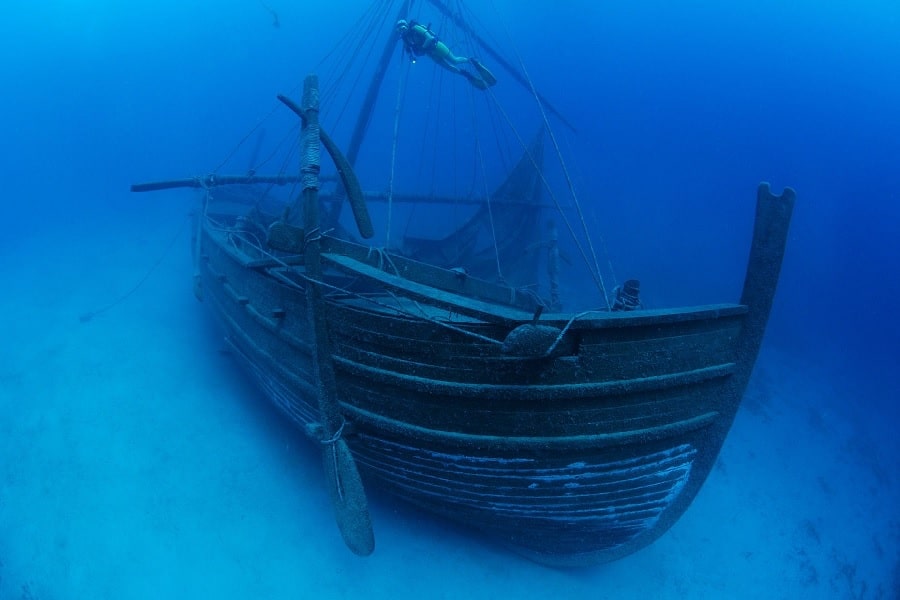
A new study of the 3,o00 years old Uluburun shipwreck revealed a complex ancient trading network during the late bronze age.
In the year 1,320 BCE, a ship sailed from modern-day Haifa carrying copper and tin, the two metals required to make bronze, the era’s high technology. The ship was scuttled in a storm, and when it was found in 1982, it had become the largest Bronze Age collection of unprocessed metals ever discovered and a superbly preserved, international treasure of marine archaeology.
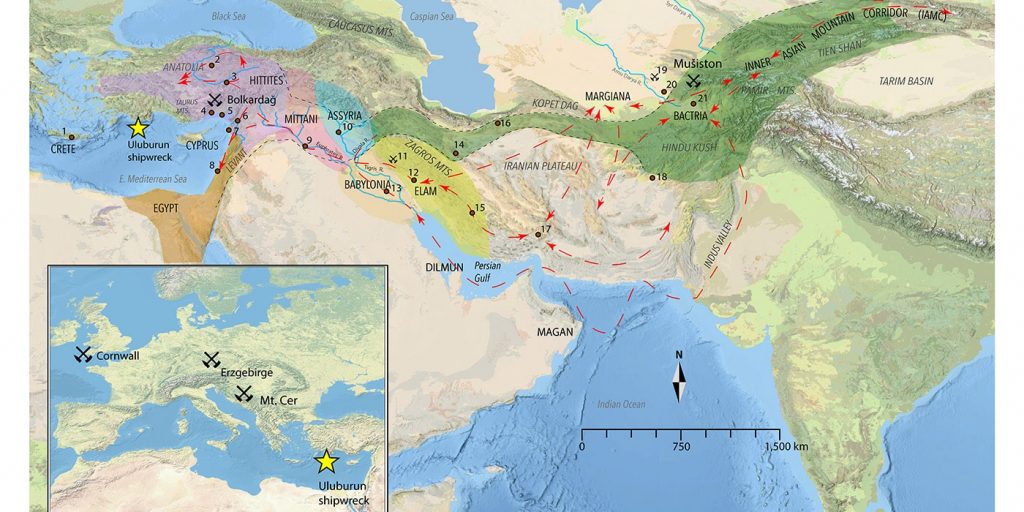
The new research called the “Uluburun shipwreck” revealed that while two-thirds of the tin onboard was mined in the Taurus Mountains within the vast Hittite empire, in modern-day Turkey, one-third came from mines thousands of miles away in Uzbekistan.
This origin, the study authors say, reveals a complex system of trading routes that moved tons and tons of material thousands of miles to the Mediterranean’s multicultural marketplaces.
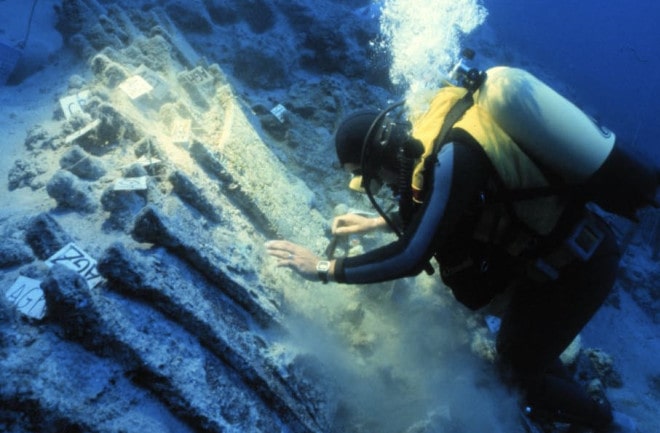

After years of investigation, advances in geochemical analysis have enabled researchers to determine that much of the tin on the ship (roughly one-third) came from an ancient mine in modern Uzbekistan, thousands of miles away from where the ship sank. According to the researchers, this discovery suggests that intricate trade networks stretched across Central Asia and the Mediterranean as early as the Late Bronze Age.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Miners had access to vast international networks and — through overland trade and other forms of connectivity — were able to pass this all-important commodity all the way to the Mediterranean,” says Michael Frachetti, a study author and an archaeologist at Washington University, according to a press release.
The terrain between the Muiston mine in Uzbekistan and Iran and Mesopotamia would have been a mix of rugged ground and mountains, no doubt filled with potential bandits, making it extremely difficult to transport tons of heavy metal.
“It’s quite amazing to learn that a culturally diverse, multiregional and multivector system of trade underpinned Eurasian tin exchange during the Late Bronze Age,” Frachetti said.
Adding to the mystique is the fact that the mining industry appears to have been run by small-scale local communities or free laborers who negotiated this marketplace outside of the control of kings, emperors or other political organizations, Frachetti said.
“To put it into perspective, this would be the trade equivalent of the entire United States sourcing its energy needs from small backyard oil rigs in central Kansas,” he said.
When the Uluburun wreck was discovered in the 1980s, experts were baffled. They simply didn’t know how to track down the source of the metals aboard the ship. However, for the first time in the 1990s, the idea of using tin isotopes to figure out where the tin in ancient artifacts came from emerged. While the required analytical methods remained inconclusive for a long time, advances in recent years have allowed scientists to begin tracing tin artifacts to specific mining sites using their unique chemical makeups.
The Uluburun ship’s tin’s isotopic composition was compared to that of tin in deposits around the world, and the results showed that about one-third of the metal came from the Muiston mine in Uzbekistan.
















