Archaeologists excavating the Rabana-Merquly mountain fortress in what is present-day Iraqi Kurdistan suggest that it may also have served as a sanctuary for the Persian water goddess Anahita.
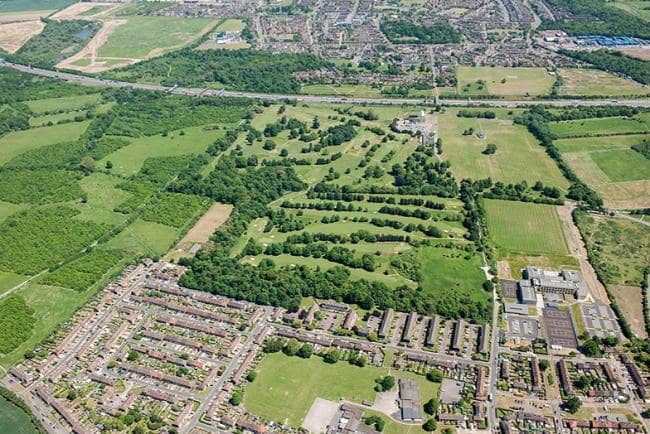
Rabana-Merquly is an archaeological site in Iraqi Kurdistan’s Zagros Mountains, on the flanks of Mt. Piramagrun. This fortified stronghold is made up of perimeter defenses that surround adjacent settlements in the Rabana Valley and on the Merquly plateau. The main Parthian-era occupation dates from the second to first centuries BCE.
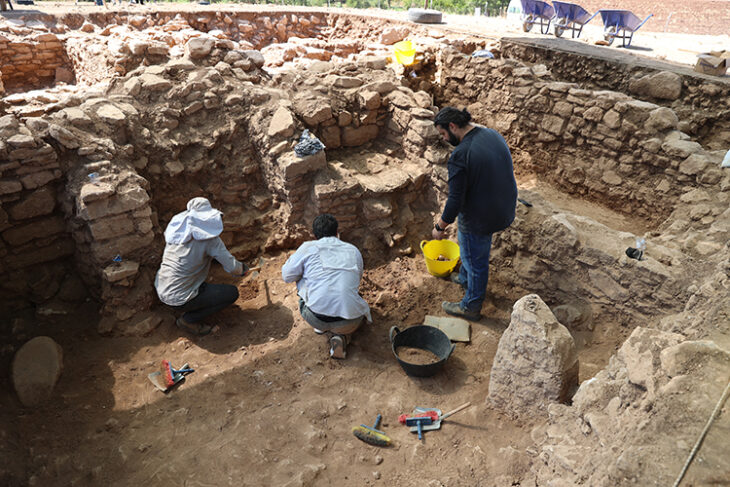
Architectural structures next to a natural waterfall and the remains of a possible fire altar indicate the existence of a worship site, according to Dr Michael Brown, a researcher at the Institute of Prehistory, Protohistory, and Ancient Near Eastern Archeology at the University of Heidelberg. Dr. Michael Brown has led excavations there for several years.
Through multiple excavation campaigns conducted since 2009 and, more recently, between 2019 and 2022, an international research team studied the archaeological remains in situ.
