The Sanctuary of Apollo at Frangissa, located near ancient Tamassos and lost for approximately 140 years, has been rediscovered through recent excavations. Joint efforts by the Universities of Frankfurt and Kiel/Würzburg have unearthed a significant quantity of important statue fragments at the temple site.
In a secluded valley south of the village of Pera Orinis, nestled in the heart of the island of Cyprus, neighboring the ancient city of Tamassos and lying in the tranquil outskirts of modern Nicosia, also known as Lefkosia, a centuries-long silence has been broken.
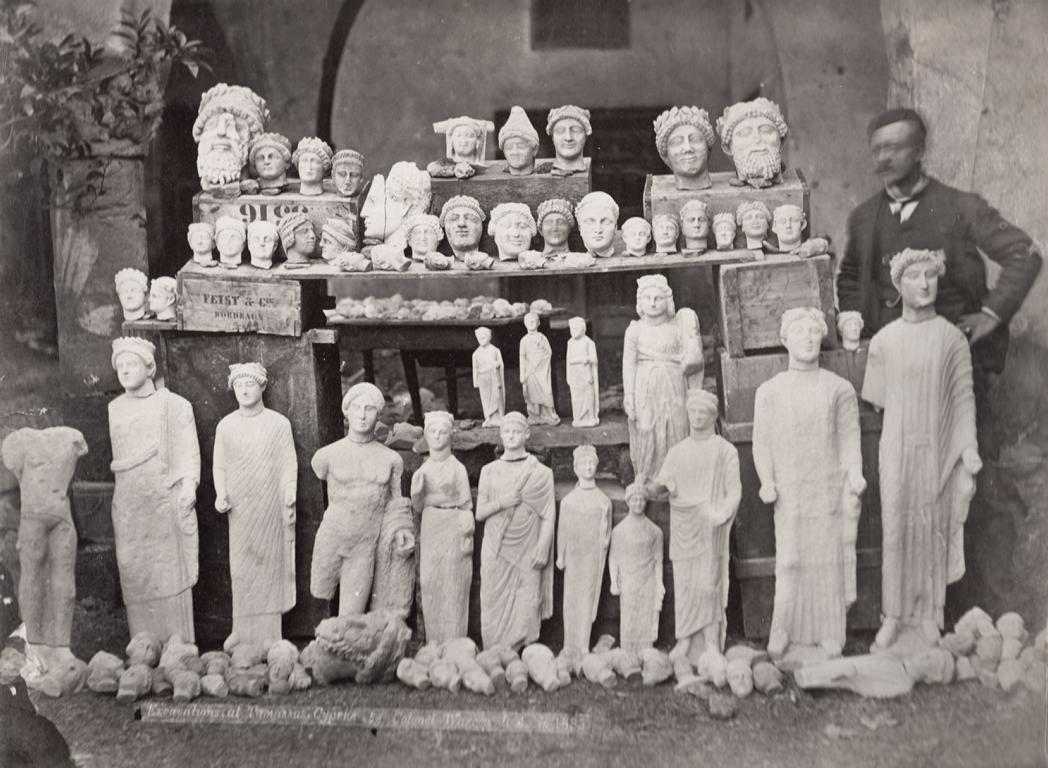
The magnificent Sanctuary of Apollo at Frangissa, its presence hinted at by a brief glimpse from German explorer Max Ohnefalsch-Richter in 1885 but subsequently lost from the memory of later generations, has been rediscovered through the meticulous efforts of modern archaeology. This thrilling event sheds new light on Cyprus’s rich history, offering a unique window into the millennia-old worship and art of this sacred site.
