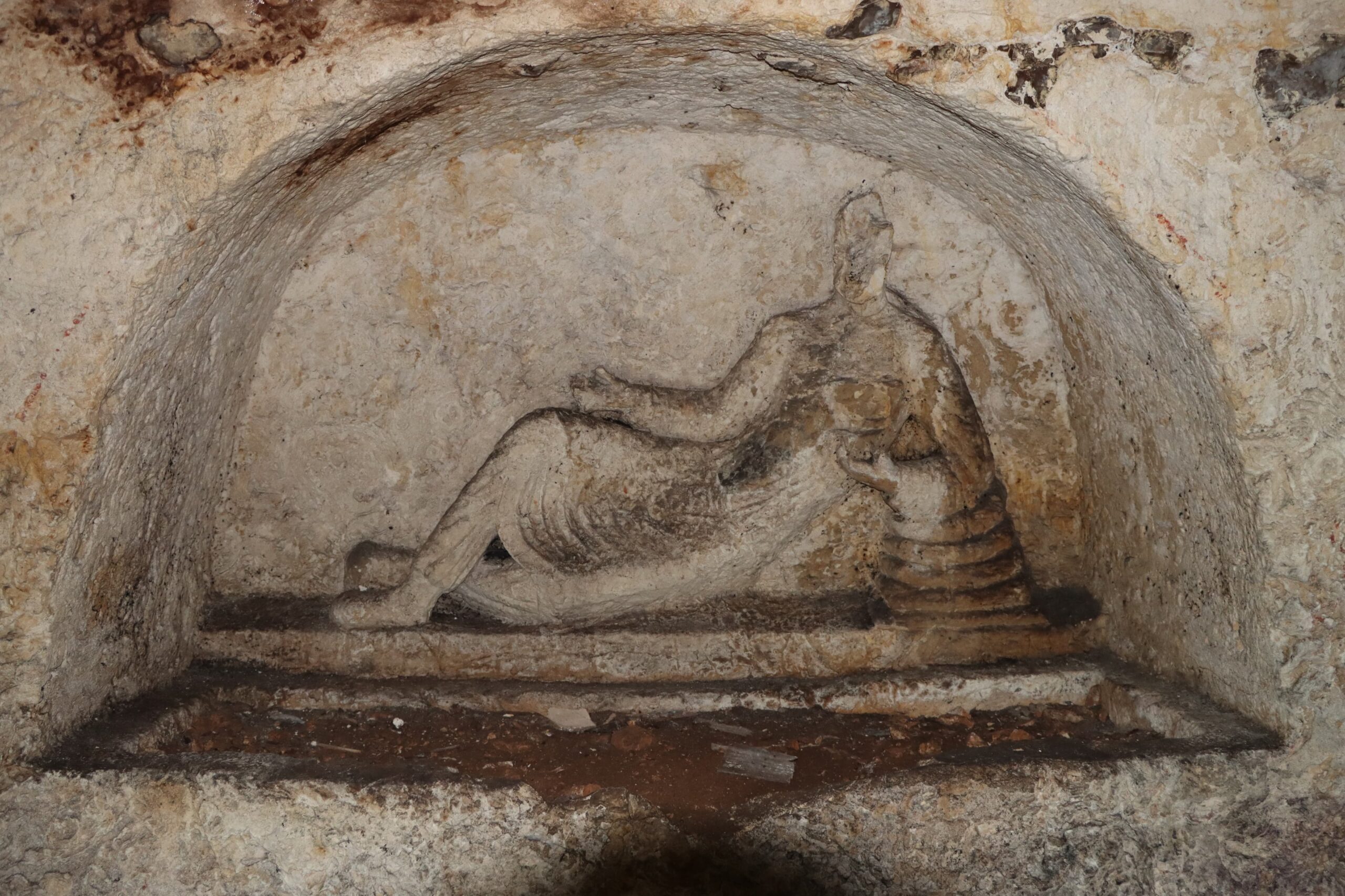
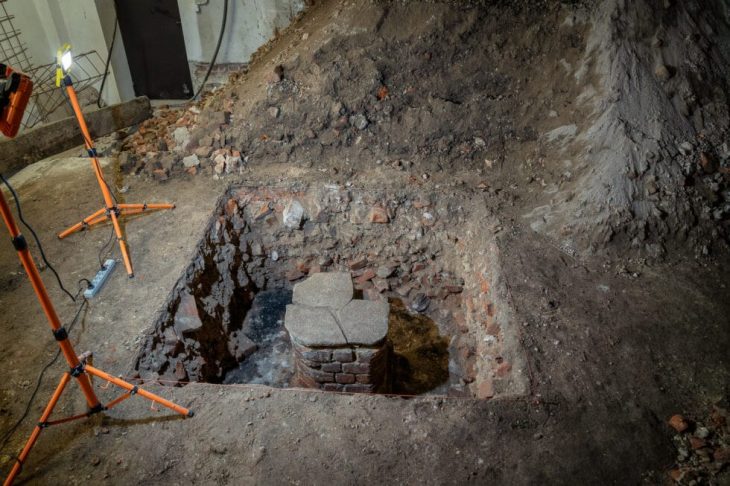
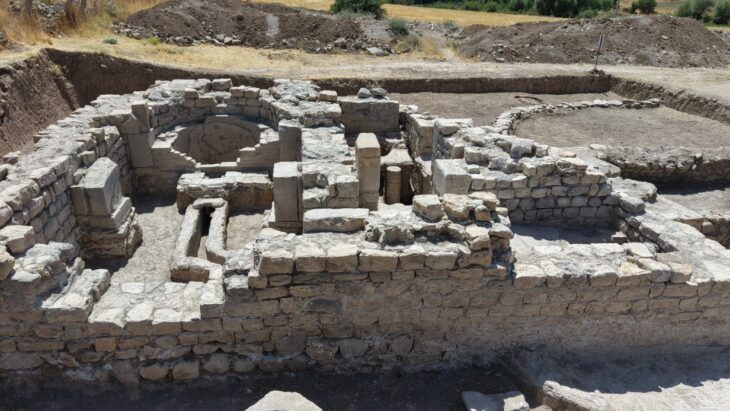
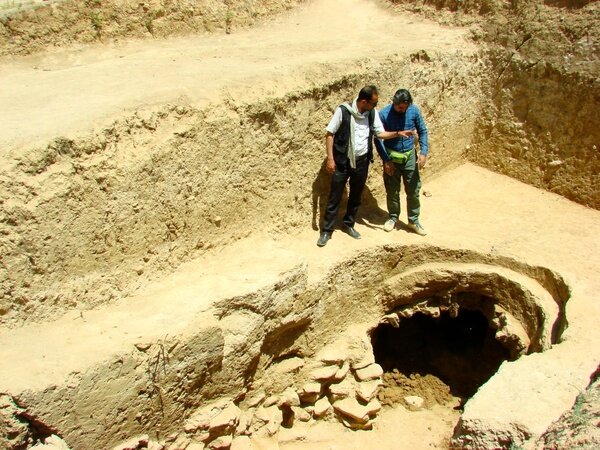
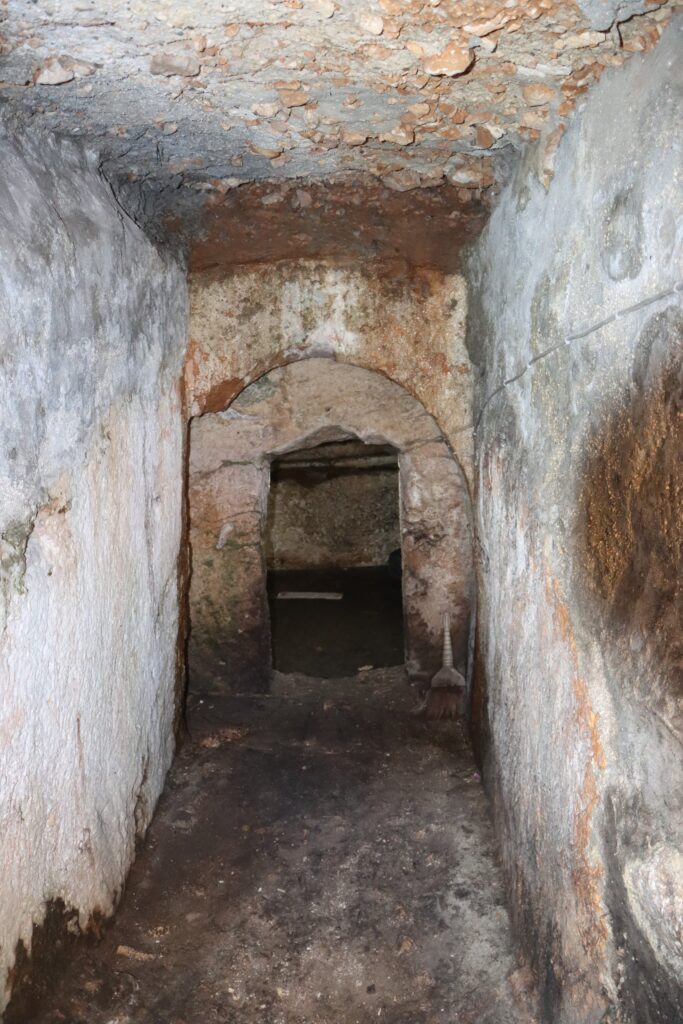
Hasan Şıldak, the governor of the city of Şanlıurfa in south-eastern Türkiye, announced on his social media account that a rock tomb was found in the courtyard of a house.
