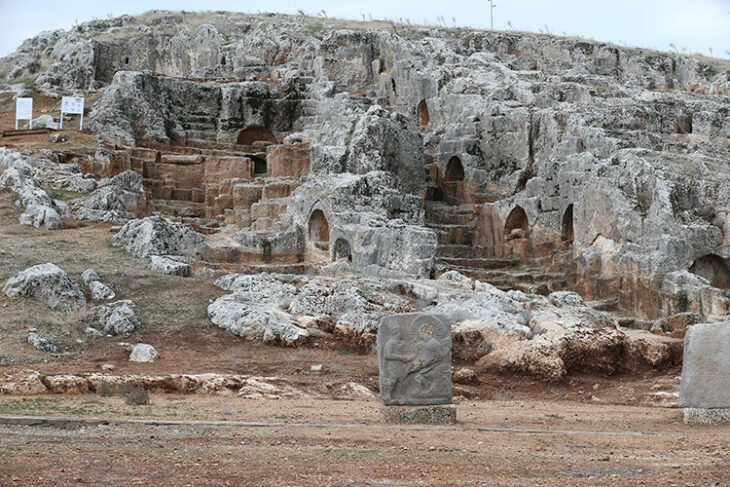
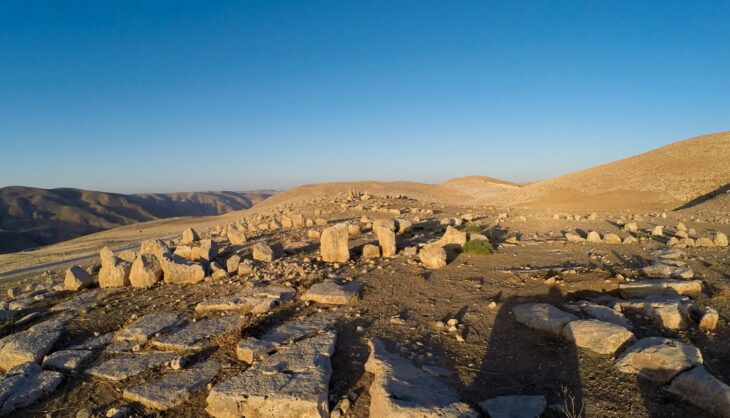
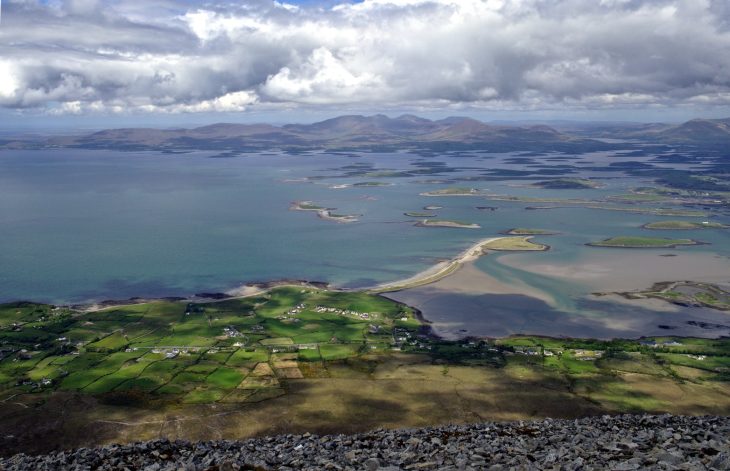
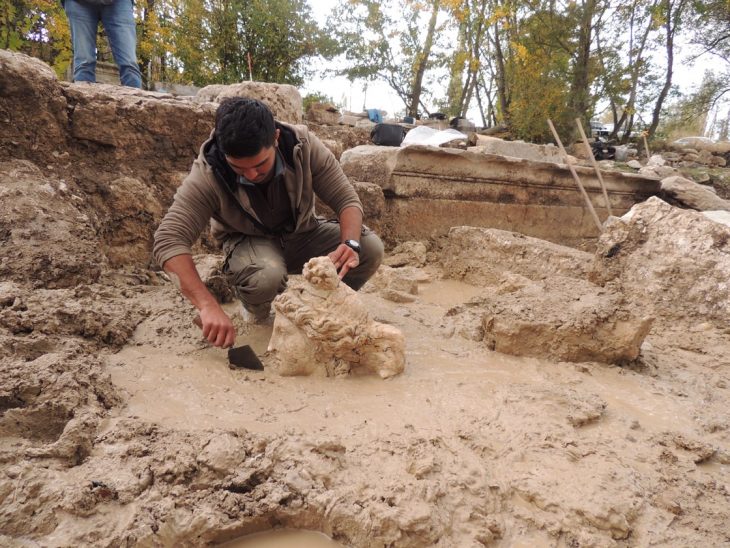
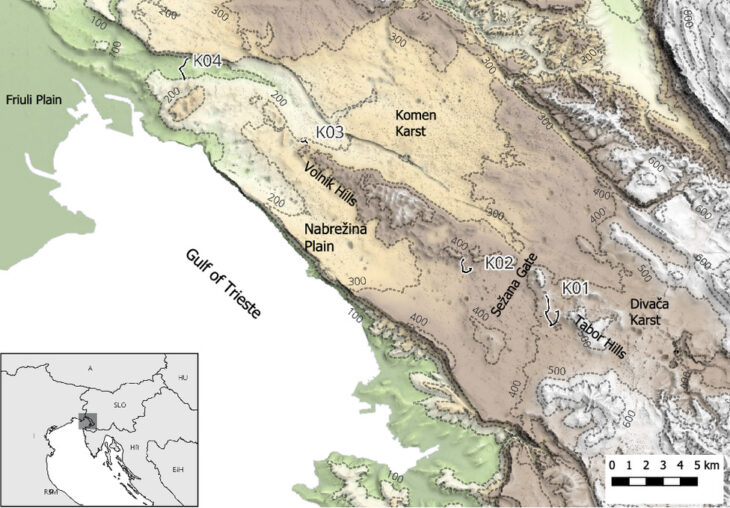
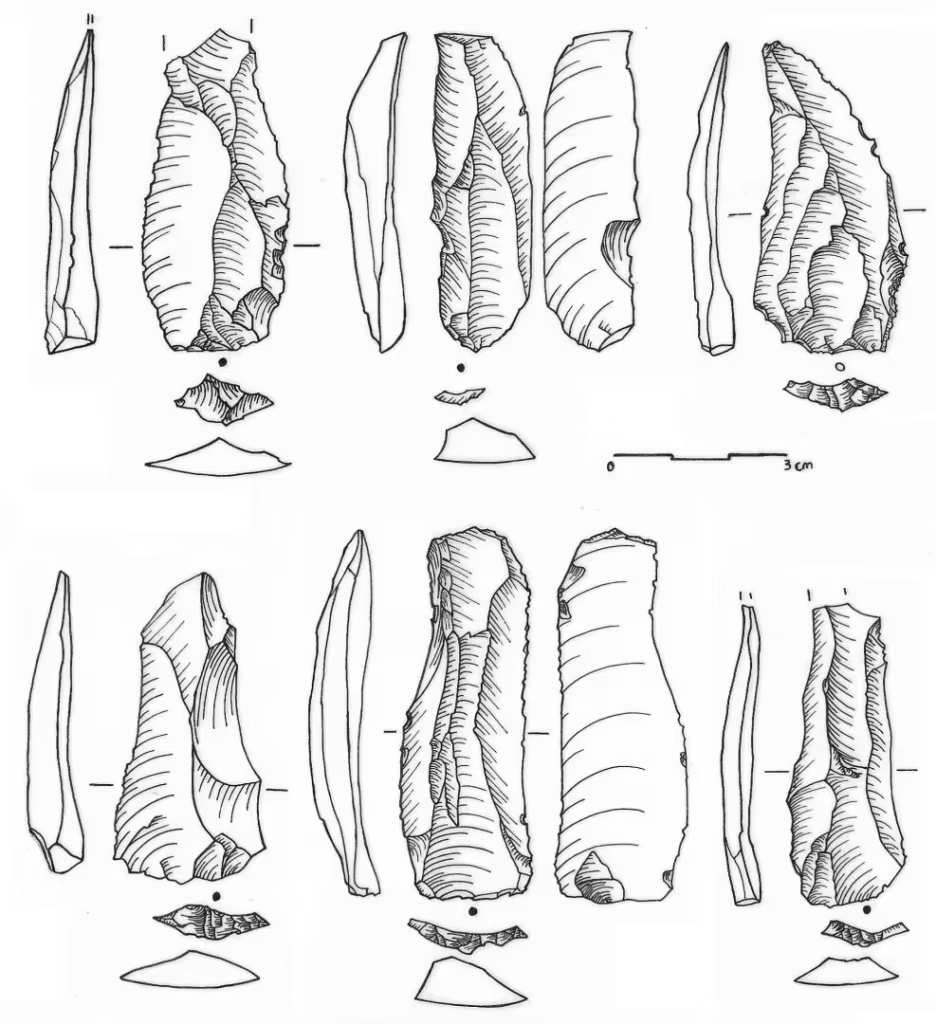
An international team of researchers led by Knut Bretzke of Friedrich Schiller University Jena uncovered 80,000-year-old stone blades at the rock shelter site of Jebel Faya in the Emirate of Sharjah.
The discovery of the oldest evidence to date of the systematic production of stone blades on the Arabian Peninsula marks a significant advancement in the understanding of prehistoric human technology in the region. This discovery provides new insights into the history of human habitation in Arabia and the possible routes used by Homo sapiens in their expansion out of Africa, highlighting the cultural practices associated with tool-making and the migration patterns of early humans.
Published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Science, the study emphasizes the crucial role of southern Arabia in the cultural evolution and diversification of early human populations in Southwest Asia, with the artifacts being dated to approximately 80,000 years using luminescence techniques.