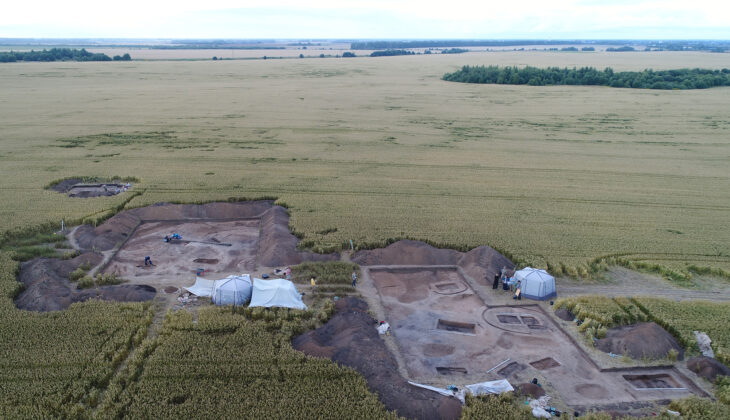
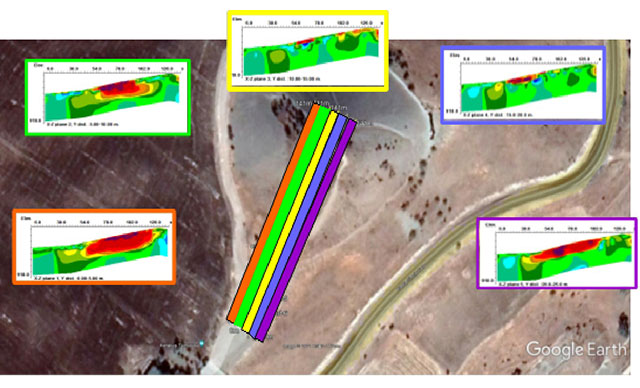
A collaborative field research project led by Dr. Matthias Recke of the University of Frankfurt, in partnership with the Archaeological Institute of the University of Kiel under PD Dr. Philipp Kobusch, successfully located the site. Generous support from the Cyprus Department of Antiquities and the AMRICHA Foundation in Leipzig enabled the team to conduct thorough investigations, including geophysical surveys that confirmed the presence of significant subsurface structures in an area rich with surface finds of ancient pottery, sculpture fragments, and terracottas.
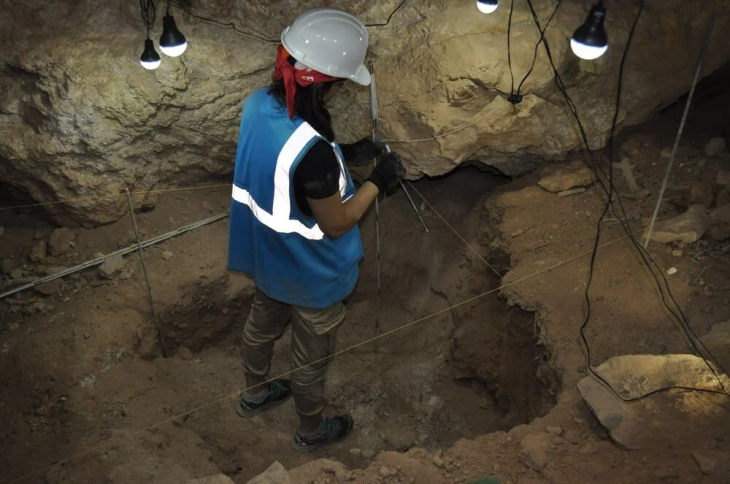
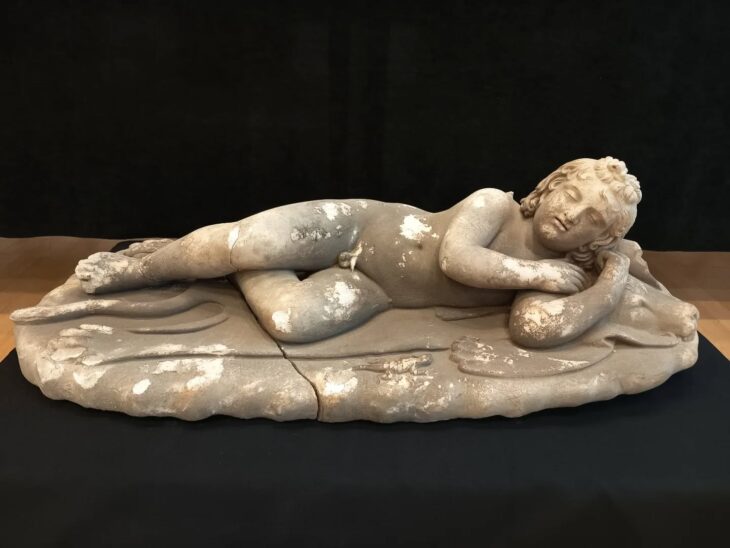
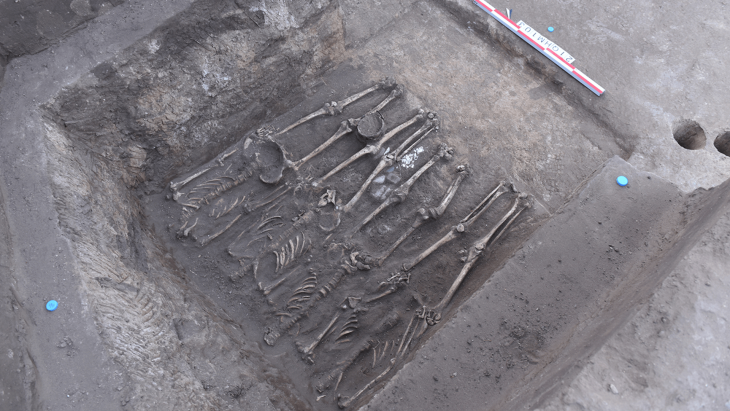
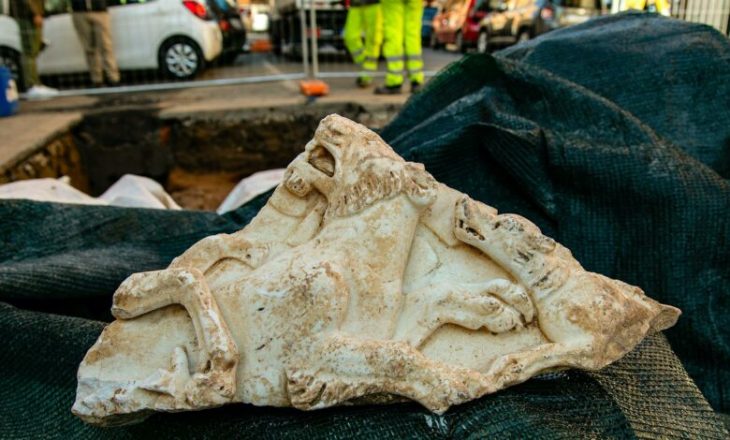
