While investigating the origins of agriculture, researchers made an unexpected discovery.
According to an unexpected finding made by an Iowa State University researcher, the earliest people may have arrived in North America more than 30,000 years ago – over 20,000 years earlier than previously assumed.
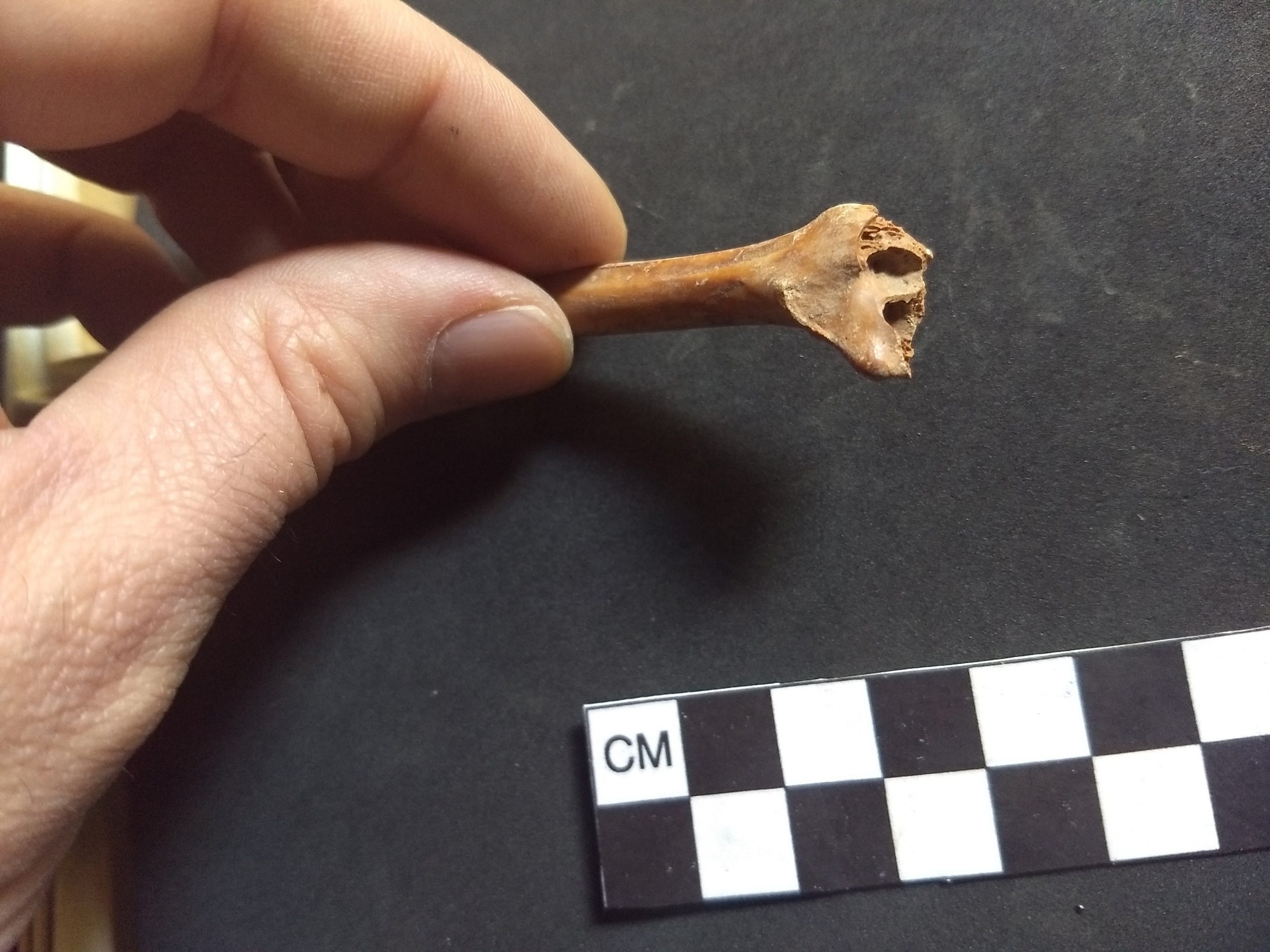
Andrew Somerville, assistant professor of world language and cultural anthropology, said he and his colleagues made this discovery while studying the origins of agriculture in the Tehuacan Valley in Mexico. As part of this work, they wanted to date the earliest human occupation of Coxcatlan Cave in the valley, so they obtained radiocarbon dating of several rabbit and deer bones that were collected from the cave in the 1960s as part of the Tehuacan Archaeological and Botanical Project. The date of the bones took the work of Somerville and his colleagues in a different direction.
