Archaeologists discovered an urn with a reddish liquid in a family mausoleum dating to the 1st century AD in the Carmona necropolis in Seville. An archaeochemical study identified this liquid as white wine, making it the oldest wine preserved in liquid form.
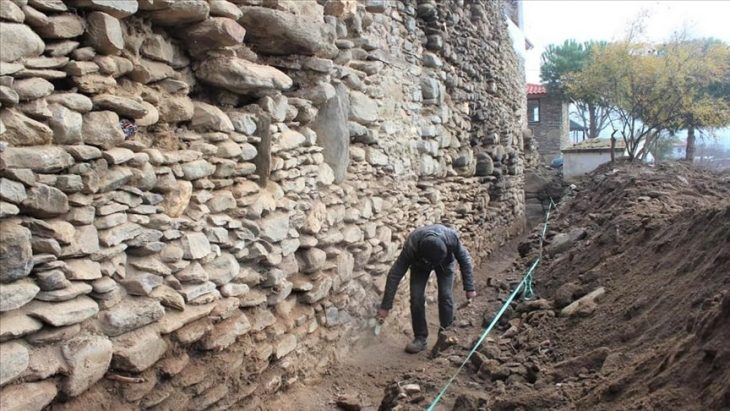
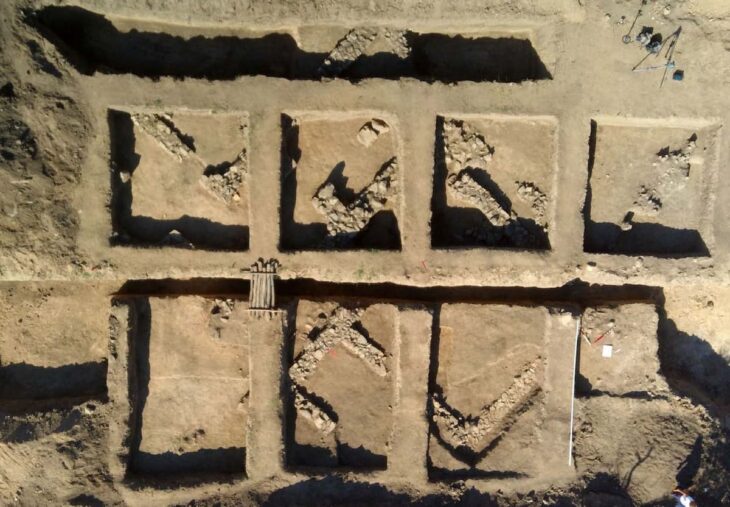
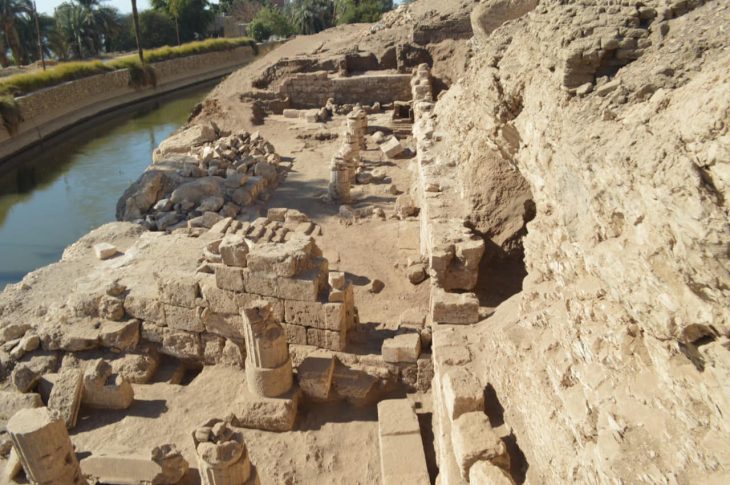
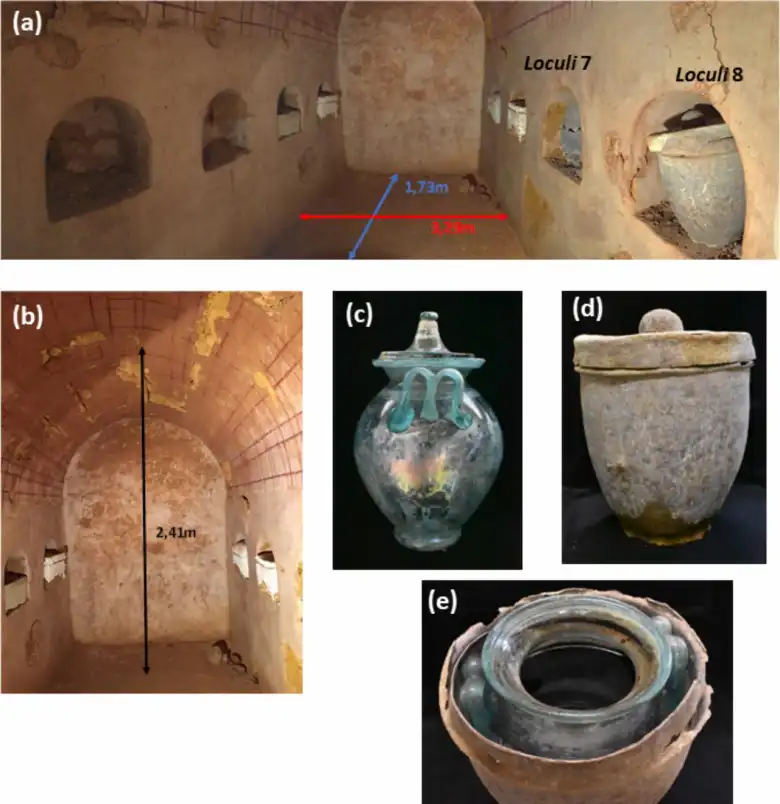
The Spanish urn was recovered in 2019 after a family having some work done on their house in Carmona stumbled across a sunken tomb on their property. This tomb, dated to the early 1st century AD, contained eight niches, six of which housed cinerary urns with cremated remains and various objects typical of Roman funeral rituals.