The recent excavation season in 2024 has yielded an astonishing array of statue fragments, including colossal figures and bases that were previously overlooked during the initial excavations. The Department of Antiquities announced that the excavation, building upon the localization of the site in 2021, revealed the walls of a dedication courtyard and over 100 statue bases, some of colossal dimensions. Surprisingly, large quantities of statue fragments, seemingly overlooked during the hurried 1885 excavation, were also recovered from the backfill.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
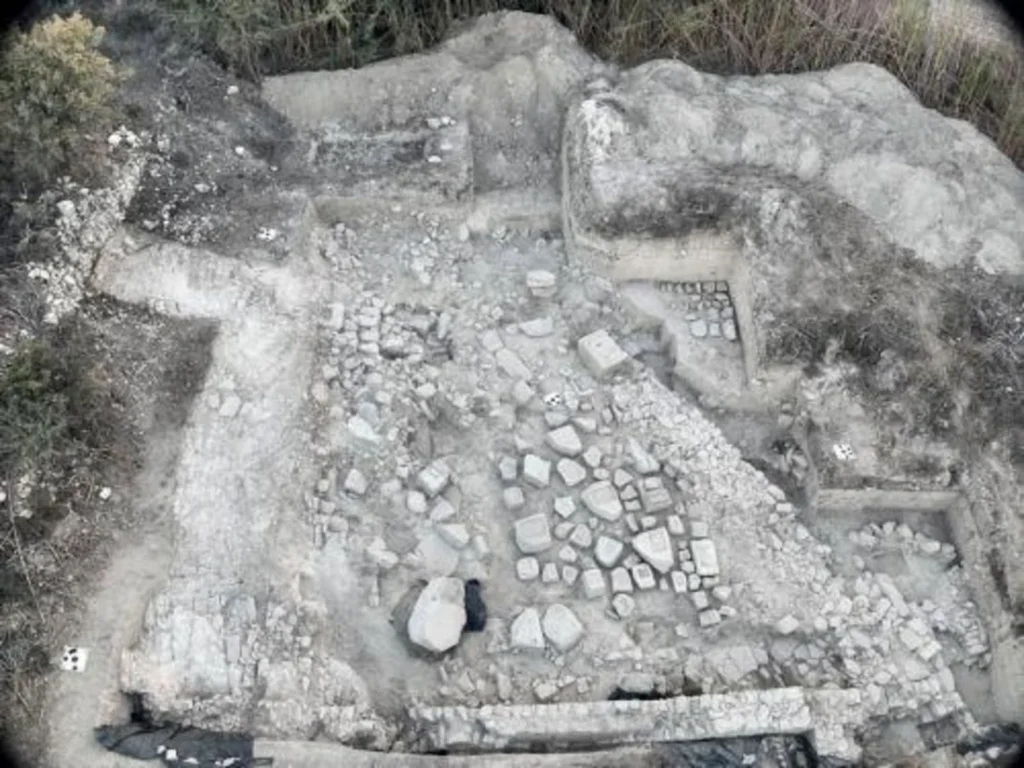

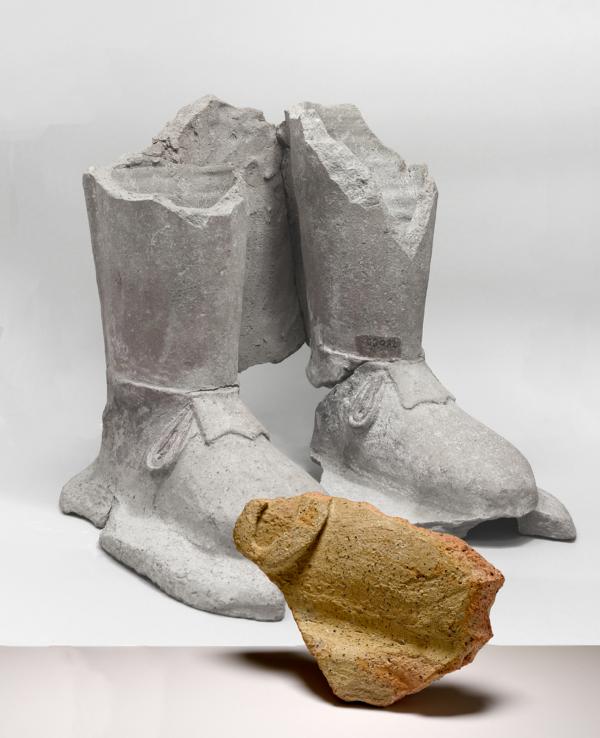
These newly discovered fragments are proving invaluable, allowing for the completion and restoration of numerous statues