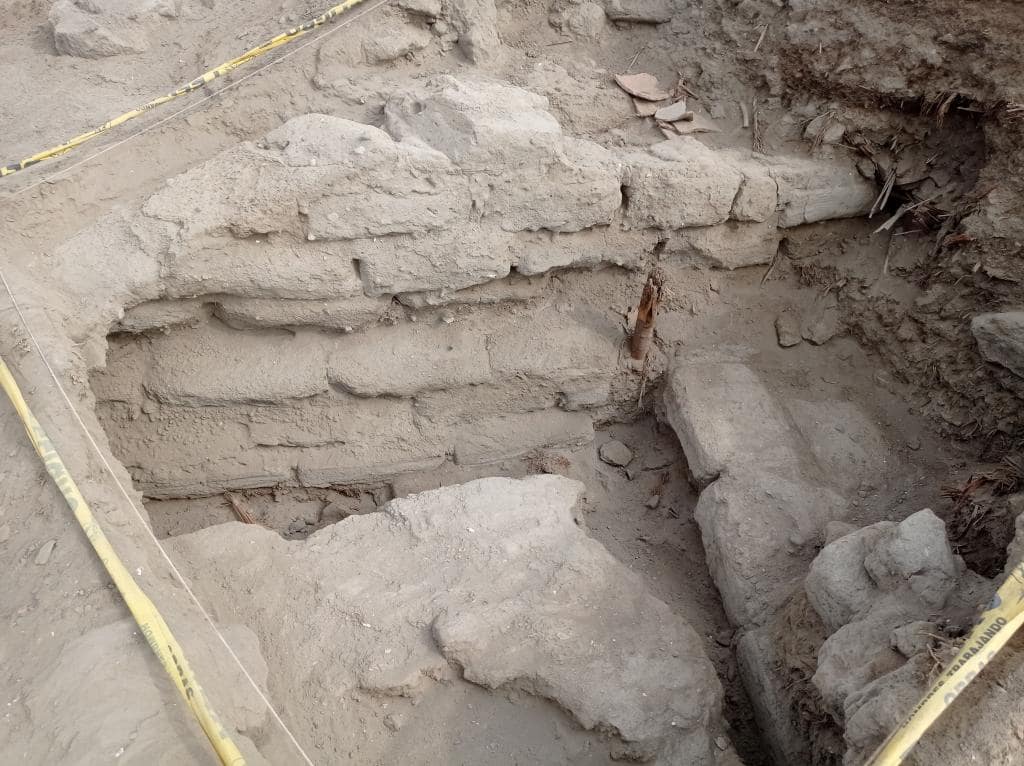

The examined graves date from the Wari Empire’s reign over the region. Castillo de Huarmey, one of the most important sites of this culture, is only 70 kilometers north of Barranca.
Two mounds have yet to be explored.
Cover Photo: Łukasz Majchrzak