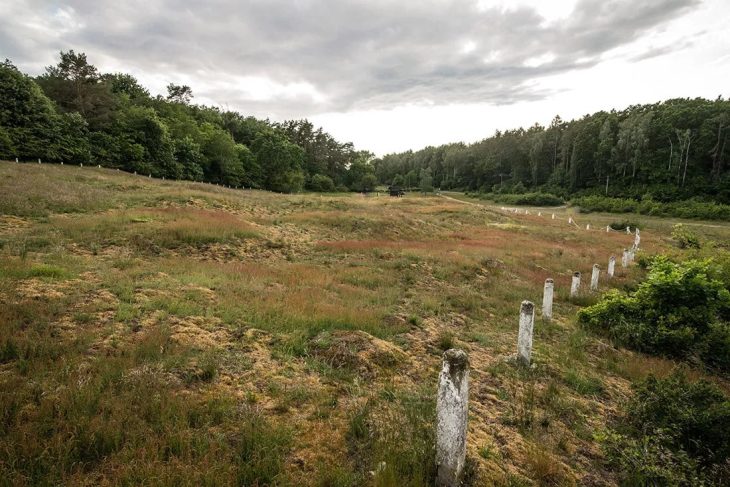
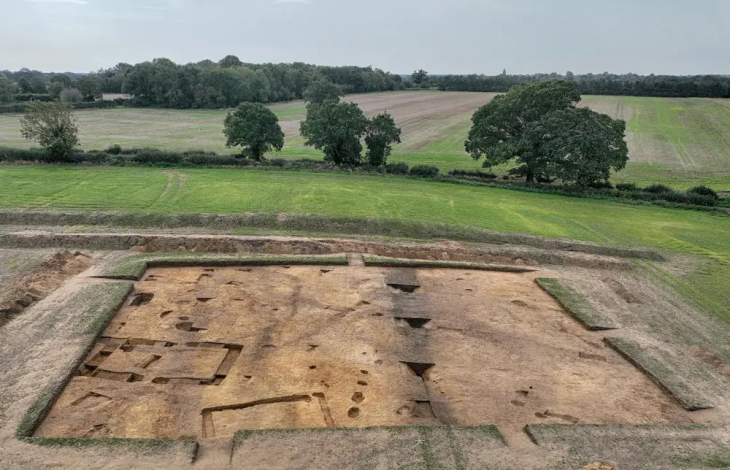
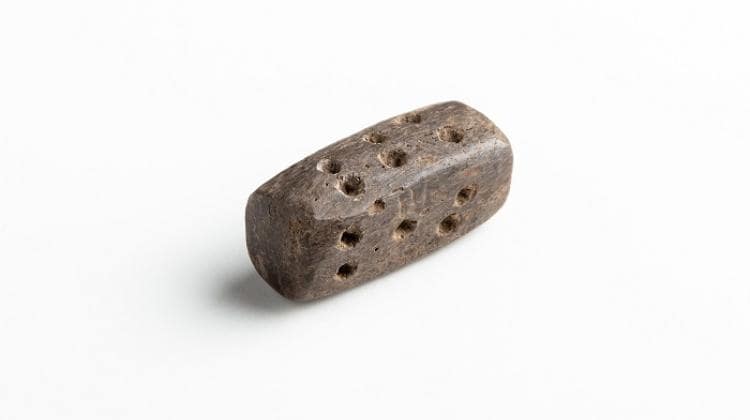
A dice, probably dating from the 3rd and early 2nd centuries BC, was discovered at the Celtic settlement of Samborowice in the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland. The oldest dice found in Poland!
Celts once inhabited southern Poland only in a few regions, including: on the Głubczyce plateau, i.e. near Racibórz (located in the southwestern part of the Silesian Voivodeship). They lived there from the turn of the 5th and 4th centuries to the end of the 2nd century BC.
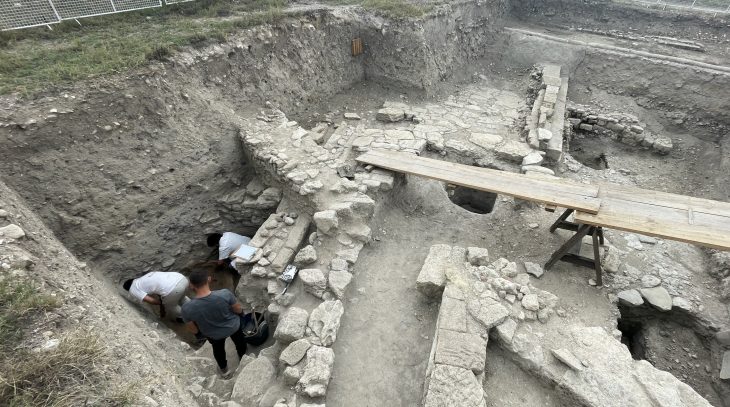
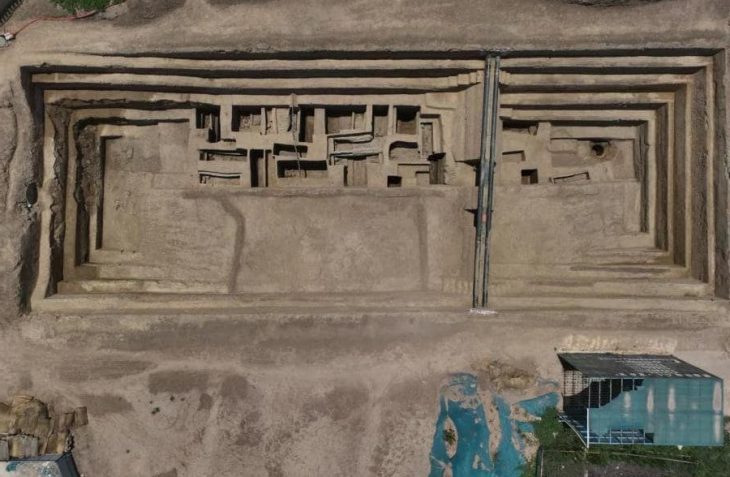
Excavations in this area have been carried out for eleven years. The work is being carried out by Jacek Soida, curator of the Archeology Department of the Silesian Museum, and Dr Przemysław Dulęba from the University of Wrocław.
