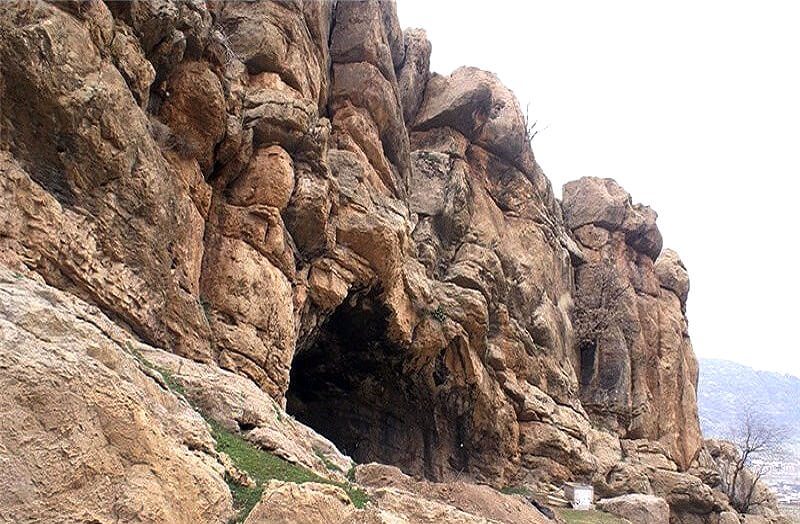
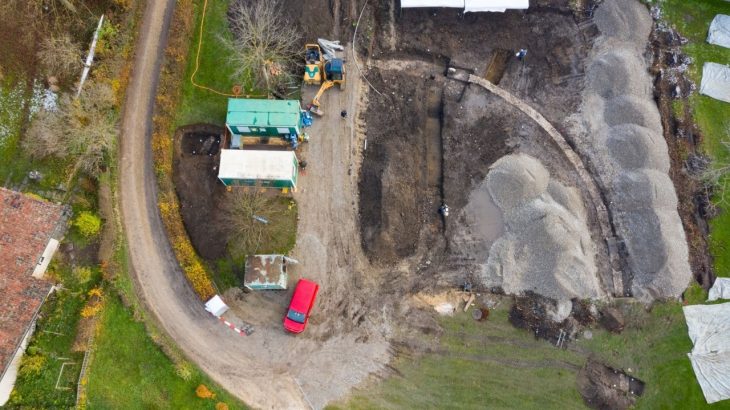
Kaldar cave is an important archaeological site that provides evidence for the transition from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic Ages in Iran. The cave is located in the Khorramabad Valley in the northern part of Lorestan Province, at an altitude of 1,290 meters. It is 16 meters long, 17 meters wide and 7 meters high.
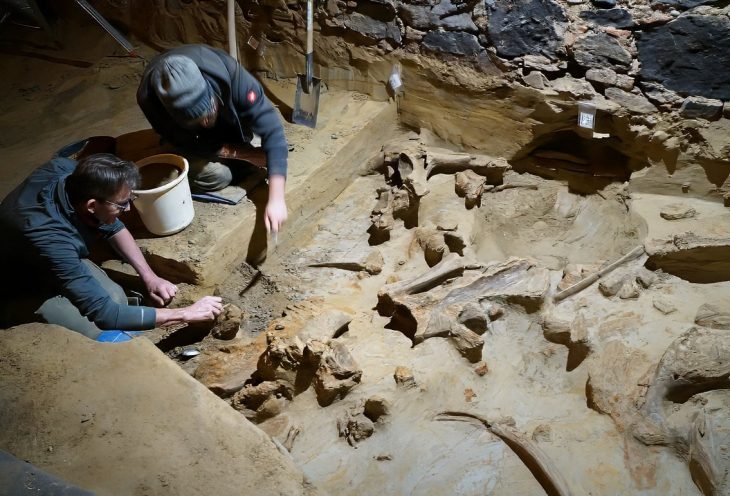
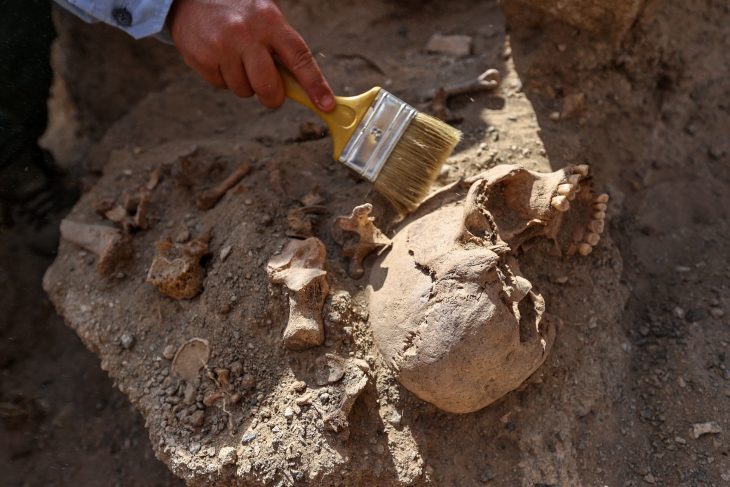
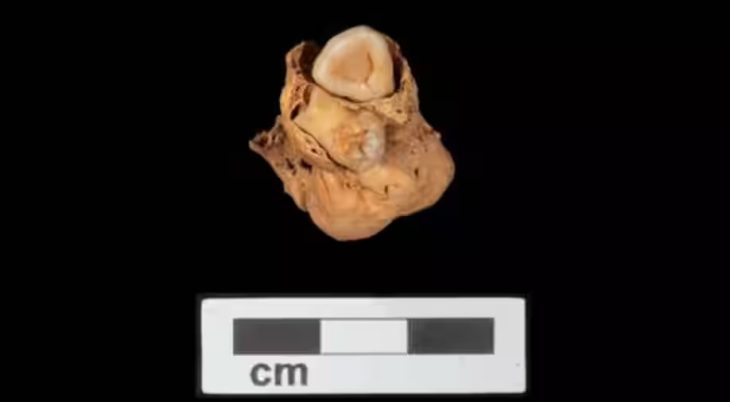
In 2019, in one of the significant archaeological finds from Iranian history, the cave provided new evidence for Palaeolithic people; including traditions of tool making [stone] related to the Middle and Upper Palaeolithic epochs. In the same year, archaeologists unearthed stone tools and a fragment of a fossil skull attributed to Homo sapiens. The cave has also yielded weapon fragments crafted by Neanderthals.
