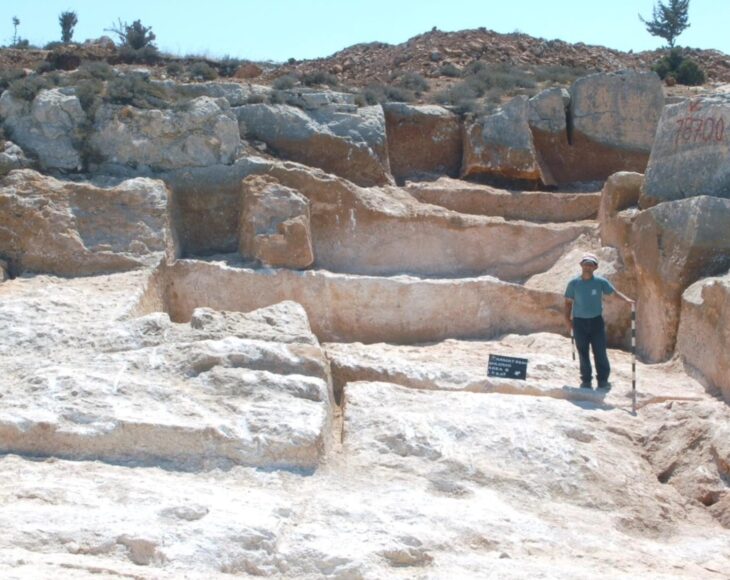
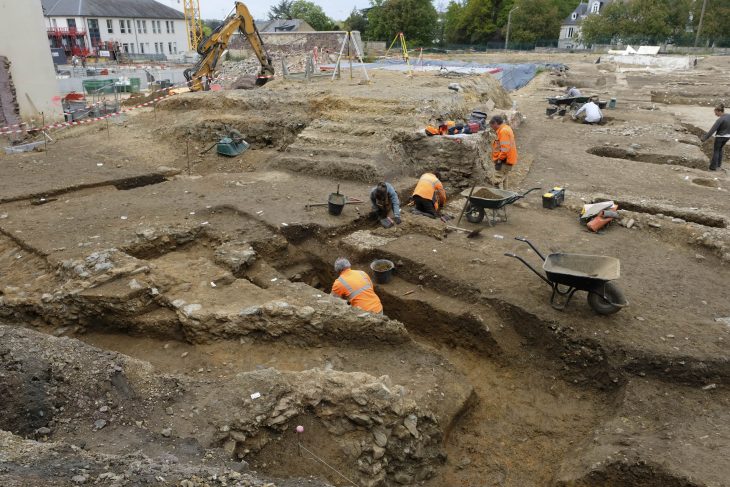
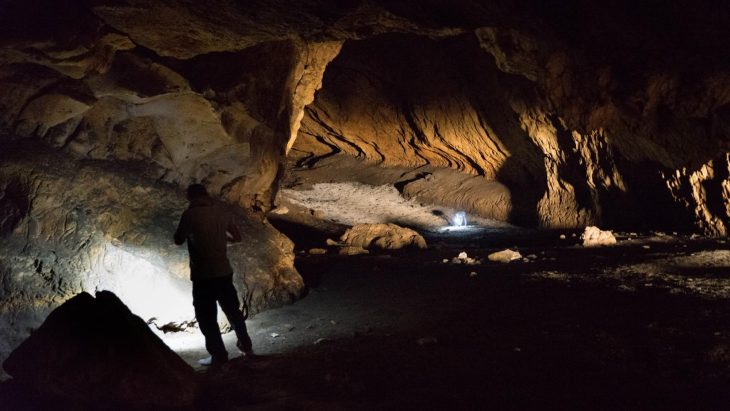
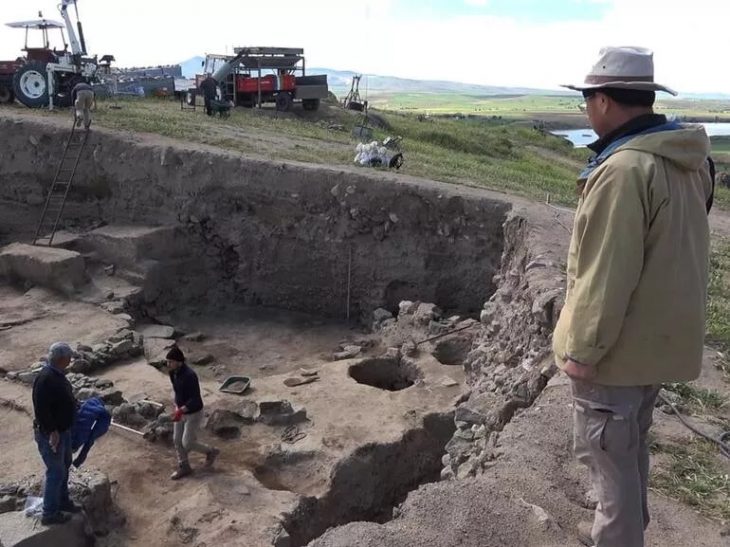
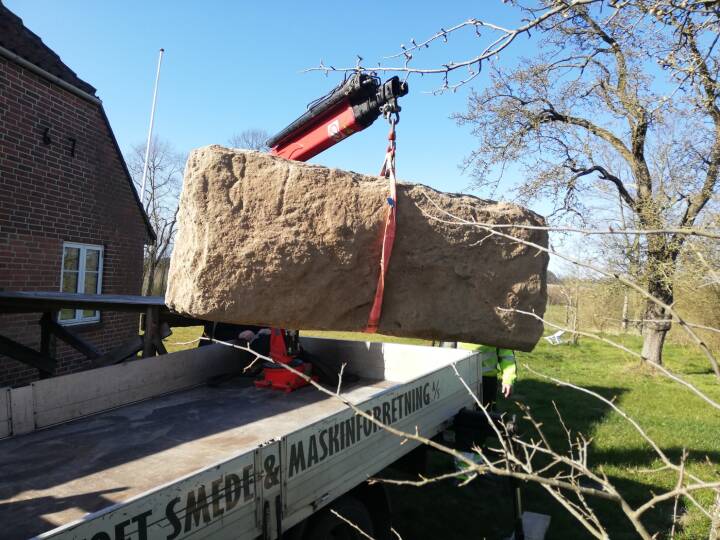
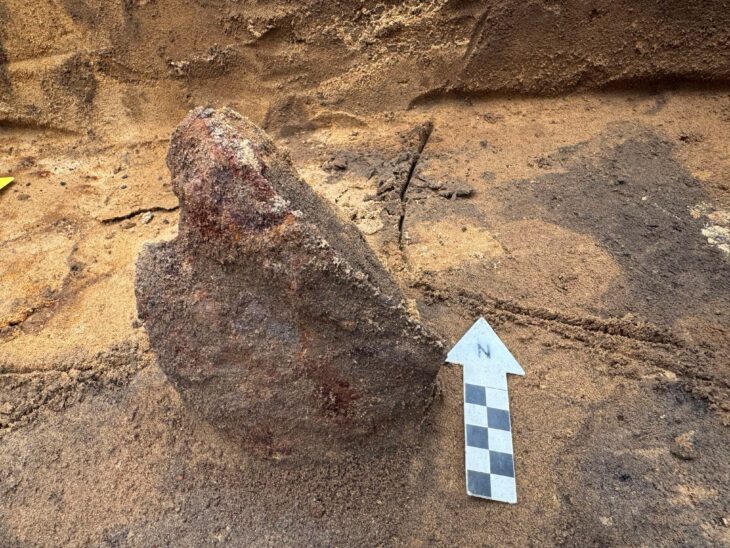
The National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters (NCCAL) has announced a remarkable archaeological find on Failaka Island, revealing a courtyard and a building that date back approximately 2,300 years to the Hellenistic period. This discovery was made by a Kuwaiti-Italian archaeological mission at the Al-Qurainiya site, which has been a focal point for archaeological research since 2014.