The date range of the bone samples at the bottom of the cave ranged from 33,448 to 28,279. The results were published in the academic journal “Latin American Antiquity“. Somerville said that although previous research did not determine the age of the objects at the bottom of the cave, he did not expect such an old age. These findings add to the debate about a long-standing theory that the first humans crossed the Bering Land Bridge into the Americas 13,000 years ago.
“We weren’t trying to weigh in on this debate or even find really old samples. We were just trying to situate our agricultural study with a firmer timeline,” Somerville said. “We were surprised to find these really old dates at the bottom of the cave, and it means that we need to take a closer look at the artifacts recovered from those levels.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Somerville says the discoveries provide researchers with a better understanding of the region’s chronology. Earlier research relied on charcoal and plant samples but says bones were the better material for dating. However, questions still remain. Most importantly, is there a human connection to the lower layer of the cave where the bones were found?
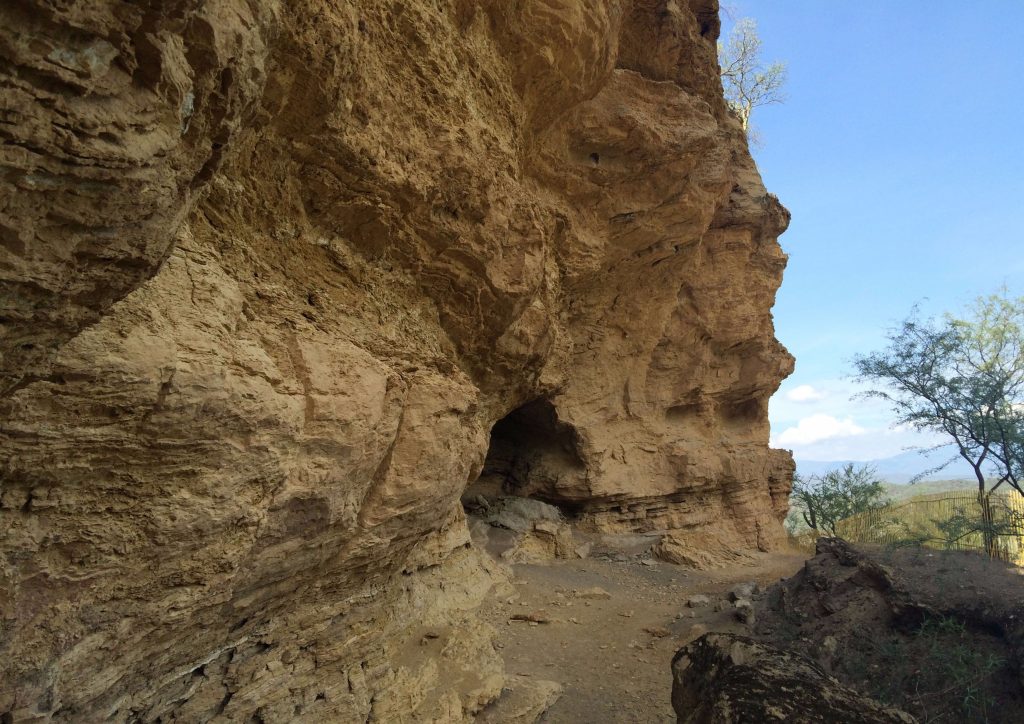

To answer that question, Somerville and Matthew Hill, ISU associate professor of anthropology, plan to take a closer look at the bone samples for evidence of cut marks that indicate the bones were butchered by a stone tool or human, or thermal alternations that suggest the bones were boiled or roasted over fire. He says the possible stone tools from the early levels of the cave may also yield clues.
