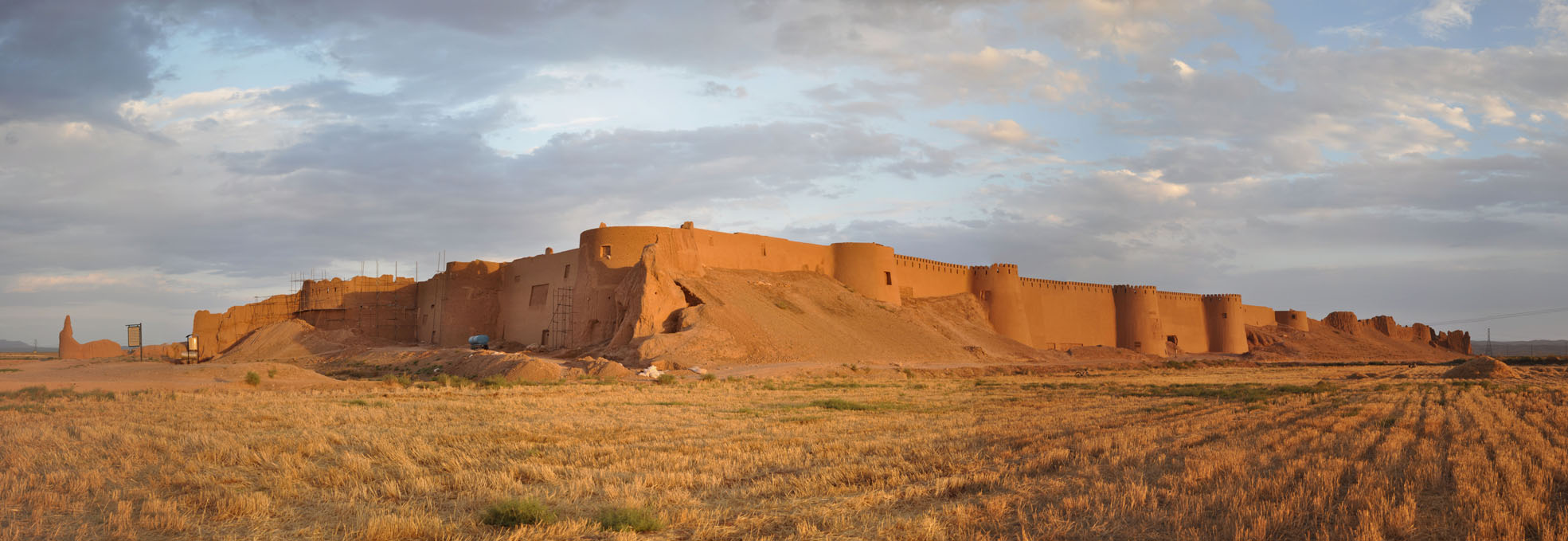
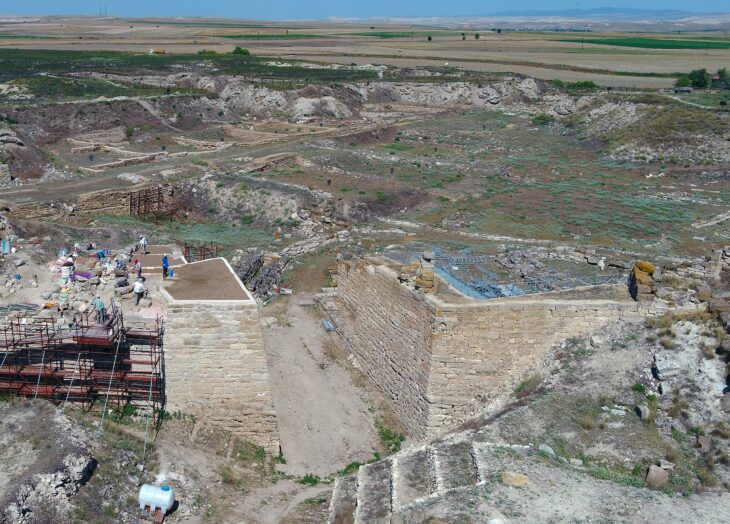
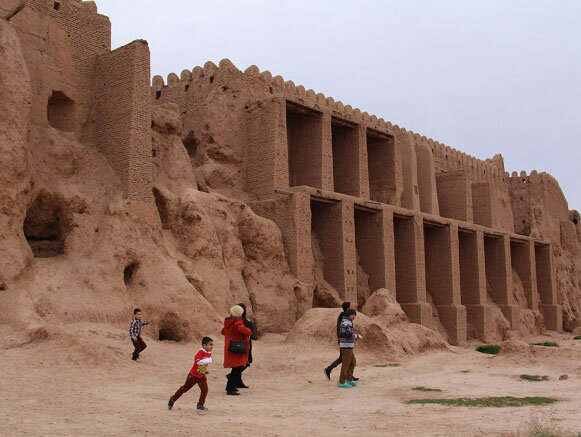
Recently, a portion of the restored walls of 1500-year-old Shahr-e Belqeys (“City of Belqeys”), a historical city made of mudbricks in northeast Iran, has collapsed, sparking concerns about the integrity of the remaining structure.
The Old City of Esfarayen is located in the northeast of Iran and the southwest of the modern city of Esfarayen. In the Qajar period, this city was cited as the “city of Belghays”.
Although Belqeys’ antiquity is estimated to be around 6,000 years old by [previous] archaeological excavations at neighboring mounts and hilltops, the area was prosperous from the late Sassanians to the early Islamic periods. Belqeys citadel is one of the largest mudbrick fortresses in Iran after the UNESCO-registered Bam Citadel.
Hossein Rahmani, the director of the National Cultural Heritage Base in the historic city of Belqeys, highlighted the significance of the
“A section of the restored walls of Shahr-e Belqeys, which is the second mudbrick-and-clay structure in Iran, has been collapsed recently,” ISNA quoted Hossein Rahmani, who presides over the national site, as saying on Tuesday.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Rahmani expressed concerns that had persisted over the past two to three years regarding the potential collapse of all the restored walls. He also called for urgent restoration work.
Approximately 160 square meters of the restored walls have collapsed, Rahmani said.

He lamented the lack of allocated funds for the restoration of this historical site in recent years, with national funds primarily directed towards employee salaries.
Regarding the cause of the collapse, Rahmani attributed it to improper restoration methods, resulting in uneven restoration depths ranging from 10 centimeters at the bottom to 70 to 80 centimeters at the top of the walls.
Moreover, he emphasized the importance of conducting thorough studies before commencing restoration work, including determining the appropriate materials and techniques.
He criticized the use of raw clay and the application of straw during the restoration process, which deviated from historical construction practices during the Safavid, Ilkhanid, and Seljuk periods.
Furthermore, Rahmani pointed out that the builders of the original structure were well aware of the presence of termites in the region, which posed a threat to the stability of the building. However, the use of inappropriate materials during restoration exacerbated the risk of collapse.
“The combination of expansive soil, erosion, and the weight of the structure led to the collapse of sections of the restored walls.”
In Iran’s history, the Sassanian era (224–651 CE) is extremely significant. Persian art and architecture saw a general rebirth during the Sassanians. Large-scale architectural designs were common, as seen in the ensemble’s highlights, the palaces at Ctesiphon, Firuzabad, and Sarvestan.
Among the artifacts that have been discovered in Belqeys thus far during excavation rounds are family quarters, irrigation channels, a cistern, and remnants of the citadel.
Cover Photo: Arghiyan