Recent research at the Palace of Cortés in Cuernavaca, Mexico, has revealed a grave historical error. For 50 years, it assumed that a skeleton on display at the palace was that of a Spanish monk – but a new analysis has shown that it actually likely belonged to an Aztec woman.
A recent study of the skeleton reveals that it corresponds to a Tlahuica woman, an Aztec tribe that founded its realm and royal residence on the Cuauhnáhuac Hill.
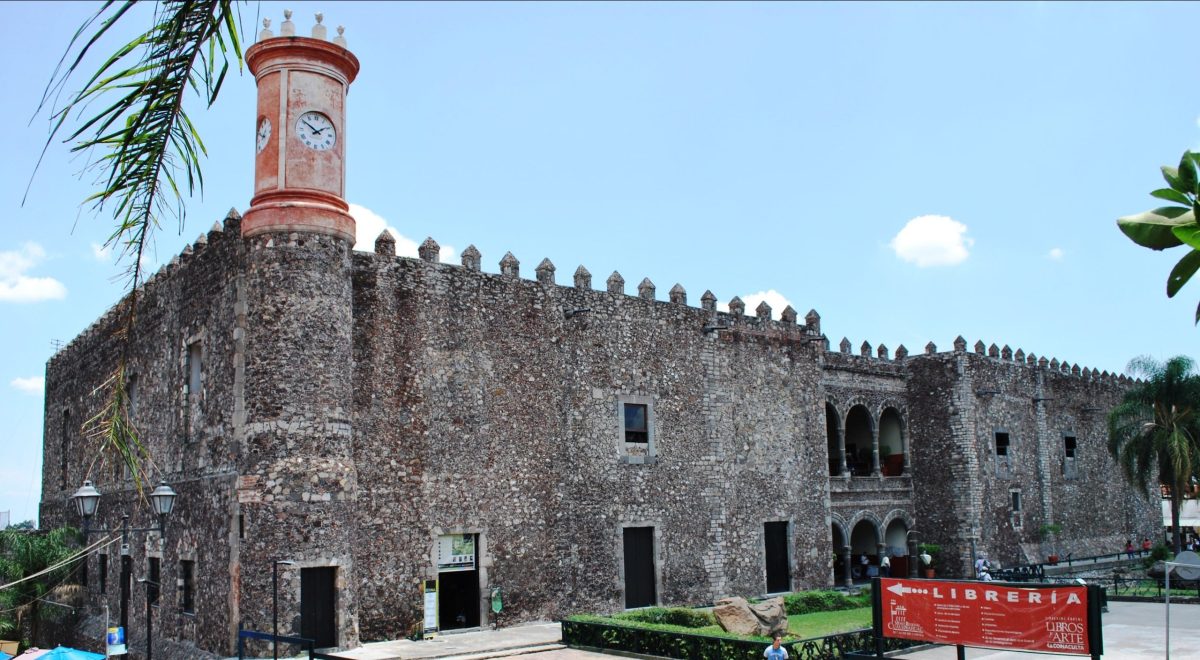
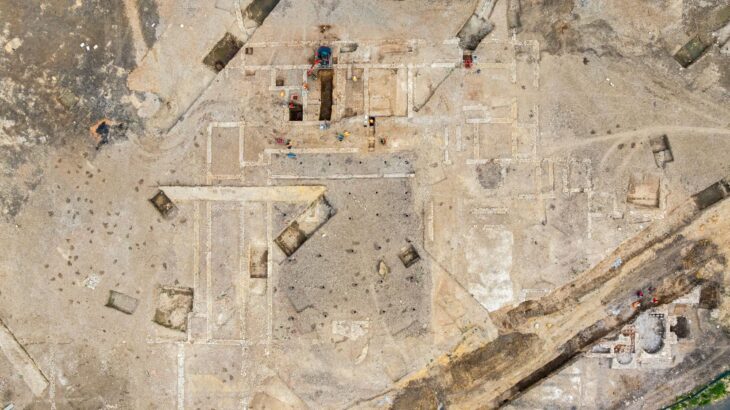
The Palacio de Cortés was damaged by the deadly Puebla earthquake in September 2017, prompting a renovation project to restore the structure to its former glory. This renovation included a reassessment of the burial near the entrance, with the evaluation of its state of conservation and a historical investigation of the individual.
