A study led by scientists at the University of Southampton, in collaboration with Queen’s University Canada and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has unveiled new evidence regarding the Late Antique Little Ice Age—a significant climate crisis in the 6th century that may have contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire.
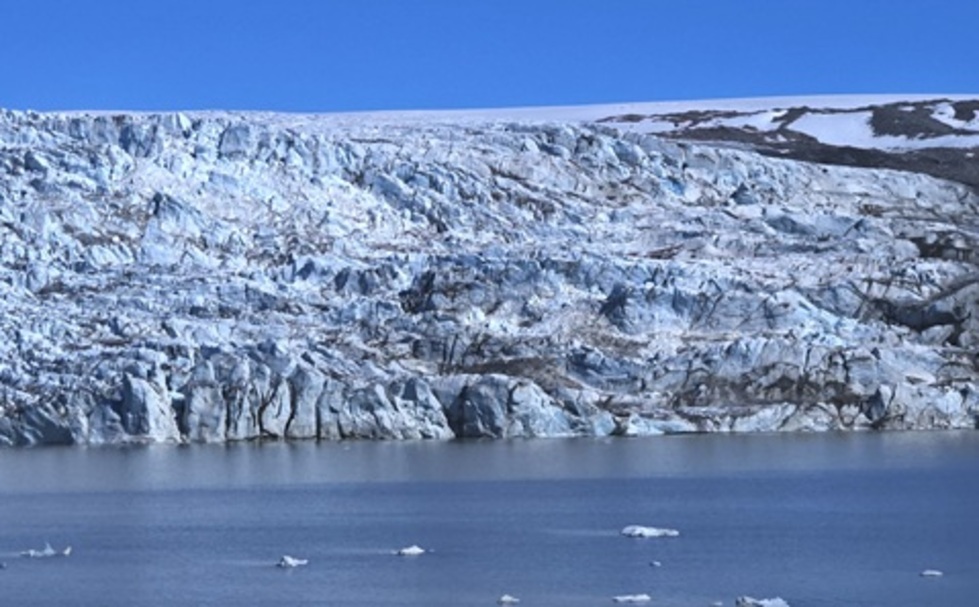
The research team focused on unusual rocks found on a raised beach terrace along Iceland’s west coast, which were transported there by icebergs during a brief ice age that began around 540 AD and lasted for 200 to 300 years. This period of climatic cooling has long been debated by historians concerning its impact on the decline of the Roman Empire. The findings of this study provide compelling evidence that this abrupt climate shift may have exacerbated the empire’s existing vulnerabilities and incited mass migrations that reshaped Europe.
Professor Tom Gernon, an Earth Science expert at the University of Southampton and co-author of the study, stated, “When it comes to the fall of the Roman Empire, this climate shift may have been the straw that broke the camel’s back.” The research, published in the journal Geology, highlights the potential role of climatic factors in historical events.
The study suggests that the Late Antique Little Ice Age was triggered by volcanic ash from three massive eruptions, which blocked sunlight and led to a significant drop in global temperatures. This cooling period coincided with a time of political and economic instability within the Roman Empire, reinforcing the hypothesis that environmental factors played a crucial role in its decline.
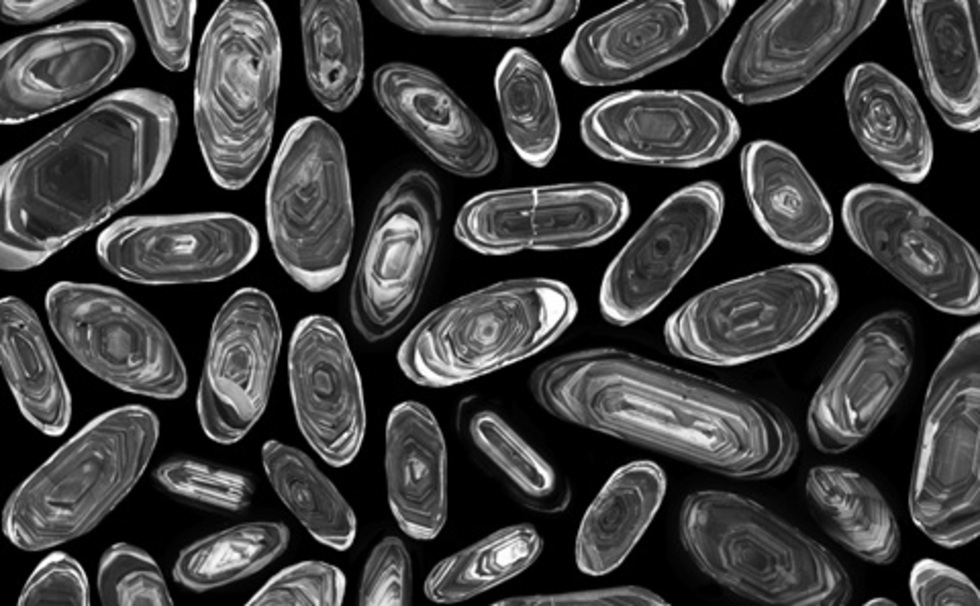
The researchers utilized advanced techniques to analyze the age and composition of zircon crystals embedded within the rocks. These minerals act as time capsules, preserving vital information about their geological history. By crushing the rocks and isolating the zircon crystals, the team was able to trace their origins back to specific regions in Greenland, providing the first direct evidence of icebergs transporting large cobbles to Iceland.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Christopher Spencer, the lead author of the research, explained, “Zircons are essentially time capsules that preserve vital information, including when they crystallized and their compositional characteristics.” The analysis revealed that the rocks originated from various geological regions of Greenland, indicating their glacial origins.