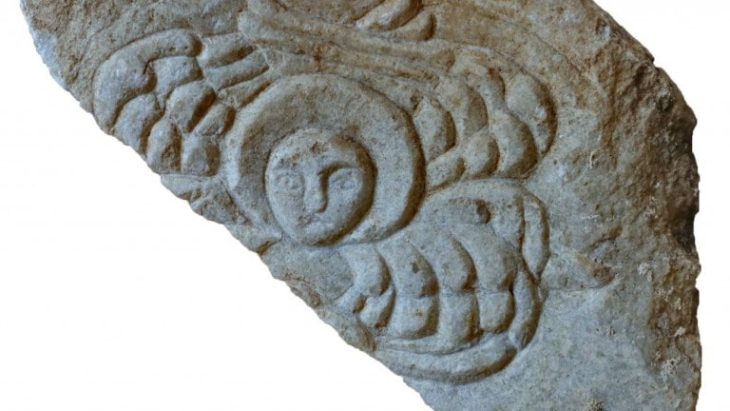
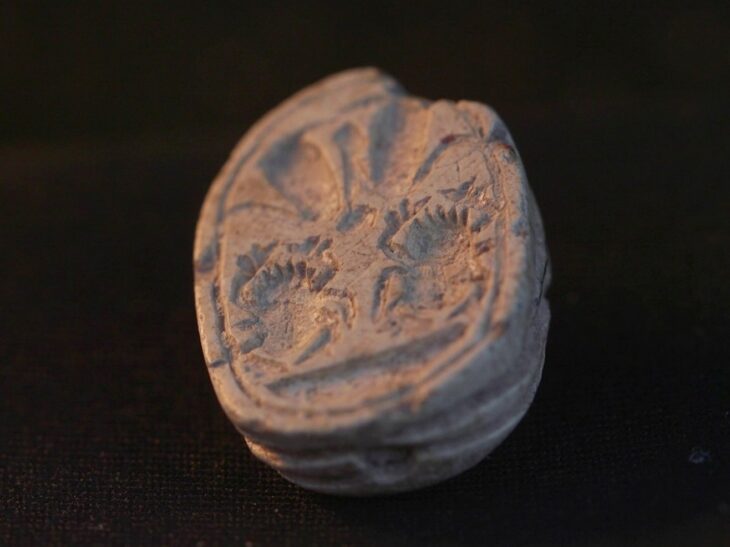
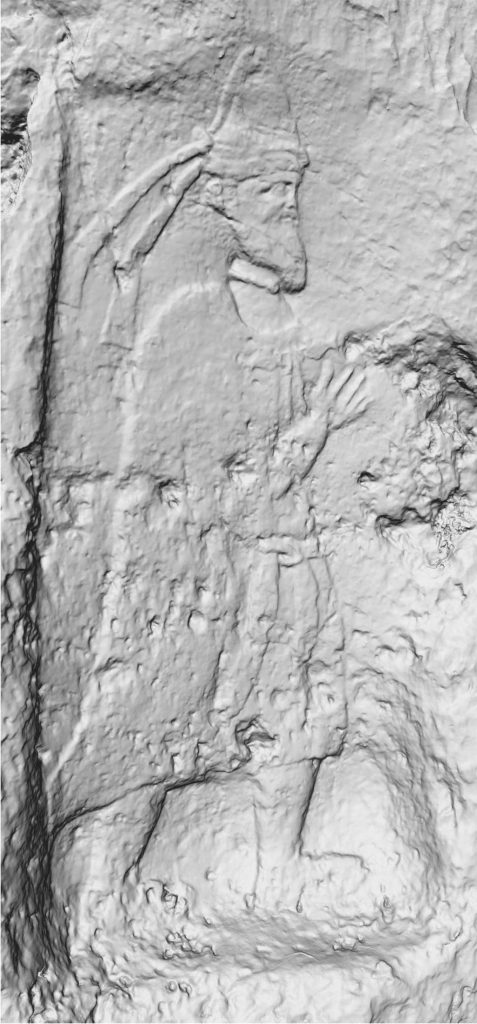
A rock relief overlooking the fortified entrance to Rabana depicts an anonymous ruler, most likely a local Parthian vassal king who is credited with founding the site. Inside Rabana Valley, the researchers discovered a religious complex that could have been dedicated to the goddess Anahita.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The water goddess Anahita was first mentioned in a manuscript collection of the Zoroastrian religion called the Avesta. There, she is portrayed as the celestial source of all the Earth’s waters and is described as an incredibly beautiful woman with the ability to take on the shape of a cascading stream or waterfall. During the Seleucid and Parthian periods, the cult of Anahita was highly revered in the western regions of Iraq.
