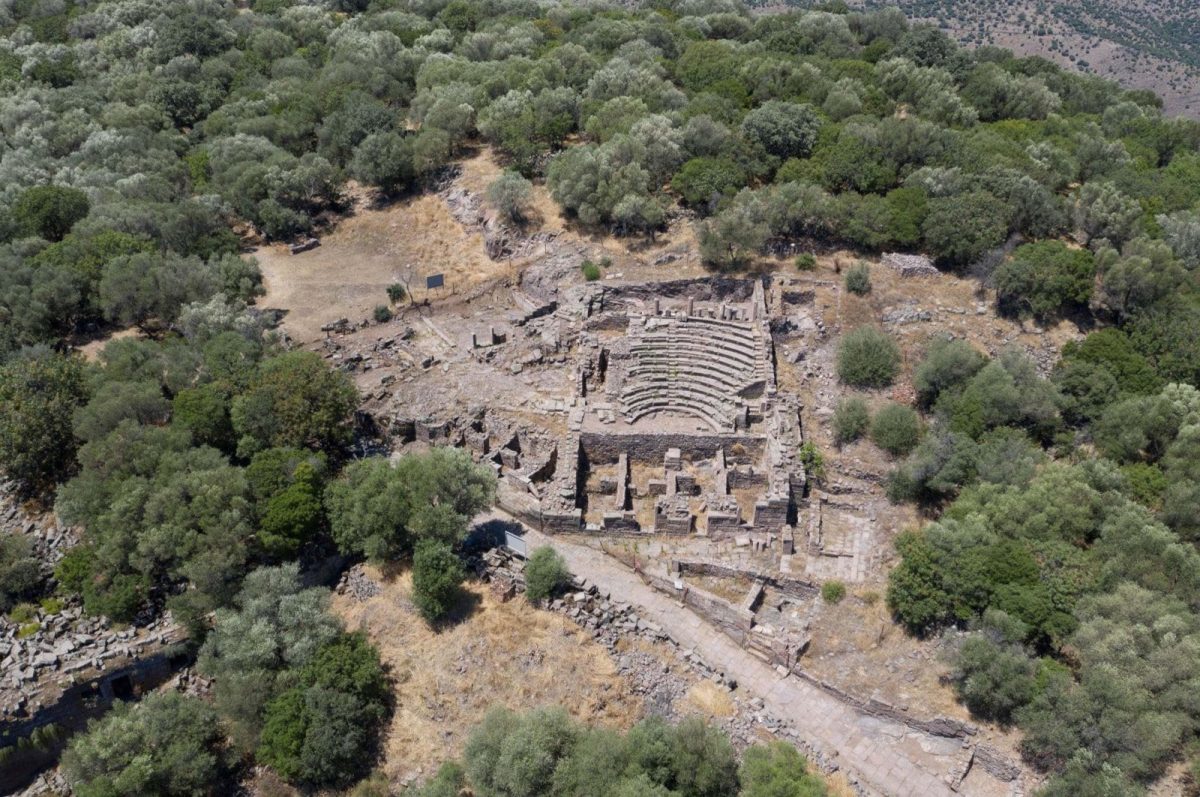
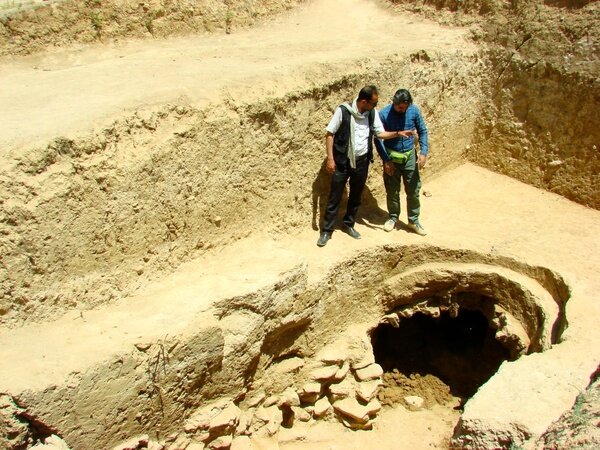
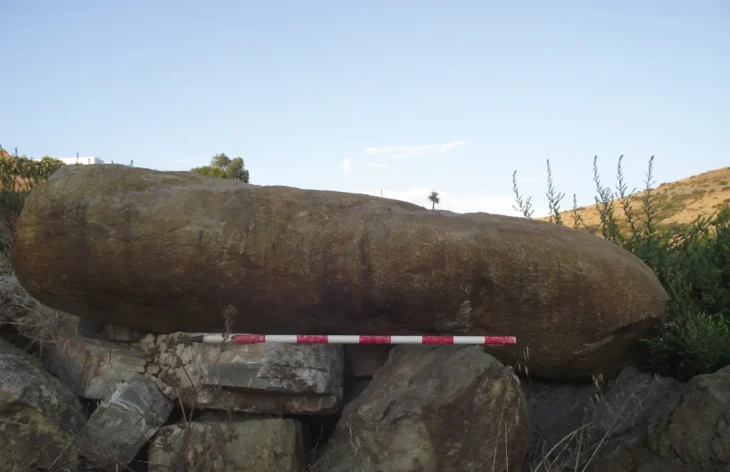
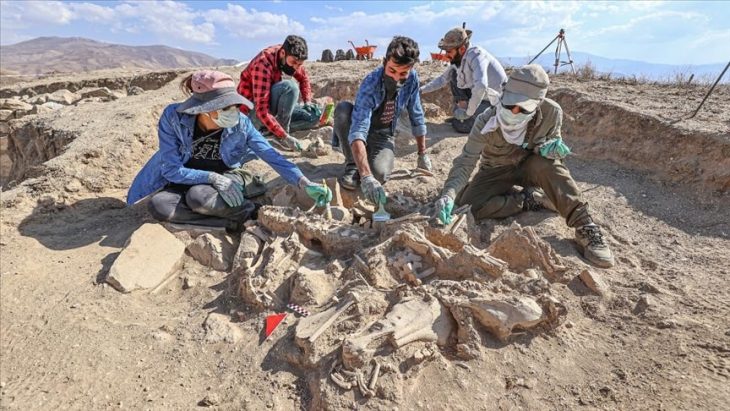
Archaeologists have uncovered an agora (city square) during excavations in the ancient city of Aigai, west of Manisa.
Aigai, located within the borders of the Yuntdağıköseler neighborhood in the Yunusemre district, is one of the 12 Aeolian cities established in western Anatolia. Archaeological excavations and research conducted at Aigai since 2004, show that the city was founded around 700 BCE. Historical records suggest that it was an important commercial center during Hellenistic times.
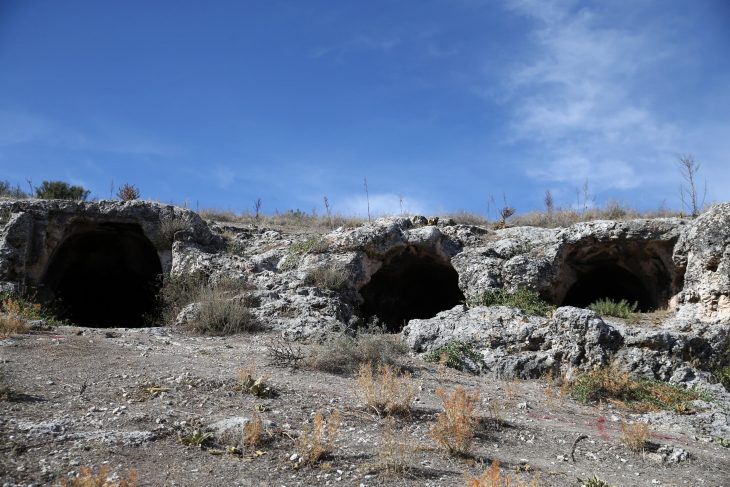
The 2,200-year-old agora was discovered as part of the “Heritage to the Future Project” by the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums.
Bull-head reliefs and inscriptions honoring the god Apollo were discovered on the square’s columns during the excavations, which are still ongoing in the agora, which is situated directly next to the parliament building.
The team, led by Professor Yusuf Sezgin, head of the Archaeology Department at Manisa Celal Bayar University, has been working on the site.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Sezgin emphasized the significance of the agora, describing it as the heart and center of the ancient city. Sezgin said, “This area is where all public buildings are concentrated and where people spend their daily lives. Around the square, there are columned porticos that we call ‘stoa.’ In this respect, this is a very important area. One of the symbols of Aigai is the agora building in this area. As a result of the work, we will focus particularly on the parts of the building that need restoration and conservation.”
Sezgin, who noted that the ancient city is 2,200 years old, emphasized that this date corresponds to the construction of the agora and the city’s parliament building, and mentioned that they have some archaeological evidence supporting this.
Stating that they came across interesting findings during the excavations in the agora, Sezgin said: “We found bull-headed reliefs under the roofs of stoas [columned porticos], which we are not very familiar with in the ancient world. We think they are important, as these bullheads are usually because they are typically associated with gods. We have found examples of this in several places in the ancient world. It is most likely related to the god of Apollo as we also found inscriptions related to the god Apollo near the area we are working on.”
“These types of stoas usually have a very simple architectural structure, but if they are related to a votive offering, it is possible to think that these embossed bullheads are related to a ritual, to the gods. This may be related to a major war or a votive offering made to the gods related to the reconstruction of the city,” Sezgin added.
Tens of thousands of artifacts and ceramic pieces discovered during the excavation of the ancient city of Aigai since 2004 were given to the Manisa Museum after being restored in the excavation house.