The study also determined that these ice-rafted rocks were likely deposited in Iceland during the 7th century, coinciding with a major climate shift known as the Bond 1 event. This timing aligns with a known episode of ice-rafting, where large chunks of ice break away from glaciers, drift across the ocean, and scatter debris along distant shores.
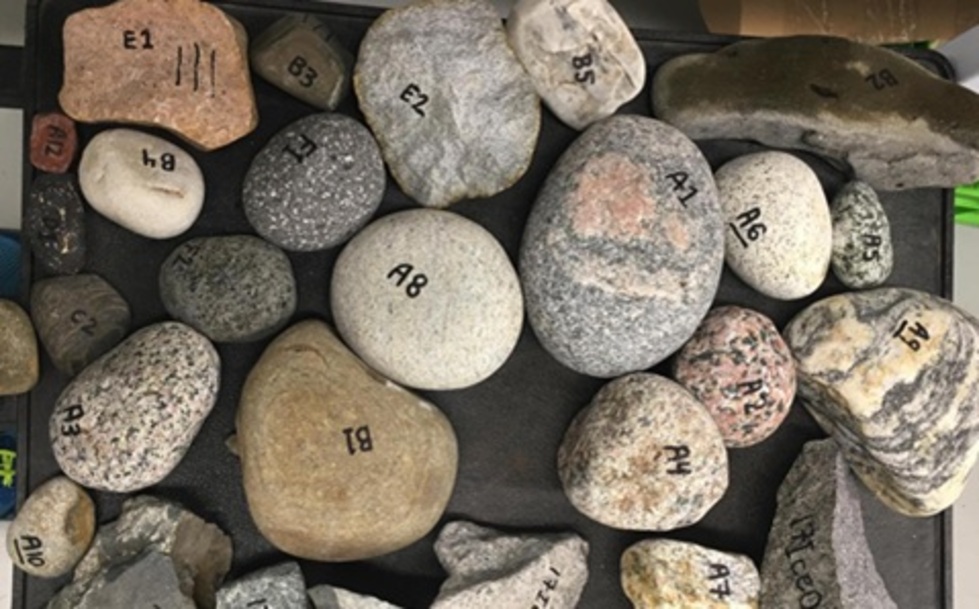
Professor Gernon emphasized the interconnectedness of the climate system, stating, “What we’re seeing is a powerful example of how interconnected the climate system is. When glaciers grow, icebergs calve, ocean currents shift, and landscapes change.” The research underscores the cascading effects of rapid cooling, which may have contributed to the mass migrations that ultimately weakened the Roman Empire.
This study not only sheds light on the historical implications of climate change but also serves as a reminder of the profound impact that environmental factors can have on human societies throughout history. As researchers continue to explore the links between climate and historical events, this research provides a crucial piece of the puzzle in understanding the complex dynamics that shaped our world.
Christopher J. Spencer, Thomas M. Gernon, Ross N. Mitchell; Greenlandic debris in Iceland likely tied to Bond event 1 ice rafting in the Dark Ages. Geology 2025; doi: doi.org/10.1130/G53168.1
Cover Image Credit: Coastal Greenland, where the rocks analysed in the study were pinpointed to. Credit: Professor Ross Mitchell, The Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
















