Researchers from the Austrian Academy of Sciences have published a new radiocarbon dataset for Tel Gezer, one of the most important Bronze and Iron Age sites in Israel. This makes it possible for the first time to check the extent to which archaeological findings correspond to historical events from written sources.
New dates provide detailed insights into the timing of events in the ancient city of Gezer, according to a new study published November 15, 2023, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lyndelle Webster of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and colleagues.
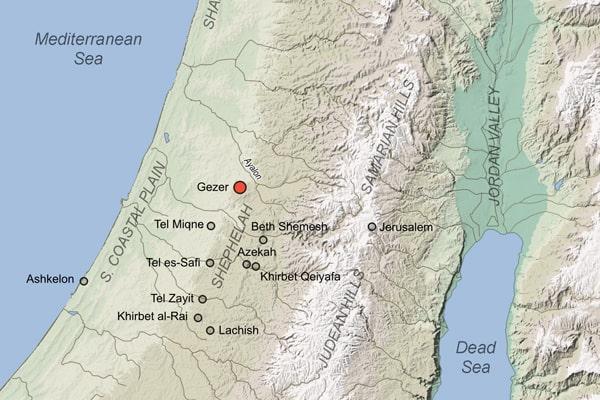
Tel Gezer is an ancient southern Levantine city, well known from Egyptian, Assyrian, and Biblical texts and associated with stories of power struggles and significant historical figures.
Due to its location along ancient trade routes, the city was one of the most important sites of the Bronze and Iron Ages (3rd to 1st millennium BC) and is mentioned in many Egyptian, biblical and Assyrian sources, where it is primarily associated with power struggles and conquests.
Lyndelle Webster, archaeologist at the Austrian Archaeological Institute of the OeAW: “We have taken more than 75 measurements on charred seeds from multiple settlement and destruction layers. The results of the 35 measurements from the Late Bronze Age and Iron Age layers published in our study date to the 13th through 9th centuries BC. The dataset allows us for the first time to set the history of Gezer on a firm timeline.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
With the results of the 14C measurements, a reliable dating of the Late Bronze Age and Iron Age layers is now available for the first time. However, the many written mentions of Gezer also make it possible to check whether the absolute dates can be related to historical events such as destruction, major architectural changes or the construction of fortifications.
The radiocarbon dates show that Gezer was heavily destroyed around 1200 BC. The event is possibly linked to a military campaign by the Egyptian king Merneptah, but is certainly connected to the general crisis that can be observed in this region and in the eastern Mediterranean at the end of the Late Bronze Age. The radiocarbon dating of the subsequent settlement layer contributes to a long-standing debate among experts about the dating of the “Philistine” culture. This arose in the nearby coastal plain and its influence reached Gezer around the middle of the 12th century BC, as evidenced by finds of “Philistine” pottery.
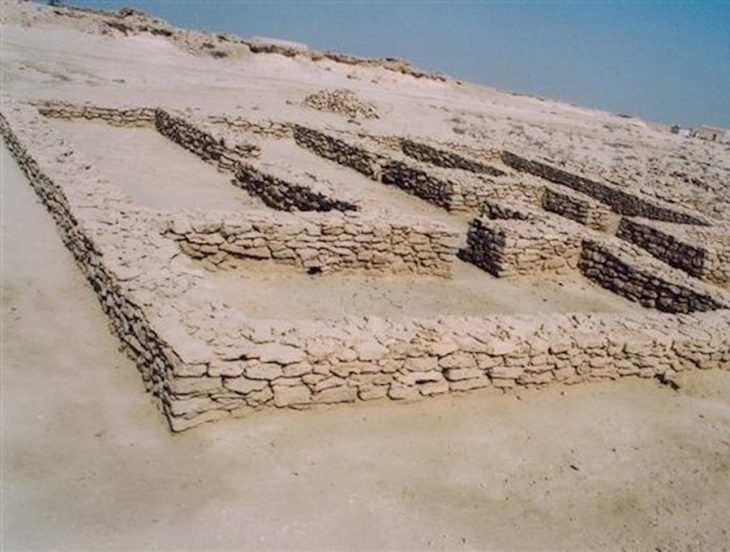
A further discussion deals with the transition to monumental public architecture and centralized administration in Gezer. According to the new radiocarbon data, this change can be dated to the first half of the 10th century BC rather than the 9th century BC. The result could mean that emerging political units, probably from the highlands, were associated with this development.