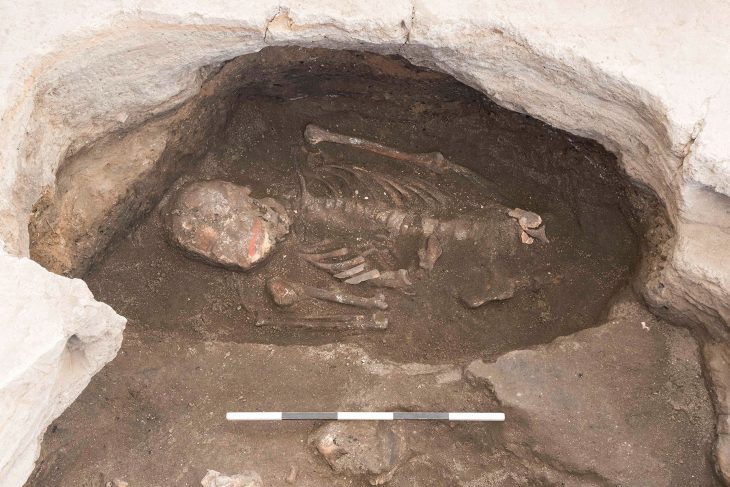
Mohammad bin Redha, the Acting Assistant Secretary-General of the Council for Antiquities and Museums, shared details of the discovery with KUNA. The Al-Qurainiya site, located in the northern part of Failaka Island and overlooking the sea, has yielded evidence of human settlement spanning multiple historical periods, from pre-Islamic times to the early and late Islamic eras.
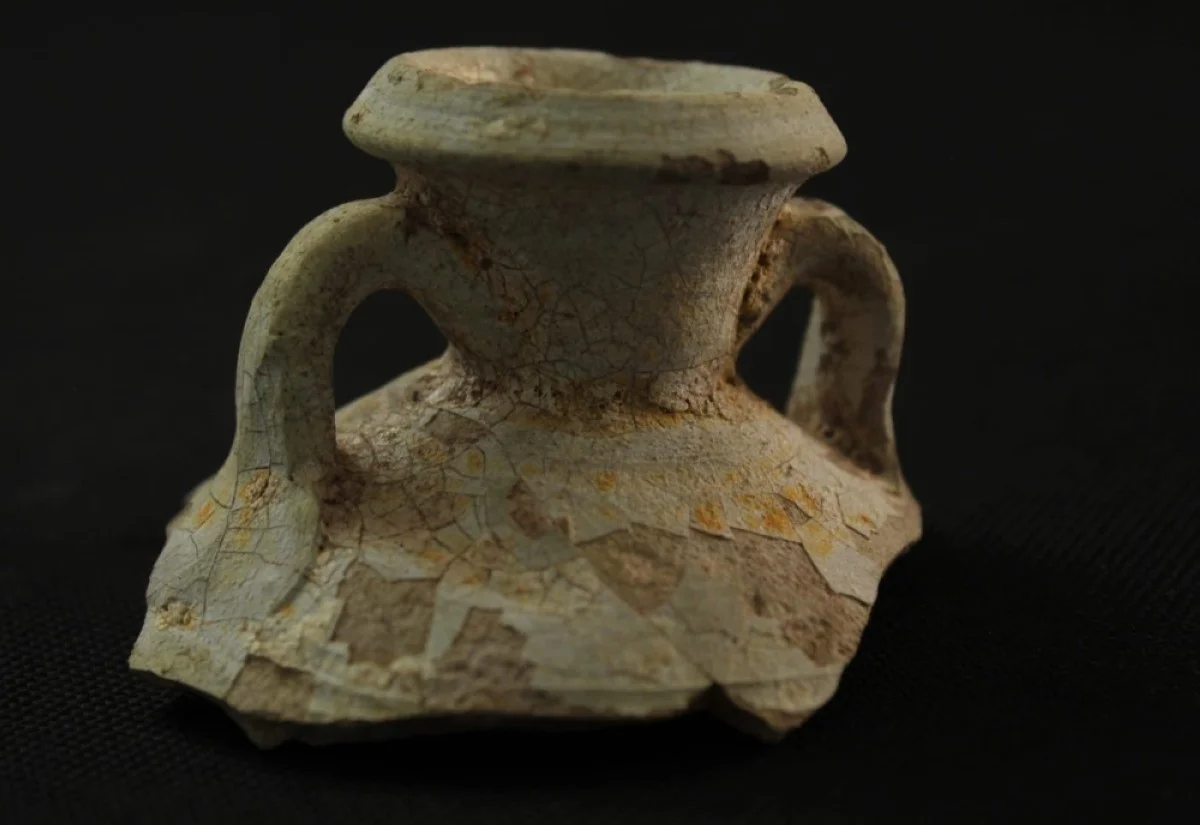
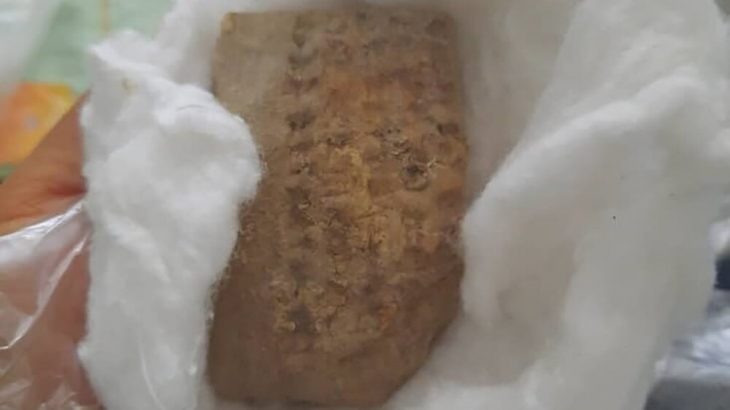
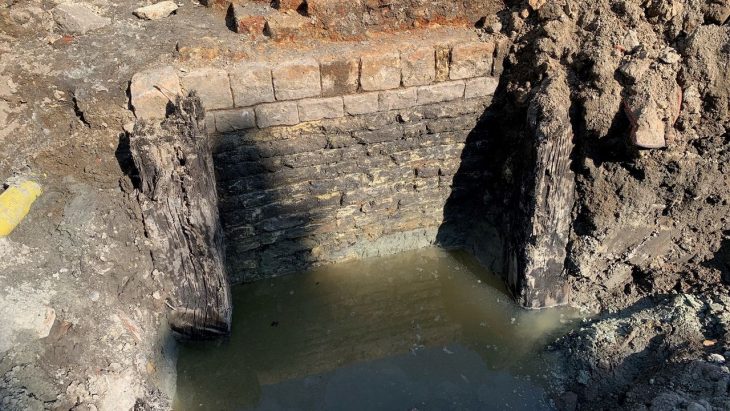
The excavation team uncovered rock foundations, an internal wall, and an entrance that connects the external courtyard to a room containing remnants of plastered walls and numerous pottery artifacts, all over 2,000 years old. Bin Redha emphasized that the oldest layers of this site trace back to the third and second centuries BC, marking it as one of the largest archaeological sites on the island.
The collaboration between the NCCAL and the University of Perugia, Italy, has been instrumental in this ongoing research, led by Dr. Andrea De Micheli. This season, the Council aims to enhance cooperation with various sectors, including Kuwait University and international laboratories, to utilize advanced laboratory techniques for analyzing materials used at the site, such as gypsum and clay types in pottery production.