Within the scope of the Culture Inventory Project, the Rock Tomb in the courtyard of a house in Eyyübiye neighbourhood was recorded in the inventory.
It was stated in the explanation that the rock tomb has a single-chamber structure and is adorned with various reliefs. On one wall of the tomb chamber, there is a relief of a man lying on his left arm, while in the other two corners, there are two-winged female reliefs. There are other reliefs in different parts of the room.
On the inner side of the entrance door, there is an inscription processed with ochre paint, but it is unreadable due to damage. The dating of the rock tomb will be established through further research and analysis, as current investigations have not yet provided conclusive results.

Şanlıurfa is a historical city located in southeastern Türkiye and has a rich cultural heritage. The rock tombs found in Şanlıurfa are among the significant structures from ancient times. These tombs are typically carved into rocks and adorned with various reliefs. The rock tombs attract attention for both their architectural features and the artworks they contain.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The dating of the rock tombs in Şanlıurfa is generally based on various criteria such as archaeological finds, architectural features, and the artworks they contain. Most of these tombs date back to the 1st millennium BC, particularly to the Late Hittite period (9th century BC – 7th century BC) and the Roman period (1st century AD – 4th century AD).
The reliefs found in the rock tombs are particularly significant as they reflect the changes in the social and religious structures of the period. These reliefs often depict various themes that provide insight into the beliefs, customs, and daily lives of the people who created them. Typically, the rock tombs in the region contain decorations and reliefs that include human figures, animal representations, and mythological scenes. These artistic elements not only serve an aesthetic purpose but also convey important cultural narratives. By examining these reliefs, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the evolving dynamics within the society, including shifts in religious practices, social hierarchies, and the relationship between humans and nature during that era.
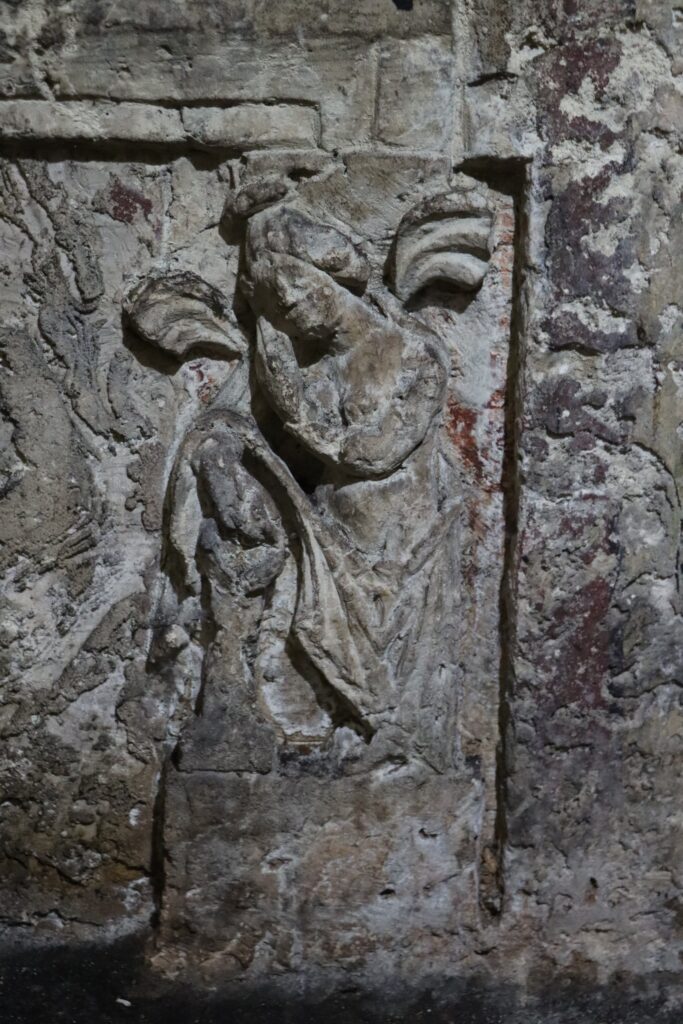

Human Figures: The interior walls of the tombs often feature human figures, typically depicted as male and female. These figures reflect the clothing styles and social structures of the period.
