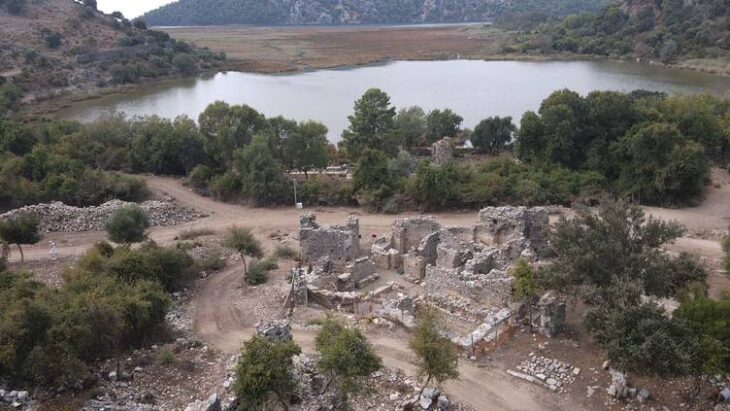
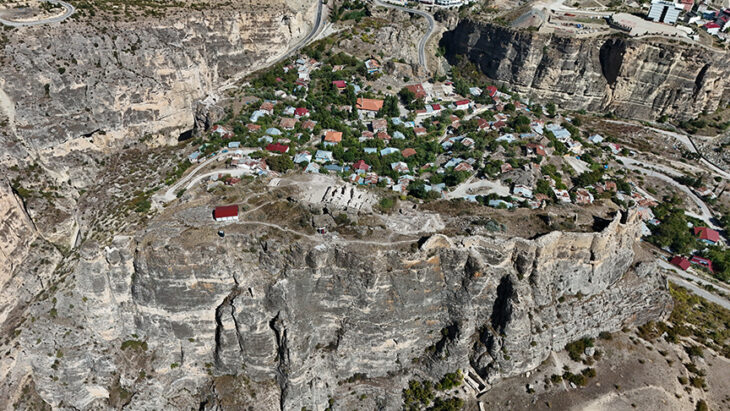
Kuruçay höyük is located near the village Of Kuruçay, fifteen kilometers south of Burdur. The mound itself is situated upon one of the hills sloping downward towards the basin of Lake Burdur.
Excavations were carried out on the Kuruçay mound between 1978-1988 under the direction of Professor Doctor Refik Duru. Although there were 13 settlement layers during the excavations of this mound, none of these layers yielded any domestic cereal grain or plant remains. Despite the examination of all the collected animal bones, no definitively domesticated animal remains were found. In addition to these results, the fact that the arable lands and fields are very limited near the mound and the mound is surrounded by deep stream beds from the south, west, and north can be shown as evidence that agriculture was not practiced.
But this does not mean that the inhabitants of Kuruçay mound were not aware of agriculture. These people were obviously not consciously engaged in agriculture. Because they must have been aware of a neighboring settlement like Hacılar, where layers of Neolithic developments can be traced.
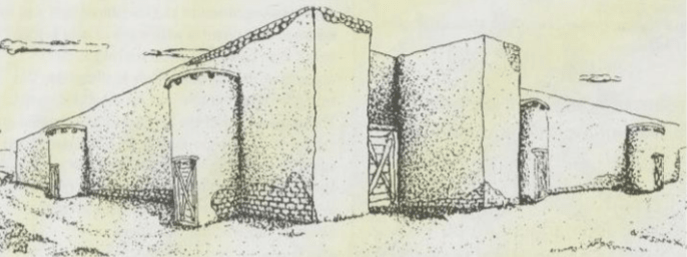
The Kuruçay people, who had seen the production techniques from the neighboring settlement Hacılar, may not have been farming, but some settlement levels had riches that required protection with very strong walls. A most provocative question is how a populace without food production accrued sufficient wealth to warrant such strong fortifications in walls. We will never know their wealth and how they got rich or why they tried to protect themselves. Most importantly, how did they build such a fortification system! Or where did they learn it?
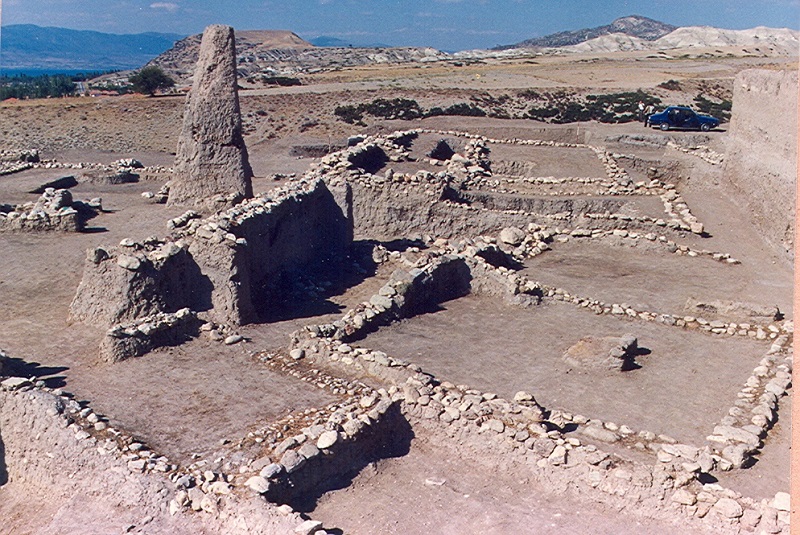
Professor Doctor Refik Duru described this fortification system as follows: “Level 11, on the other hand, was represented by a 26-meter stretch of impressive stone foundations running east-to-west. Clearly a fortification wall, it incorporated towers half-circular in the plan against its southern face. the western part of the wall had been washed down the slope of the mound; there was a gateway at the east end where the fortifications formed a right angle to the north with rounded towers there as well.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The second important criterion of a Neolictic lifestyle is a permanent habitation, be it in a village or in a relatively fair-sized town. A developed architecture with sturdy walls on a stone foundation is attested at Kuruçay from level 12vonward. This earliest building phase at Kuruçay can by no means be considered primitive. In level 11 we came suddenly face-to-face with a fortified town.”