Dr. Bretzke notes that the region’s climatic history has been marked by dramatic changes, transitioning from a period of favorable conditions—characterized by permanent rivers and lakes—beginning around 130,000 years ago, to an extreme arid phase that significantly influenced human settlement and cultural practices.
The findings suggest that while northern and southern Arabia experienced distinct cultural developments during this transition, the shared traditions in stone tool production indicate a complex interplay of human activity across the peninsula. This differentiation is crucial for understanding the timeline and pathways of early human migrations from Africa to Asia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research indicates that the global expansion of Homo sapiens occurred in multiple waves, with evidence from Jebel Faya suggesting that one such migration along the southern Arabian Peninsula took place around 80,000 years ago. However, a notable challenge remains: the absence of Paleolithic human remains in southern Arabia limits the ability to conduct genetic analyses that could provide deeper insights into the populations that once inhabited the area.
Excavations at Jebel Faya have revealed evidence of human activity spanning from approximately 210,000 to 10,000 years ago, with extensive digging reaching depths of five meters. Despite the wealth of stone tools discovered, the lack of fossilized remains hinders direct connections between these artifacts and specific genetic lineages.
The interdisciplinary project, involving researchers from Jena, Tübingen, and Freiburg in Germany, as well as Oxford Brookes University in the UK, collaborates closely with local authorities in Sharjah to facilitate ongoing excavations and analyses.
This discovery not only deepens our understanding of early human migrations but also indicates that southern Arabia had a more complex and vital role in the expansion of Homo sapiens than previously thought. As research progresses, archaeologists are hopeful that further evidence will emerge, shedding light on the region’s ancient history and the innovative strategies early humans employed to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena
Knut Bretzke, Frank Preusser, Kira Raith, Gareth Preston, Seolmin Kim, Sabah Jasim, Eisa Yousif und Adrian Parker: Archaeology, chronology, and sedimentological context of the youngest Middle Palaeolithic assemblage from Jebel Faya, United Arab Emirates, Archaeological and Anthropological Science, DOI: 10.1007/s12520-025-02164
Cover Image Credit: The Jebel Faya archaeological site on the Arabian Peninsula.
Credit: Knut Bretzke