currently housed in museums worldwide, including the Cyprus Museum in Nicosia and the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto. Furthermore, the excavations have unveiled entirely new types of statues previously unknown from Frangissa. The discovery of clearly larger-than-life feet, for instance, now confirms the existence of colossal male limestone figures from the Archaic period, complementing the previously known terracotta giants like the famed “Colossus of Tamassos.”
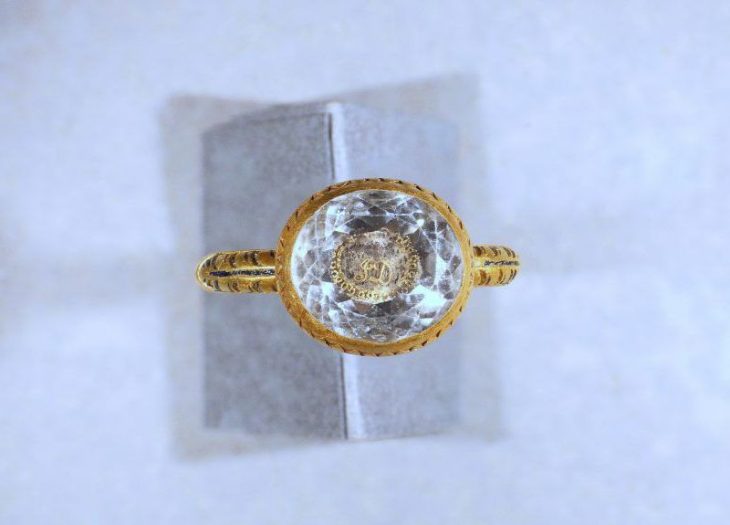
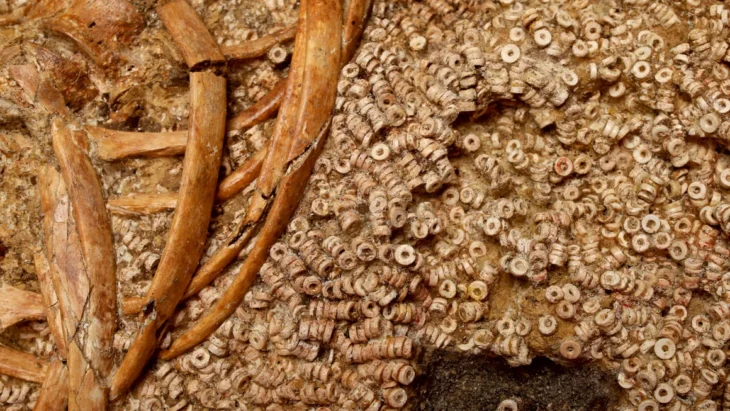
Beyond the statues, the team unearthed evidence of other previously undocumented votive offerings, such as marbled glass beads and Egyptian faience amulets, suggesting a broader range of devotional practices and potential cultural connections.
