New research provides new insights into how the inhabitants of the “oldest city in the world” in Çatalhöyük (Turkey) buried their dead.
Their bones were partially painted, excavated several times, and reburied. The findings provide insight into the burial rituals of a fascinating society that lived 9000 years ago.
The research was done by an international team with the participation of the University of Bern and is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
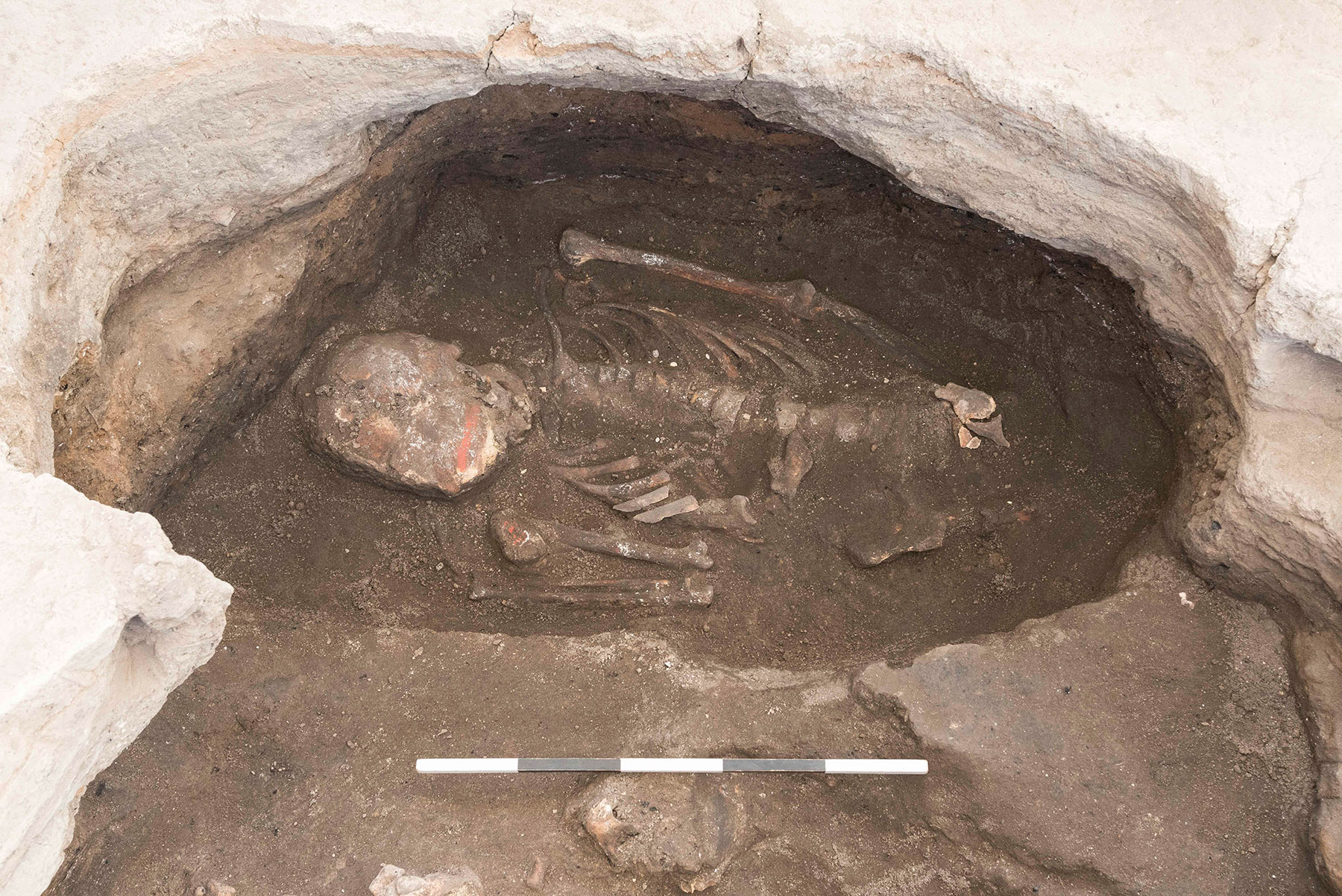
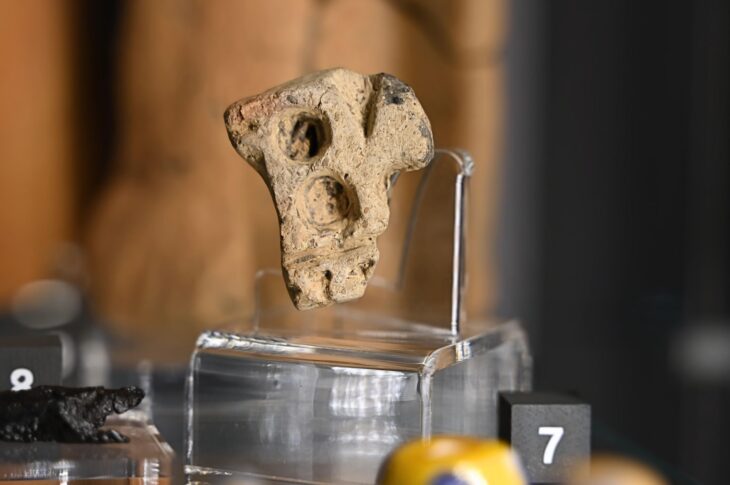
Çatalhöyük (Central Anatolia, Turkey) is one of the most important archaeological sites in the Near East, with an occupation that dates back to 9000 years ago. This Neolithic settlement, known as the world’s oldest city, covers an area of 13 ha and features densely aggregated mudbrick buildings. The houses of Çatalhöyük present the archaeological traces of ritual activities including intramural burials with some skeletons bearing traces of colorants, and wall paintings.
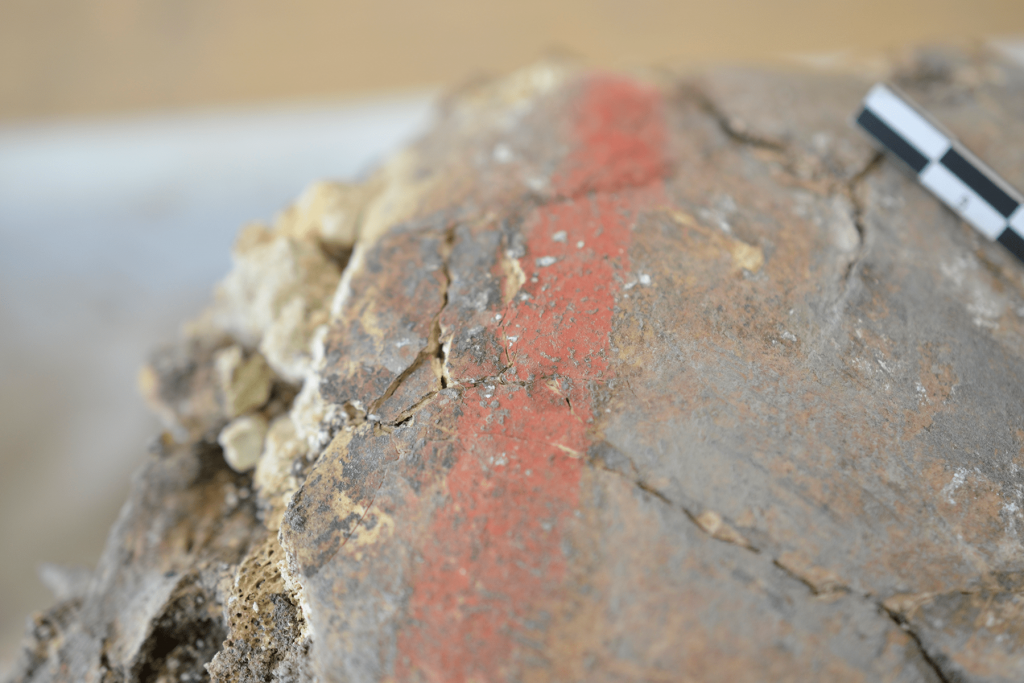

The association between the use of colorants and symbolic activities is documented among many past and present human societies. In the Near East, the use of pigments in architectural and funerary contexts becomes especially frequent starting from the second half of the 9th and the 8th millennium BC. Near Eastern archaeological sites dating back to the Neolithic have returned a large body of evidence of complex, often mysterious, symbolic activities. These include secondary funerary treatments, retrieval and circulation of skeletal parts, such as skulls, and the use of pigments in both architectural spaces and funerary contexts.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The first analysis of the pigments used in funerary and architectural contexts from this essential Neolithic site. According to the senior author of the study Marco Milella (Department of Physical Anthropology, Institute of Forensic Medicine, University of Bern): “These results reveal exciting insights about the association between the use of colorants, funerary rituals and living spaces in this fascinating society”.