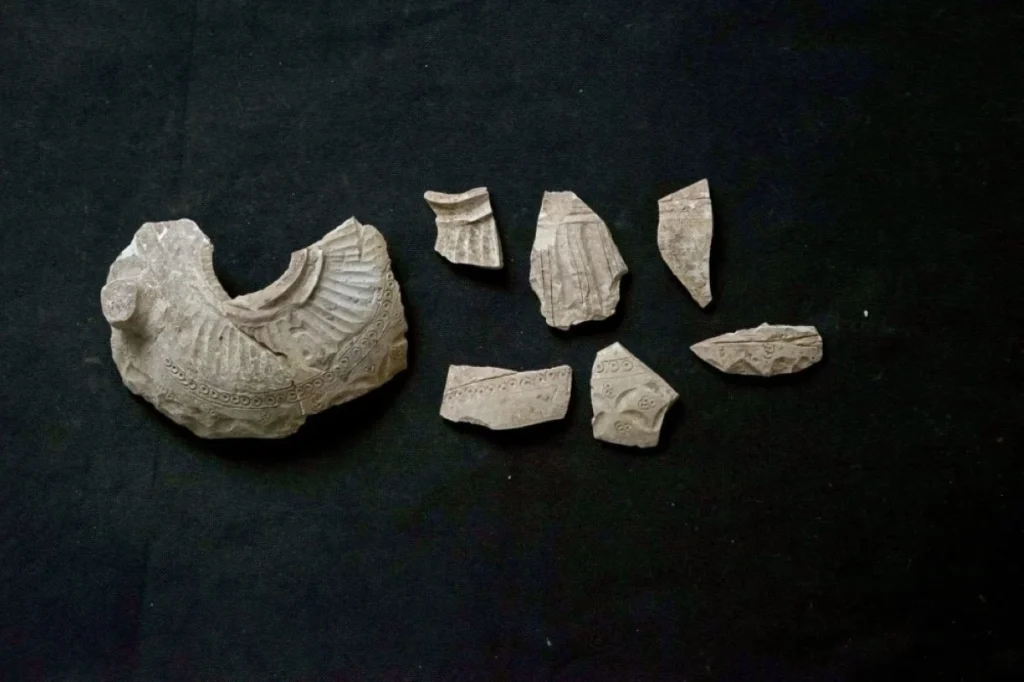

Dr. Hassan Ashkanani, a Professor of Archaeology and Anthropology at Kuwait University, hailed the discovery as a significant achievement for Failaka Island. He noted that previous findings from the Hellenistic period were primarily located in the southwest of the island, while the newly discovered structures in the north suggest a broader Hellenistic presence. This indicates that the Al-Qurainiya site may have served as a strategic control point or port in addition to housing Hellenistic dwellings, castles, and temples.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Looking ahead, Dr. De Micheli indicated that the focus for the 2025 excavation season will be on the western part of the Al-Qurainiya settlement, which predates the Islamic period. Excavations have already revealed remnants of a courtyard and building from the Hellenistic era, alongside evidence of early and late Islamic periods, showcasing a continuous human presence at the site for over 1,800 years.