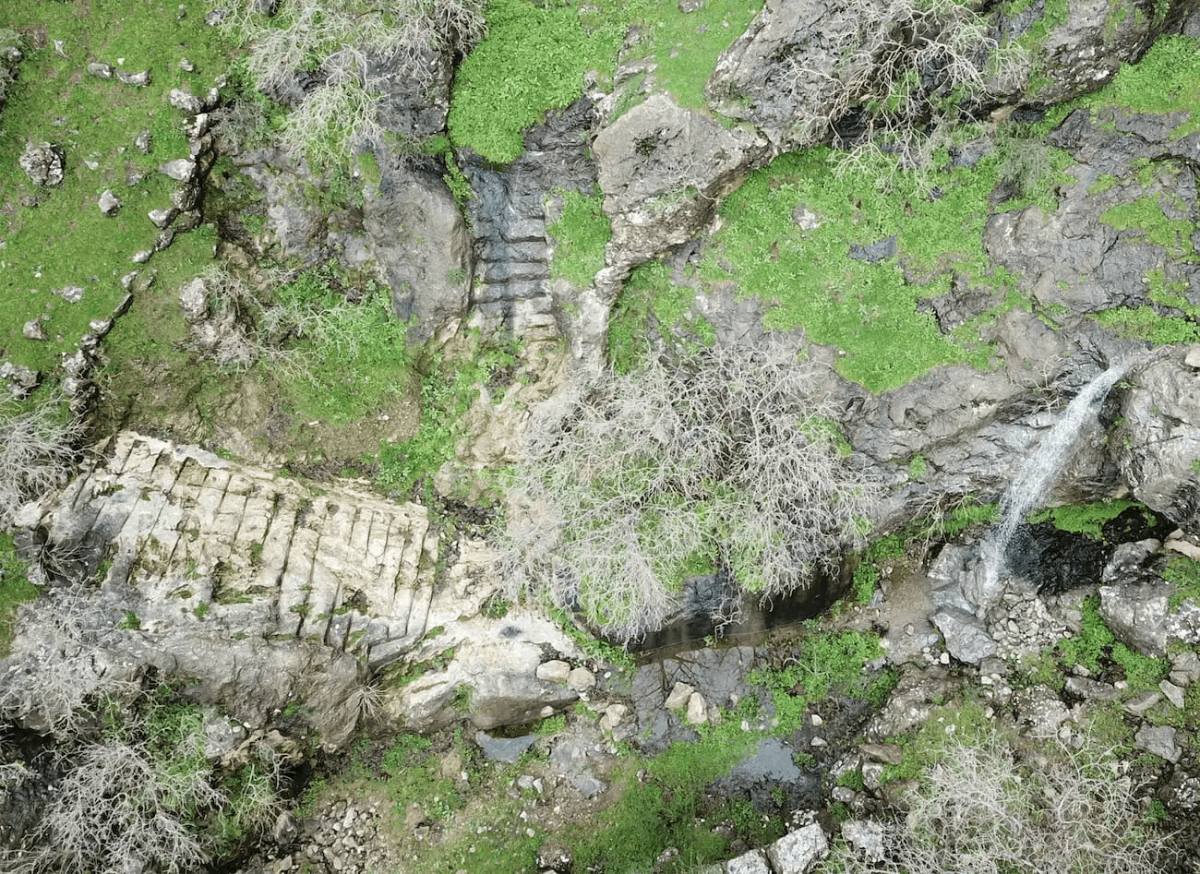
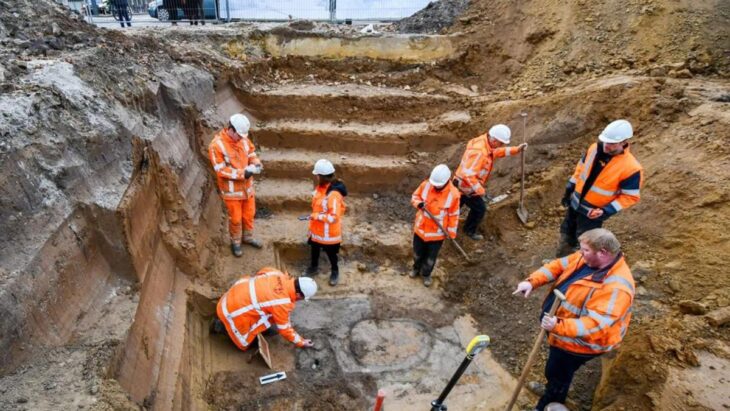
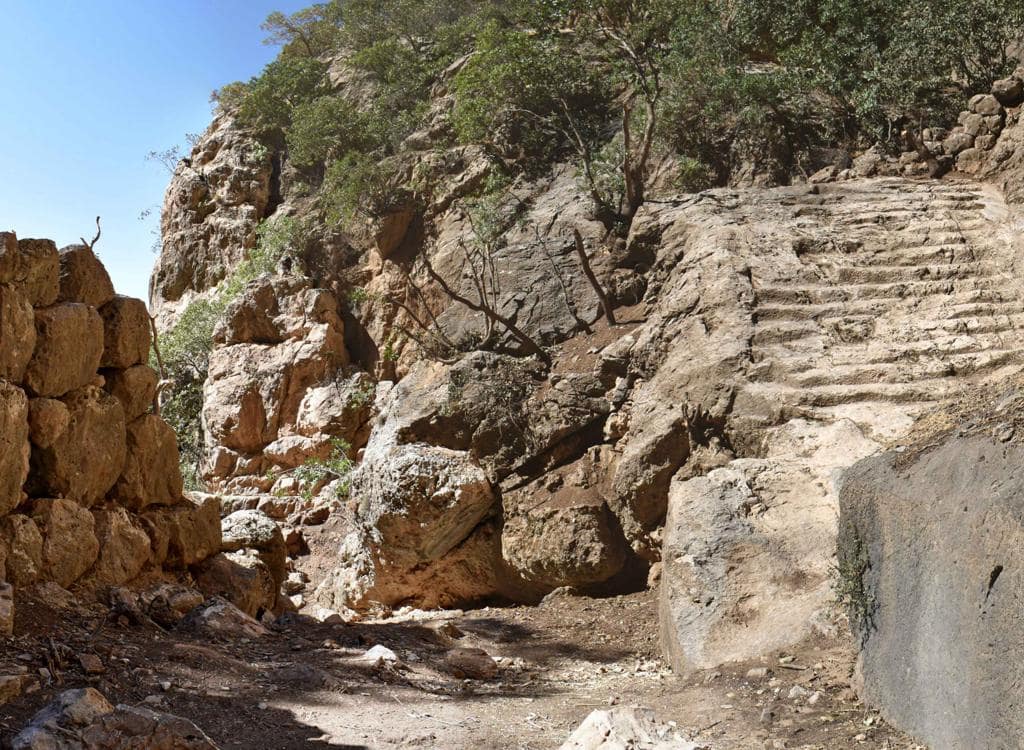
Inside Rabana, the focus of occupation was in the northeast, where the wadi that runs through the valley enters from a narrow gorge high up in the mountain. Following heavy rain and snowmelt, this creates an ephemeral waterfall with monumental stone architecture at its base. A small (fire?) altar within a sub-rectangular niche has been carved into the escarpment nearby. The overall impression is of a sanctuary complex, with the presence of water implying a cultic connection to the goddess Anahita.
Therefore, the main evidence supporting the theory that a potential Anahita sanctuary was a part of the Rabana-Merquly mountain fortress comes from the discovery of architectural extensions in the natural setting of a seasonal waterfall inside the complex.
“The proximity to the waterfall is significant because the association of fire and water elements played an important role in pre-Islamic Persian religion,” states Michael Brown.