Animal Figures: Various animal figures, especially those of hunting animals, are frequently seen in the tomb decorations. These figures symbolize beliefs related to hunting and the lifestyle of the people.
Mythological Themes: Some tombs include mythological figures and scenes. Such reliefs reflect the ancient belief systems and legends.
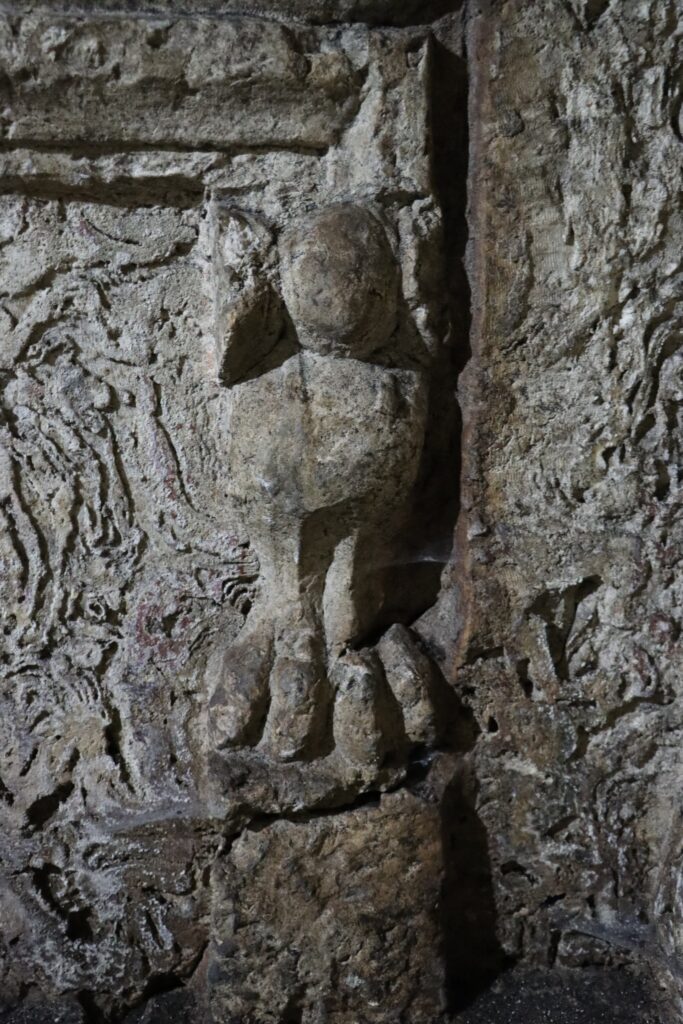

Plant Motifs: Plant motifs that symbolize nature are commonly used in tomb decorations. These motifs emphasize the connection to life and nature.
Geometric Patterns: Geometric patterns can also be found in some tombs. These patterns not only provide an aesthetic appearance but also reflect the artistic understanding of the period.
These new discoveries demonstrate that the rock tombs in Şanlıurfa are not only a part of our historical and cultural heritage but also serve as significant resources that help us understand the changes in the social and religious structures of ancient societies.
Cover Image Credit: Hasan Şıldak, Governor of Şanlıurfa, via [Media Source/Social Media Platform].