Shortly afterwards, around the middle of the 10th century BC, this first monumental architecture was destroyed. The city was then rebuilt, but suffered another major destruction soon afterwards, which is now clearly dated to around 900 BC. This is in contrast to earlier ideas, which linked it to a campaign by the Aramean king Hazael around 840 BC. The new radiocarbon dates clearly rule out this later scenario. Alternatively, non-military causes or conflicts between Judah, Israel and their neighbors are conceivable.
The data was collected by researchers from the Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (OeAW) in collaboration with the US excavation team.
Austrian Archaeological Institute
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293119
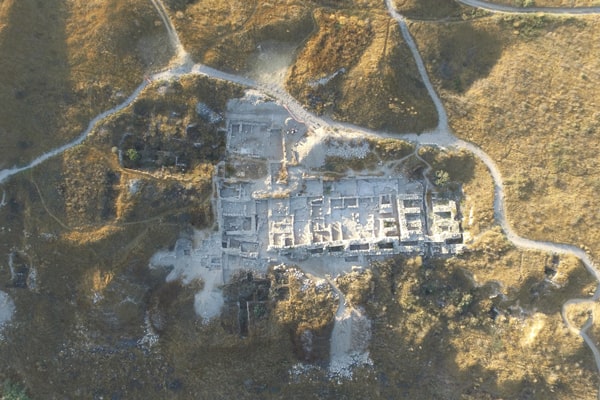
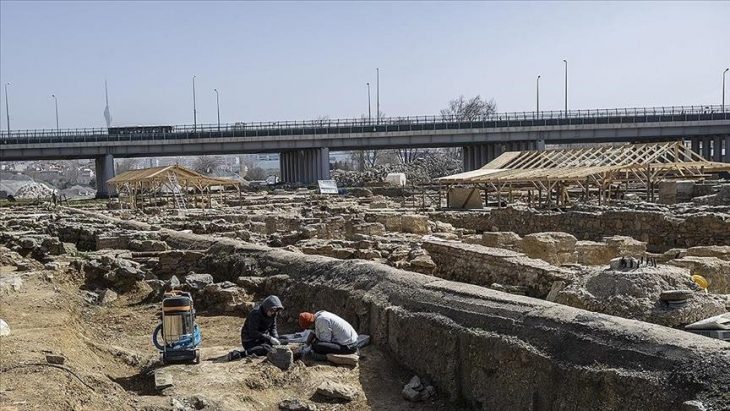
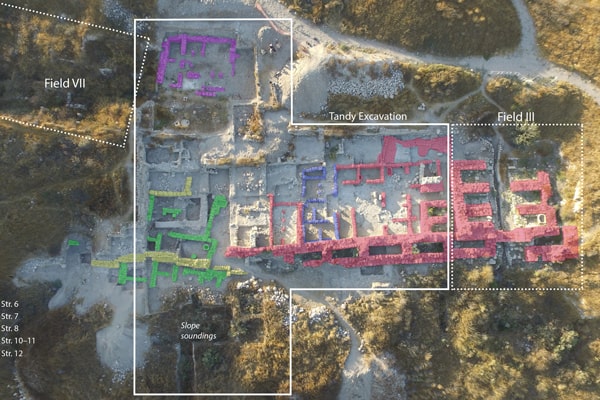
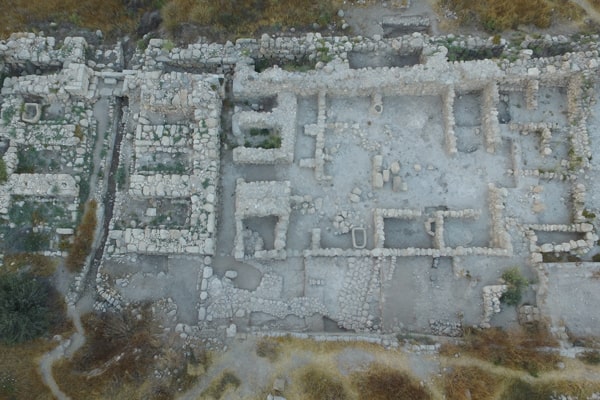
Cover Photo: Aerial view of excavations along the southern edge of the mound. © Lanier Center for Archaeology