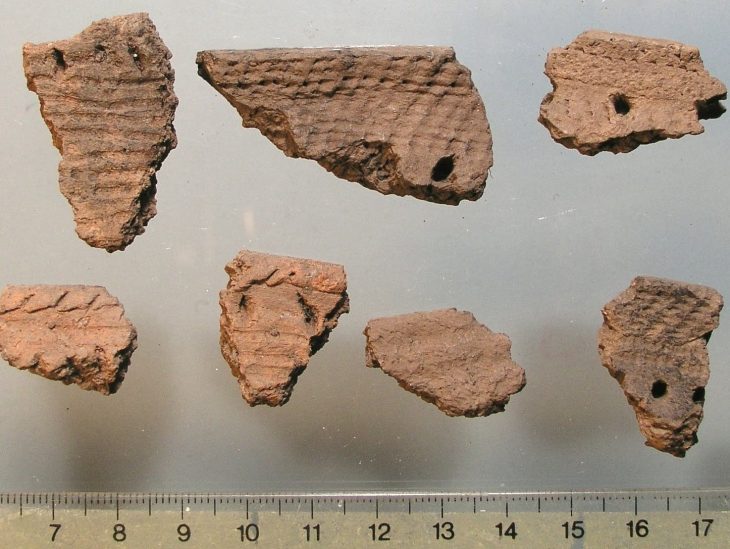
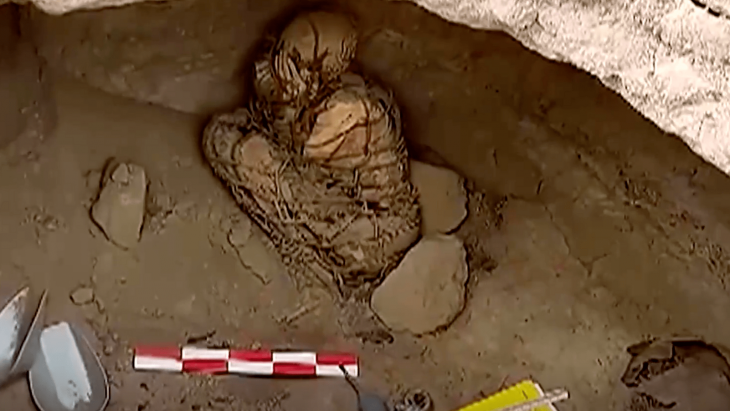
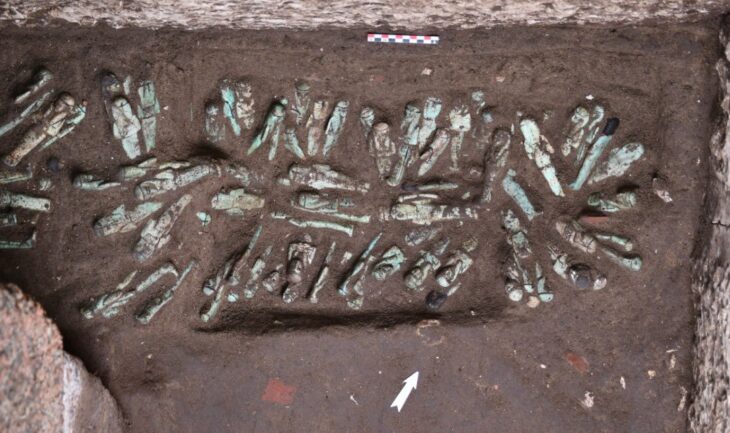
The site contains the remains of a building, where archaeologists discovered two distinctive burial vessels radiocarbon dated to the second to first centuries BC in 2022. This suggests that the shrine was in use when the fortified settlements of Rabana and Merquly were established.
According to Dr. Brown, there may have been a pre-existing shrine that was absorbed into the Anahita cult during the Parthian era, which could have been pivotal in the occupation of the mountain.
Dr. Brown believes there may have been a pre-existing sanctuary that was absorbed into the Anahita cult during the Parthian era, which could have been pivotal in the occupation of the mountain. At that time, many religious sites also functioned as dynastic cult places honoring the king and his ancestors, explains the Heidelberg archaeologist.
“Even if the cult site cannot be definitively attributed to the water goddess Anahita due to the lack of similar archaeological finds for direct comparison, the Rabana sanctuary still provides us with a fascinating glimpse into the regional sacral and geopolitical interconnections during the Parthian era,” states Dr. Brown.
The paper is published in the journal Iraq.
Cover Photo: Waterfall with main staircase and boulevard, in the fortress. Rabana-Merquly Archaeological Project