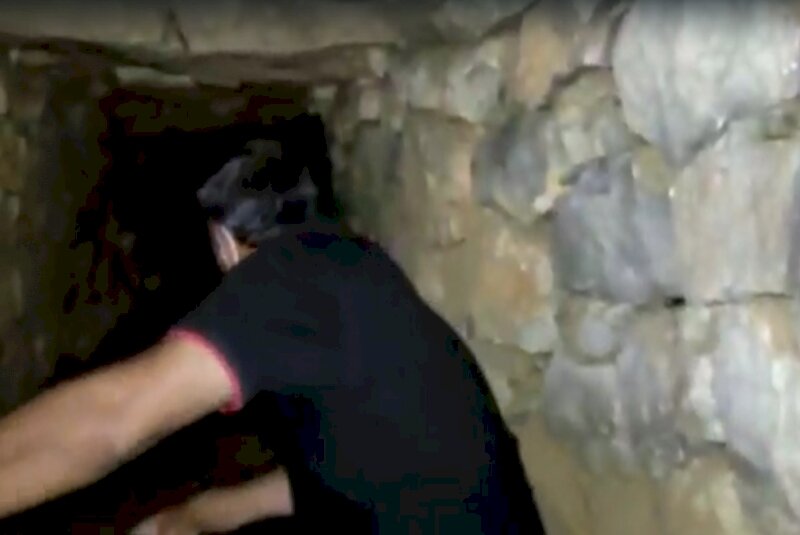
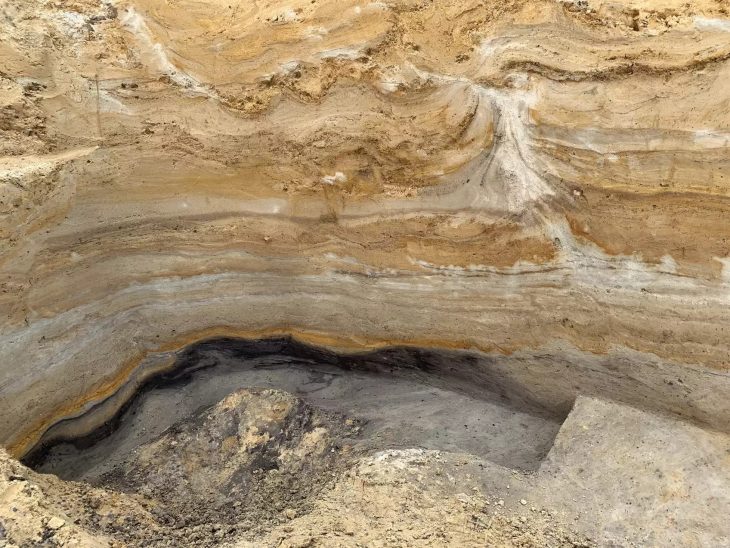
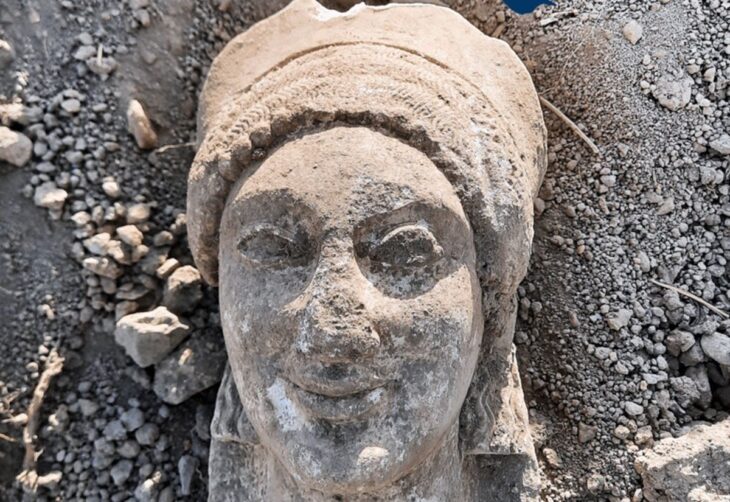
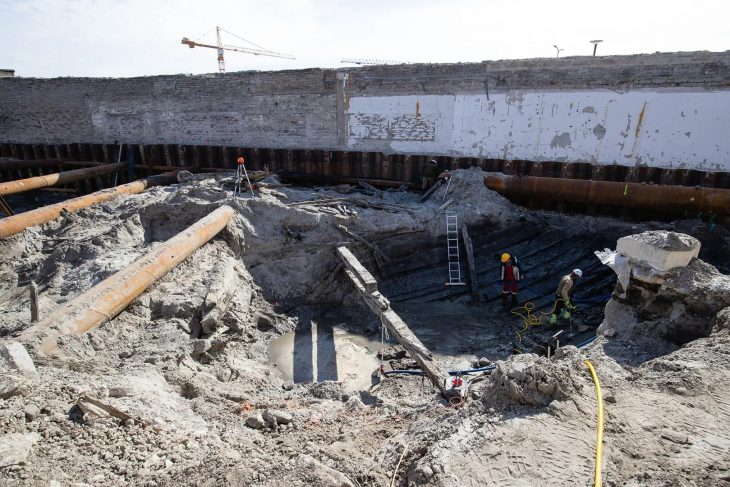
A cultural heritage protection team has recently discovered a stone-arched tunnel located near an Achaemenid embankment dam in southern Iran.
“A stone-arched tunnel, which is 1.5 meters in height, has recently been found adjacent to a historical dam that is named after the Achaemenid king Darius (the Great) in Marvdasht plain of Fars province,” a local official said.
So far, 40 meters of the tunnel, which is believed to be once an aqueduct, have been explored, the official added.
“However, a careful study by heritage and cultural experts is expected to reveal the original usage of the tunnel.”
Archaeologists believe embankment dams constructed during the Achaemenid era (c. 550 – 330 BC) and their role in water management is still a source of inspiration for modern architects and engineers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Achaemenid-era embankment dams were built with such knowledge, extent, and durability that after 25 centuries, [modern] earthen dams are still built per the Achaemenid engineering model,” Hamia Karami says.
The archaeologist pointed to “Bostan Khani” Dam, which is registered in the National Heritage list, as one of the “engineer masterpieces” the Achaemenids, saying: “Excavations and surveys on Bostan Khani Dam, as one of the engineering masterpieces of the Achaemenid period… can increase our knowledge and understanding of the methods and techniques of dam construction and architectural structure that is currently being practiced.”
Located on a branch of the Pulwar River, near the UNESCO-registered Pasargadae, the dam is designed to contain floods and store large amounts of water for public use as well as use in agriculture and horticulture.
The Achaemenid [Persian] Empire was the largest and most durable empire of its time. The empire stretched from Ethiopia, through Egypt, to Greece, to Anatolia (modern Turkey), Central Asia, and to India.
Building activity was extensive during the height of the empire, and of the several Achaemenian capitals, the ruins at Pasargadae and Persepolis are probably the most outstanding. Achaemenian sculptured reliefs and a great number of smaller art objects present a remarkably unified style for the period. Metalwork, especially in gold, was highly developed, and a variety of carefully executed examples survive.
AFM