From 2014 to 2020, excavations uncovered various buildings, primarily dwellings from the eighth century AD, during the early Islamic period. These findings suggest that the site was abandoned by the end of the eighth century or the beginning of the ninth century, but human activity resumed in the latter half of the 18th century and continued into the early 20th century.
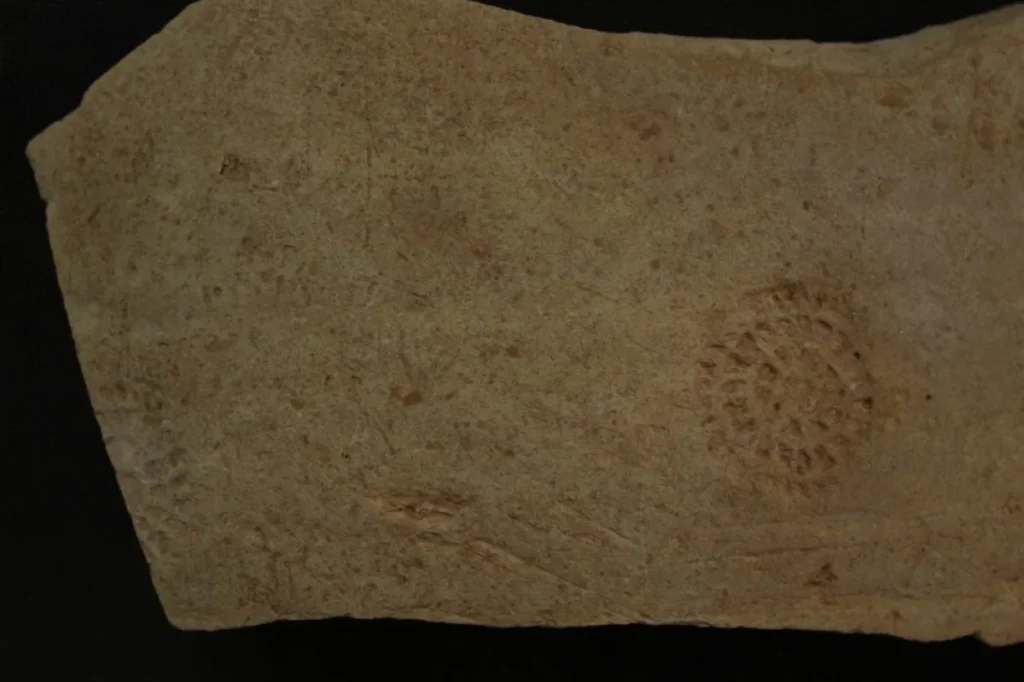

The discovery of extensive pottery and ovens provides valuable insights into the daily lives of the inhabitants of the Al-Qurainiya site. The archaeological remains extend approximately 500 meters along the coastline and 250 meters inland, featuring numerous structures made from limestone, mud bricks, and pottery from various historical periods, solidifying its status as one of the largest archaeological sites on Failaka Island.
Cover Image Credit: Remains of Pottery jars discovered from the Hellenistic courtyard site. Credit: KUNA