The tomb contained eight burial niches, six of which held urns made from limestone, sandstone, or glass and lead. Each urn contained the cremated bone remains from a single individual and two of the urns were inscribed with the names of the deceased: Hispanae and Senicio.
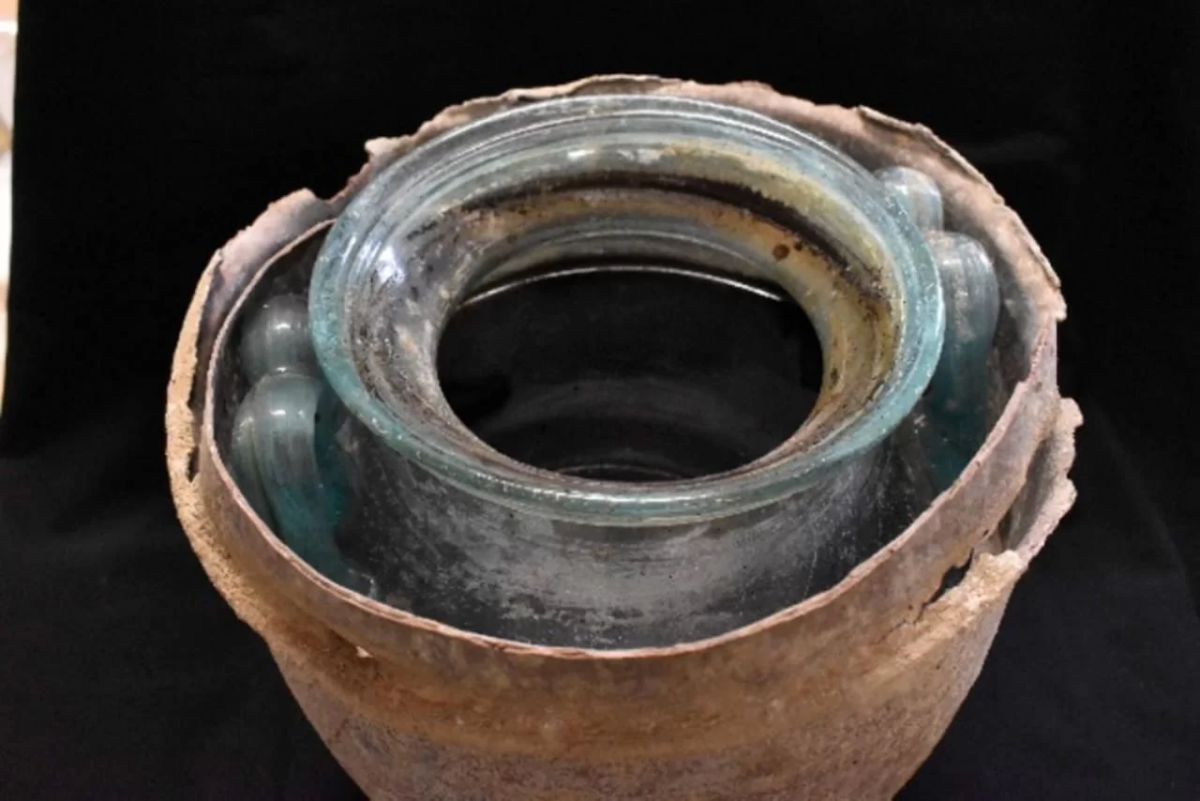
The urn in Niche 8 was what set this discovery apart. Inside an oval lead box with a flat-domed lid was this urn, a glass ossuary pot with M-shaped handles. Inside it, five liters of a reddish liquid were discovered, presumed to be part of the original content along with the cremated bone remains.
