When talking about the architecture of the ancient Roman Empire, most people usually think of the mental image of white marble statues, columns, or slabs. Indeed, many buildings and squares at that time were decorated with marble, but it is not white but colored marble that is usually used, such as the green-veined Cipollino Verde, which was extracted from the Greek island of Euboea. Because marble is very expensive, it is usually placed in a thinner thick slab as cladding on other cheaper stones.
“To date, however, no actual remains of marble workshops from the Roman imperial era have been found, so little is known about marble processing during this period,” said Professor Cees Passchier of the Institute of Geosciences at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU).
Now, together with other researchers in Mainz, Turkey, and Canada, he has completed the analysis of the marble exterior walls of Roman villas in the second century AD. As the researchers detailed in the online edition of the Journal of Archaeological Science: Report, they used special software commonly used for 3D modeling of geological structures. They discovered that during the manufacture of marble slabs during the time, the material loss was likely smaller than it is now.
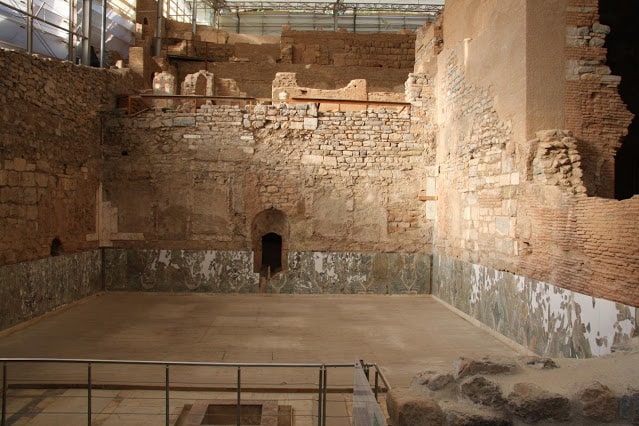
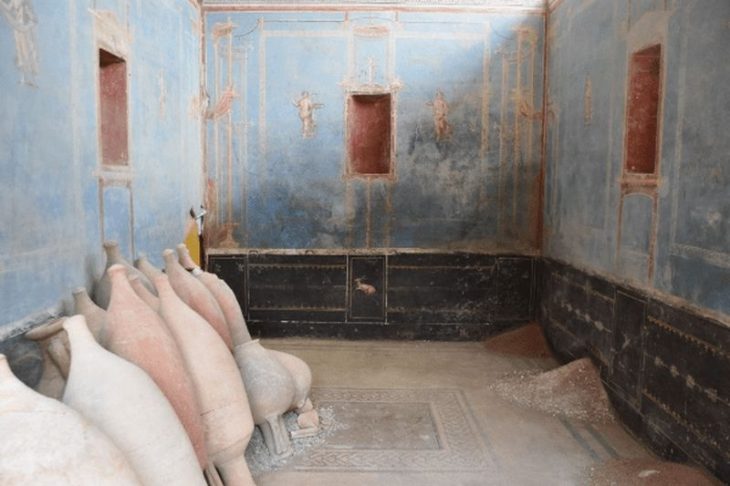
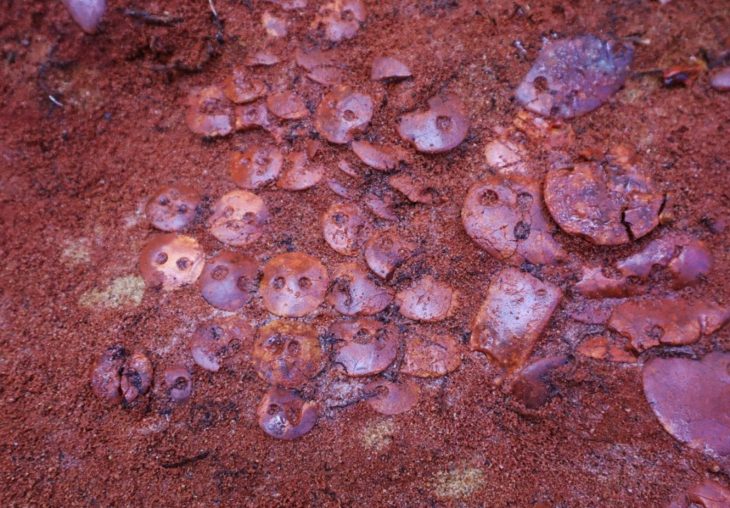
Researchers inspected, photographed, and measured 54 restored Cipollino Verde panels, each about 1.3 square meters. These panels had used to decorate the walls of a villa in ancient Ephesus on the west coast of Turkey.
Given the saw marks on one of the plates, they were able to infer that the plates were cut in a water-powered sawmill, in fact using what we know today as hydraulic hacksaws. Using reconstructions based on patterned slabs, the research team was also able to conclude that a total of 40 slabs were cut from a single marble block weighing between three and four tons. They were then installed on the wall in the order of production and arranged side by side in pairs of books to form a symmetrical pattern.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
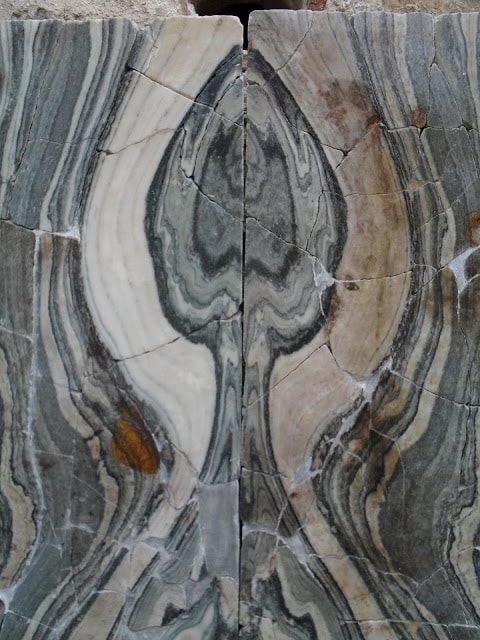

book-matched fashion [Photo: Cees W. Passchier]
“The slabs are about 16 millimeters thick and the gaps between them, caused by sawing and subsequent polishing, are about 8 millimeters wide. This material loss attributable to production equates to around one-third and is, therefore, less than the rates now commonly associated with many forms of modern marble production,” Passchier pointed out. “We can therefore conclude that marble extraction during the imperial period was remarkably efficient.”
The researchers also found that, despite the fact that 42 slabs had been sawn from one initial marble block, two had not been secured to the hall’s walls. “The arrangement of the slabs on the villa walls suggests these slabs were most likely broken, possibly during polishing or their subsequent transportation,” added Passchier.
“This would mean that the amount lost due to breakage would be 5 percent, which would also be an astonishingly low figure.” This small loss leads Passchier to assume that the entire marble block had been transported to Ephesus and that the slabs were then cut and polished there.
Cover Photo: Sinan Ilhan