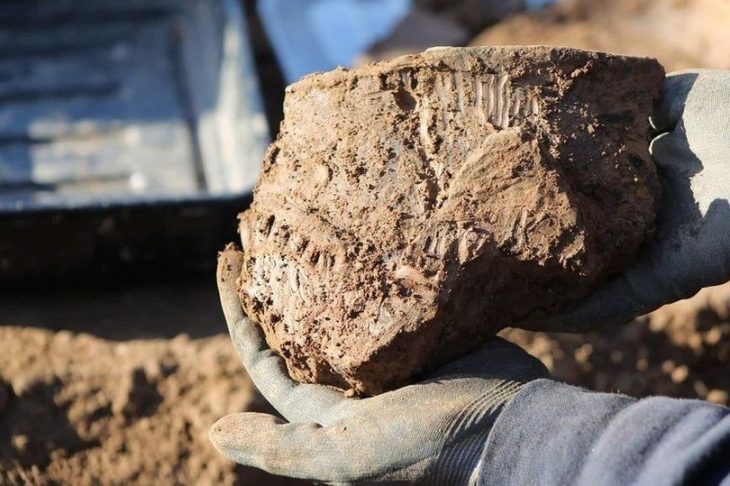
As Jacek Soida said in an interview with Nauka w Polsce (PAP), one of this year’s curiosities is the discovery (inside a dugout) of a dice, probably from the turn of the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. “This is the oldest dice ever found in Poland,” the archaeologist emphasized.
The artifact is a cuboid made of bone or antler. As Soida explained, due to the low probability of rolling the dice so that it lands on the smaller two sides, the longer sides were usually marked with higher values (3, 5, 4, and 6). “However, there were exceptions to this rule, and in the case of the Samborowice dice, the sides were marked only with the two highest values – 5 and 6. We are not sure whether it was a forgery or whether the item was used for a game unknown to us today,” Soida added.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Similar dice are known primarily from the central settlements of Lower Austria, Bohemia, and Moravia. “In smaller settlements, like the one in Samborowice, they are rarely discovered. Although this is not the first example of a gaming item found in this settlement – a few years ago we discovered ceramic tokens that were probably used for gaming,” Soida said.

Another discovery this year is a well-preserved iron fibula, a type of decorative clasp for fastening clothes. “Fragments of brooches are often discovered in sediments, but very rarely in such good condition, which makes this find unique. Iron objects that rest in the ground, over the years and due to corrosion, undergo significant destruction. In this case, the brooch in the past fell into the fire, where, due to high temperature, a layer of scale was formed on its surface, protecting the object against harmful corrosion. Of course, we still need to remove layers of mineral sinters in several places, but there is certainly intact metal underneath,” the archaeologist said.
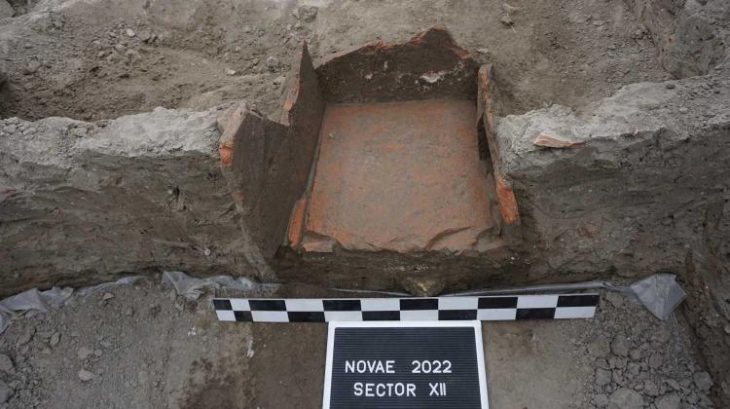
During this year’s fieldwork, archaeologists discovered two more relics of buildings that were originally dug into the ground (so-called semi-dugouts). “In such buildings, the Celts conducted various types of craft activities, such as weaving, iron and non-ferrous metallurgy, horn-making, and pottery. This is proven by discoveries from previous years,” said Soida.
Every year discoveries bring archaeologists more and more answers about the life of the Celts in this area. Among those discovered in recent years were the remains of a weaving workshop and relics of a pottery kiln.
Cover Photo: Jacek Soida – Silesian Museum