Analysis by experts at the University of Córdoba has established that the ancient tawny liquid inside the urn is a local, sherry-like wine.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
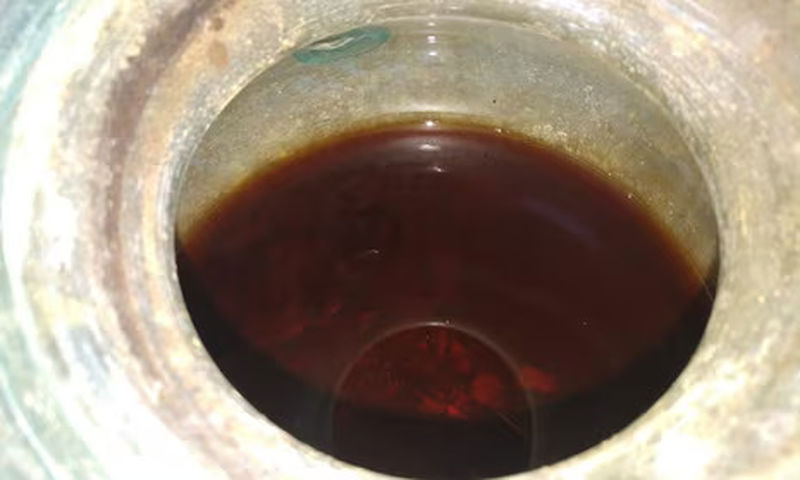

“The wine turned out to be quite similar to wines from here in Andalucía: Montilla-Moriles; sherry-type wines from Jerez, and manzanilla from Sanlúcar,” said José Rafael Ruiz Arrebola, an organic chemist at the University of Córdoba who led the analysis of the wine.
By using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), scientists were able to identify the chemical components of the wine’s mineral salts, which included common elements found in old wines like potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Additionally, they identified polyphenols—compounds found in grapes and, consequently, in wine—using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry or HPLC-MS. Researchers were able to identify the liquid as white wine due to the presence of specific polyphenols and the mineral salt profile.
The remarkable longevity of the wine in its liquid state bears witness to the sophisticated Roman methods of preservation and storage, as well as the distinct climatic circumstances that permitted its preservation for nearly two millennia.
Before the discovery, which is reported in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, the oldest wine preserved in a liquid state was the Speyer wine bottle, which was excavated from a Roman tomb near the German city of Speyer in 1867 and dated to about AD 325.
According to the researchers, the use of wine in Roman funeral rituals is well-known and documented. Therefore, once the cremated remains were deposited in it, the urn must have been filled with wine in a kind of libation ritual during the burial ceremony or as part of the funeral rite to help the deceased in their transition to a better world.
They conclude that the results obtained in this work strongly suggest that the reddish liquid in the ash urn was originally wine that decomposed over time and that it was about 2,000 years old, making it the oldest wine found to date.
Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports
doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104636
Cover Photo: Daniel Cosano et al.
