A time travel into a world of colors, houses, and dead
Marco Milella was part of the anthropological team who excavated and studied the human remains from Çatalhöyük. His work involves trying to make ancient and modern skeletons “speak”. Establishing the age and sex, investigating violent injuries or special treatment of the corpse, and solving skeletal puzzles are routine activities at the Department of Physical Anthropology.
The study shows that red ochre was most commonly used at Çatalhöyük, present on some adults of both sexes and children, and that cinnabar and blue/green were associated with males and females, respectively. Intriguingly, the number of burials in a building appears associated with the number of subsequent layers of architectural paintings. This suggests a contextual association between funerary deposition and application of colorants in the domestic space. “This means: when they buried someone, they also painted on the walls of the house”, Milella says. Furthermore, at Çatalhöyük, some individuals “stayed” in the community: their skeletal elements were retrieved and circulated for some time, before they were buried again. This second burial of skeletal elements was also accompanied by wall paintings.
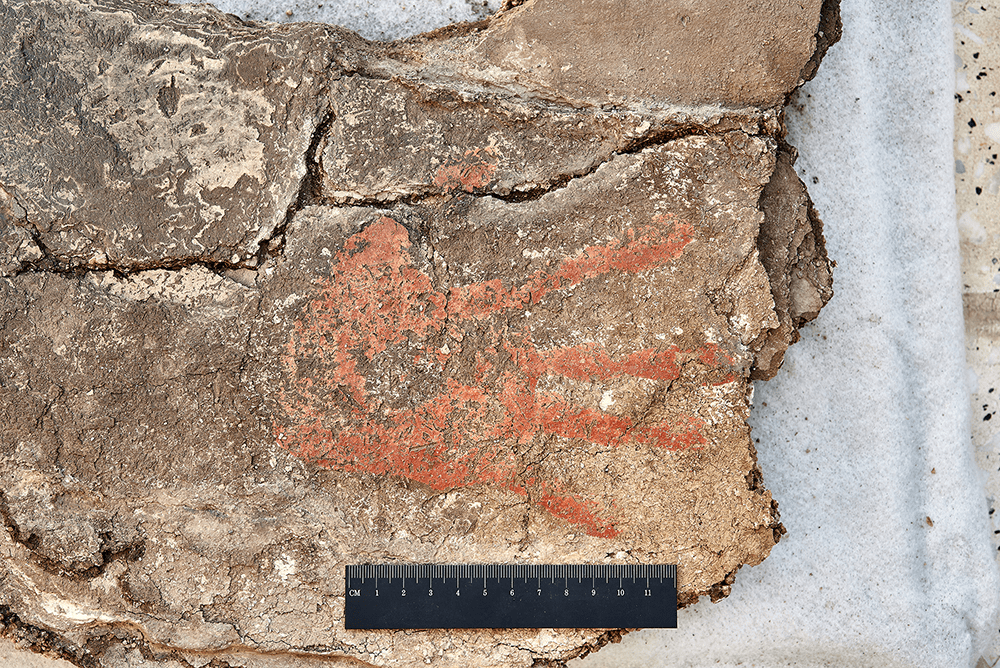
Neolithic mysteries
Only a selection of individuals was buried with colorants, and only a part of the individuals remained in the community with their circulating bones. According to Marco Milella, “the criteria guiding the selection of these individuals escape our understanding for now, which makes these findings even more interesting. Our study shows that this selection was not related to age or sex”. What is clear, however, is that visual expression, ritual performance, and symbolic associations were elements of shared long-term socio-cultural practices in this Neolithic society.