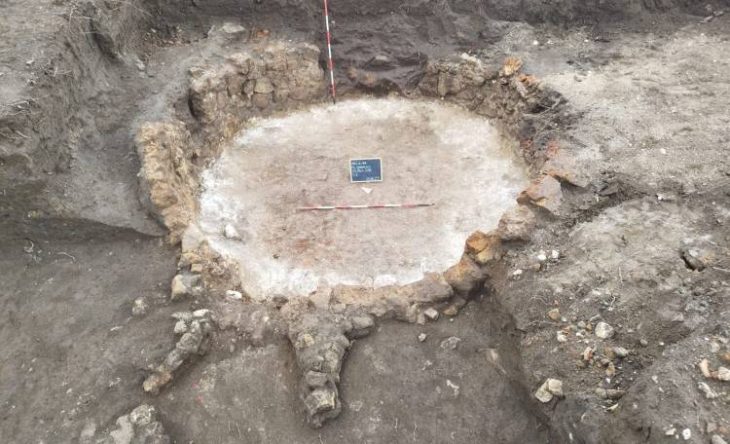
Excavated in 1971, the burial was thought to be that of Juan Leyva, a Spanish monk who served Marchioness Juana de Zúñiga y Arellano, wife of Hernán Cortés. The identification was based on a Franciscan codex from the 16th century that described Leyva’s burial near the old house’s gate. However, differences in skeletal features, such as a fetal-like burial position and cranial modification, raised doubts about the identification.
Due to this seemingly valid conclusion, the description plaque that accompanied the archaeological window for almost half a century read: “Burial found in situ of a man with deformed vertebrae. Traditionally it is stated that it may be the monk Juan Leyva, who served the Marchioness Doña Juana de Zúñiga de Arellano, wife of Hernán Cortés and resident of this palace, however, due to the type of posture it may be an indigenous burial.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

As the physical anthropologists pointed out, archaeologist Jorge Angulo already warned that history could be rewritten.
Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) recently announced the results of a new analysis conducted by anthropologists Pablo Neptalí Monterroso Rivas and Isabel Bertha Garza Gómez.
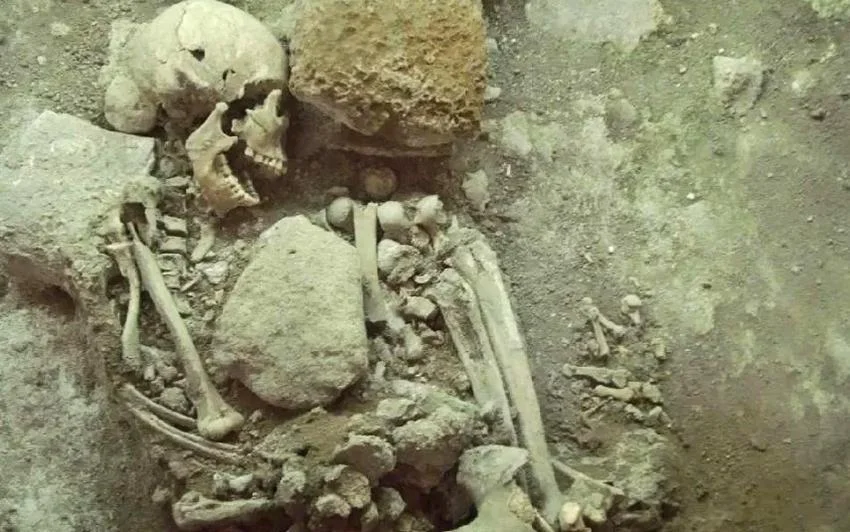
The skeletal analysis revealed that the individual was a female aged 30 to 40 at the time of death. The presence of cranial flattening, a fetal-like burial position, and other distinguishing characteristics indicated an Indigenous origin. The researchers proposed that the woman was buried ritualistically, possibly as part of a series of events, such as sacrifices, during the Spanish invasion between 1500 and 1521.
Jorge Angulo, an archaeologist with INAH, commented on the significance of the findings, stating, “It is more related to a pre-Hispanic burial, which could belong to the contact period or earlier.

Other remains from two other people, including an infant and a child, were also found during the study, raising the possibility of a family relationship. Researchers suggested conducting a DNA study to help clarify relationships.
The burial of the Tlahuica woman is especially significant because of its connection to the Palace of Cortés. The palace was built by the Spanish in the 1520s on the ruins of the Aztec city of Cuauhnáhuac. The recently restored archaeological window, which has a plaque identifying the burial as that of a “Tlahuica Woman,” is a moving reminder of the intricate past ingrained in the location.
Cover Photo: INAH