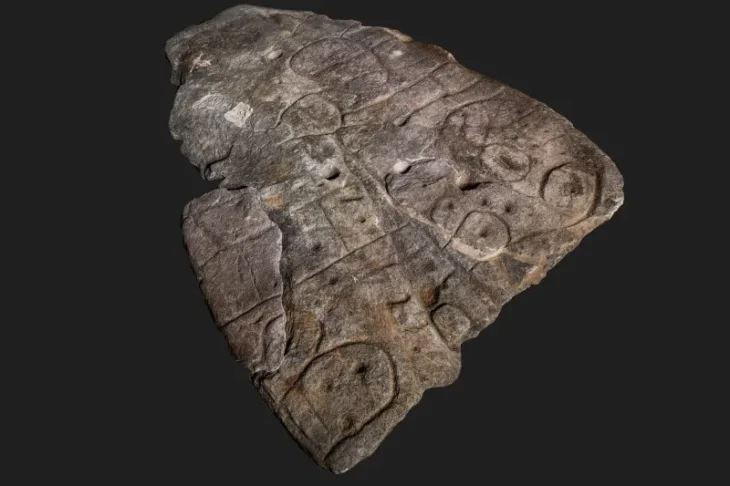
Among the notable discoveries are two inscribed bases, one featuring Cypro-Syllabic characters and the other referencing the Ptolemaic dynasty, indicating the sanctuary’s continued importance beyond the archaic period.
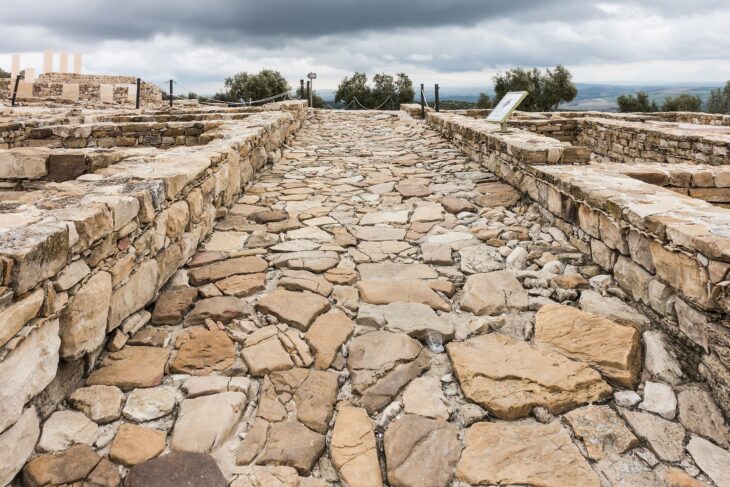
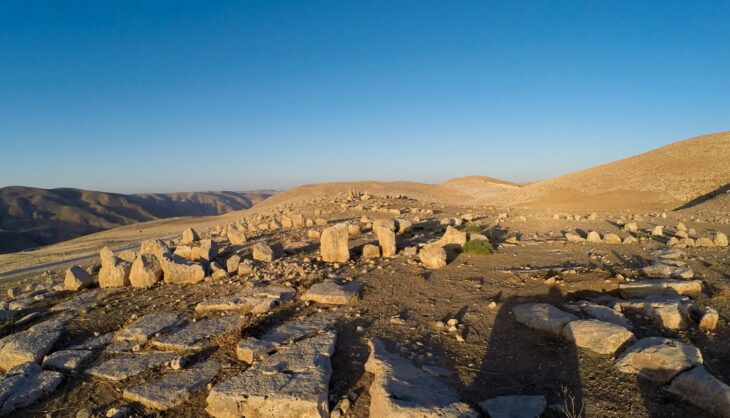
The architectural layout of the sanctuary is also being re-evaluated, with evidence suggesting that it underwent significant expansions, including the construction of a large peristyle courtyard likely used for communal banquets. This new information promises to illuminate the ritual behaviors of ancient worshippers and provide insights into the sanctuary’s role in the broader cultural landscape of Cyprus.

The rediscovery of the 13-meter-long search trench from the 1885 excavation further corroborated the site’s identification and provided insights into the early exploration efforts. The trench revealed remains of ancient double-walled masonry, undoubtedly part of the sanctuary’s original architecture.
The ongoing investigation of the preserved remains promises to reveal crucial details about the ritual behaviors and spatial organization of this significant ancient sanctuary, offering a vivid glimpse into the religious life of ancient Cyprus.
Cover Image Credit: The German explorer Max Ohnefalsch-Richter with the statues unearthed from the excavations. Credit: Universities of Frankfurt