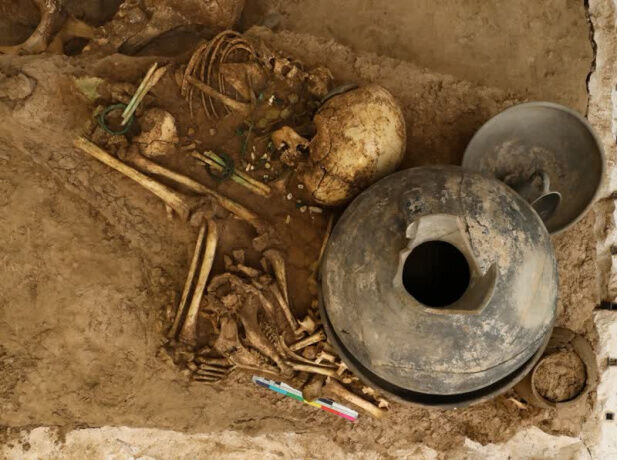
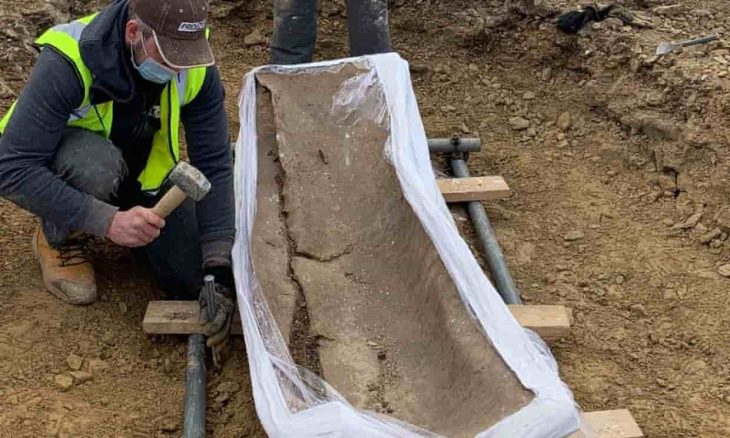
A human fossil found in Kaldar cave, western Iran, is part of a “missing link” in Homo sapiens’ migrating, Iranian archaeologist Behrouz Bazgir has said.
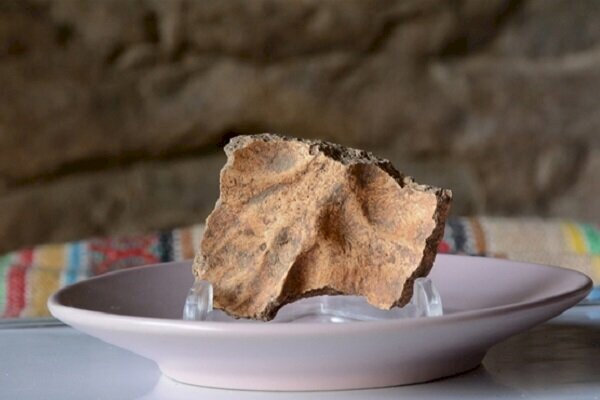

“Given the handful of Homo sapiens human fossils so far revealed across the world, the discovery of human fossils not only in the Kaldar cave but anywhere in the world could reveal a large part of the missing link in the migration of intelligent humans,” CHTN quoted Bazgir as saying on Monday.
The discovery was made during the third archaeological season conducted in Kaldar cave seeking to achieve the historiography of the Middle Paleolithic strata, and to obtain human fossils, the archaeologist explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
He made the remarks during the 18th Annual Symposium on the Iranian Archaeology, jointly organized by the Iranian Center for Archaeological Research (ICAR), Research Institute of Cultural Heritage & Tourism (RICHT), and National Museum of Iran.
Nearly one decade of archaeological surveys at Kaldar cave has concluded that parts of this western Iranian shelter date more than 63,000 years.
Lorestan was inhabited by Iranian Indo-European peoples, including the Medes, around 1000 BC. The Cimmerians and Scythians sporadically ruled the region from around 700 to 625 BC. Luristan bronzes, known for their eclectic variety of Assyrian, Babylonian, and Iranian artistic themes, date from this turbulent period. The region was incorporated into the growing Achaemenid Empire around 540 BC and was successively part of the Seleucid, Parthian, and Sassanid dynasties.
Source: Tehran times