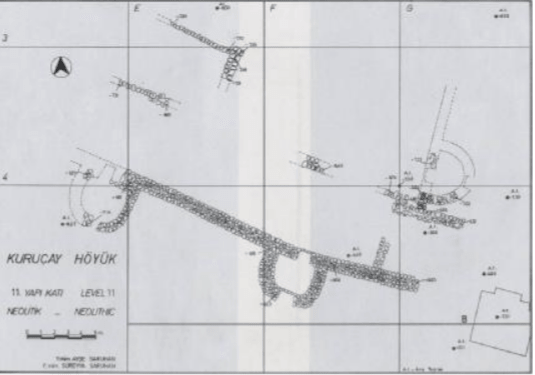
A thick-founded fortification wall with half-round towers, whose existence was found on 11 building levels, was unearthed in 1984. The long wall of this fortification wall, between 1.10 meters and 1.20 meters thick, was usually built with medium-sized collected stones. The two sides of the wall were made of relatively thicker stones, and the middle part was made of small stones and fragments.
On the outer face of the wall facing south, there are two towers with a half-round plan. There are 1 meter wide gaps at the ends of the towers. On the same axis, gaps were left in the main wall and these gaps were closed with a single stone series. This row of stones in the passages most likely indicates the sills.
During the researches carried out in the eastern part, the existence of a second wall, parallel to the main wall, was found at 4 meters intervals. This wall, which continues for 5 meters, is thinner and unlike the main wall, its foundations were built with two rows of stones on top of each other. A wall coming from the north joins this wall by making a right angle. On this wall, the presence of semi-circular towers was detected.
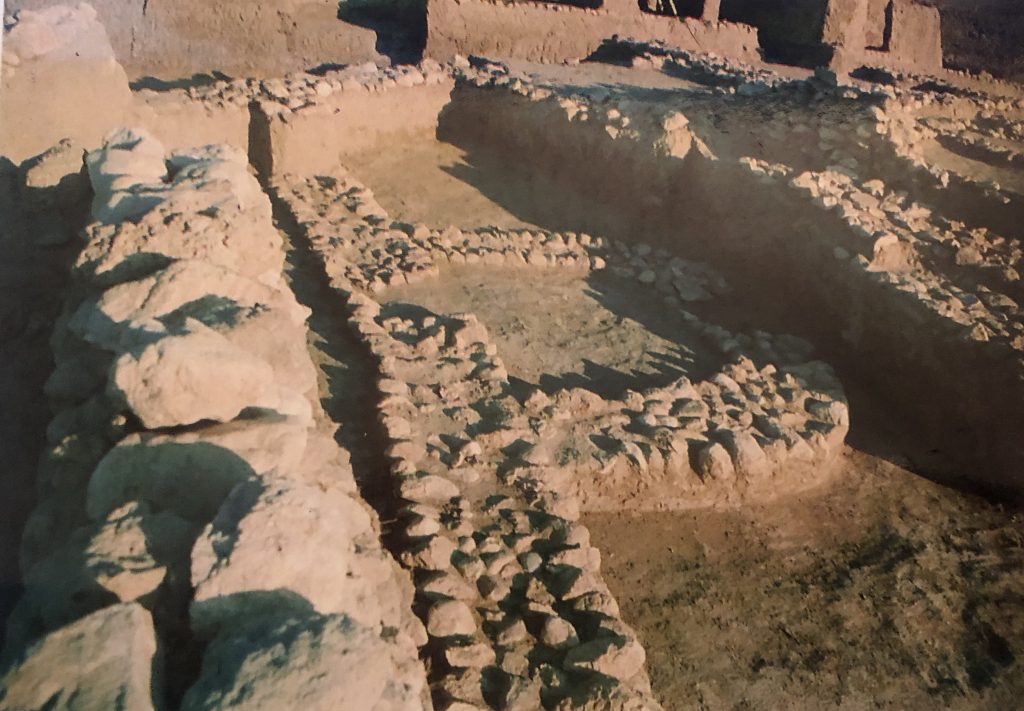

Following the destruction of the level 11 habitation, settlement on the mound moved slightly to the south. After a short break new habitation representing the early chalcolithic period was founded.
From the Early Neolithic through the early Chalcolithic periods (levels12-8) the architecture in general follows a normal sequence of development without out standing innovations . First in Level 7 does a significant change appear. It would seem that new forms and standards had been introduced in the layout of the settlements as well as in the house plans themselves.
It is possible to say that for the time being, there is no parallel between Kuruçay and the other centers of Anatolia that yielded Neolithic and Early Chalcolithic settlements, except for the last building phase of the Early Chalcolithic Age. The situation is not different in contemporary settlements outside Anatolia. Especially Kuruçay 11’s Level castle is completely unique for now with its general plan and half-round towers. In Southern Mesopotamia, Southern Syria and Palestinian Neolithic centers, this type of defense understanding and architecture does not exist. If the round-planned tower in the PPNA settlement of Jericho is not taken into account, the tradition of the round tower is not a practice seen in these ages. Round towers appear in the Early Bronze Age in Near Eastern architecture.
The 11 layers of the Kuruçay mound are dated between 5850/5800 BC. The oldest layer, 13 layers, dates back to 7100 BC.
Source: DURU. R. “KURUÇAY HÖYÜK– Results of the Excavations 1978-1988 The Neolithic and Early Chalcolithic Periods”, TTK, 1994, ANKARA
