“Determining whether the stone artifacts were products of human manufacture or if they were just naturally chipped stones would be one way to get to the bottom of this,” Somerville said. “If we can find strong evidence that humans did in fact make and use these tools, that’s another way we can move forward.”
It took a year to find the bones
The Tehuacan Archaeological-Botanical Project’s artifacts were dispersed to various museums and labs in Mexico and the United States in the 1960s, but it was unknown where the animal bones were sent.
After a year of searching, the lab director, Joaquin Arroyo-Cabrales, agreed to give Somerville and Casar a tour to help search for the missing collection. The tour proved to be beneficial. Among the countless boxes of artifacts, they found what they were looking for.
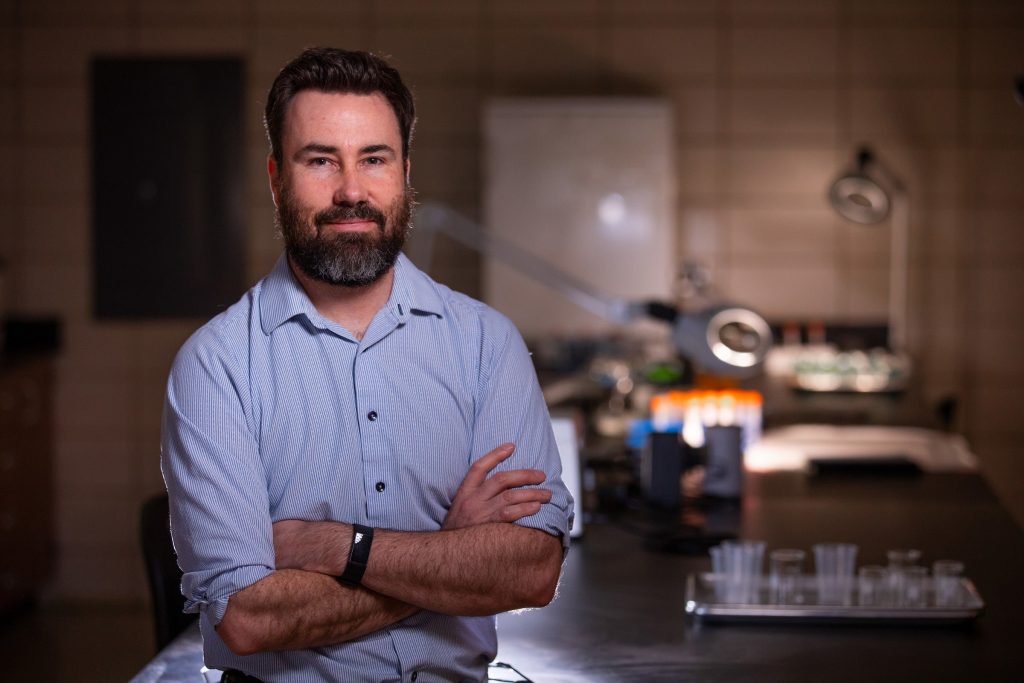

“Having spent months trying to locate the bones, we were excited to find them tucked away on the bottom shelf in a dark corner of the lab,” Somerville said. “At the time, we felt that was a great discovery, we had no idea it would lead to this.”
Once he located the bones, Somerville got permission from the Mexican government to take small samples – about 3/4 inch in length and 1/4 inch in width – from 17 bones (eight rabbits and nine deer) for radiocarbon dating. If closer examination of the bones provides evidence of a human link, Somerville says it will change what we know about the timing and how the first people came to America.
“Pushing the arrival of humans in North America back to over 30,000 years ago would mean that humans were already in North America prior to the period of the Last Glacial Maximum, when the Ice Age was at its absolute worst,” Somerville said. “Large parts of North America would have been inhospitable to human populations. The glaciers would have completely blocked any passage over land coming from Alaska and Canada, which means people probably would have had to come to the Americas by boats down the Pacific coast.”
Isabel Casar, a professor at the National Autonomous University of Mexico, and Joaquín Arroyo-Cabrales, a researcher with the National Institute of Anthropology and History in Mexico, contributed to this research. The work was funded by the National Science Foundation and the Wenner-Gren Foundation.
Source: Iowa State University