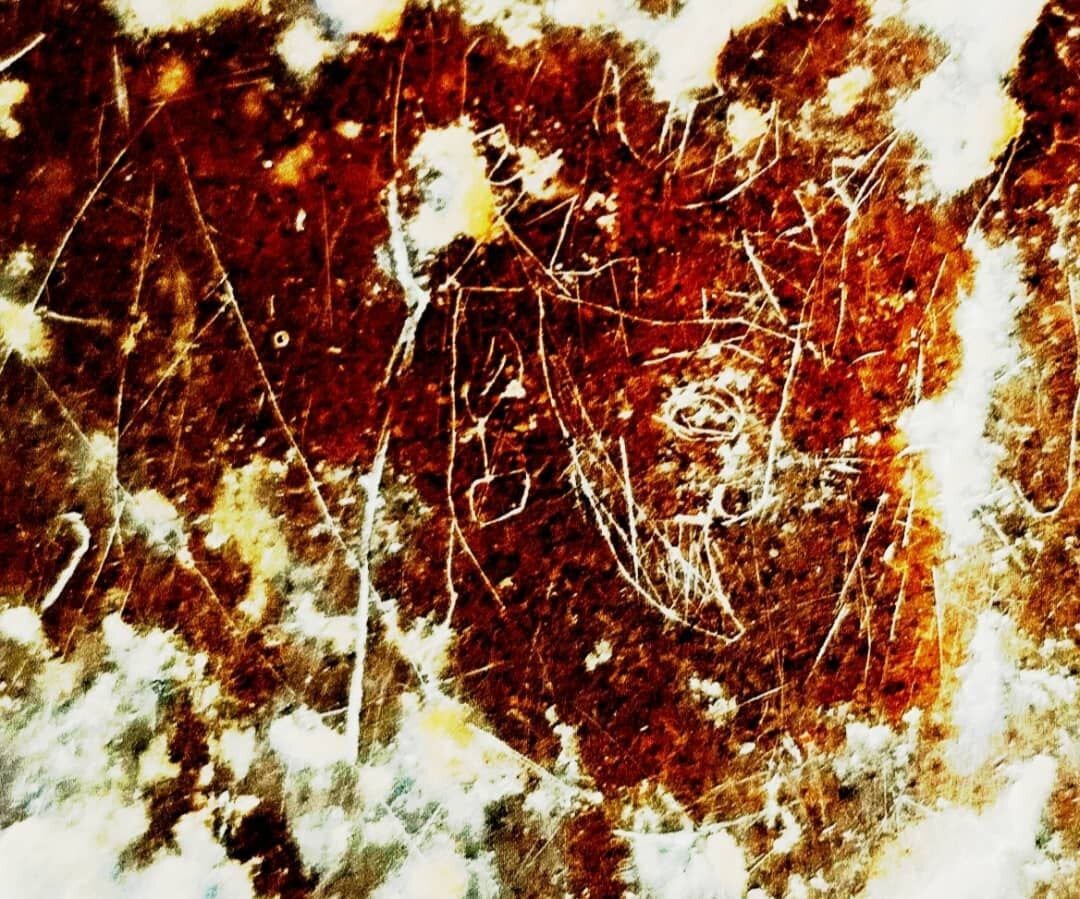
Archaeologists have uncovered a rare needle-carved rock image believed to depict a Sasanian king, etched into the cliffs of the ancient city of Istakhr in southern Iran’s Marvdasht Plain, near the world-famous ruins of Persepolis. The discovery offers valuable insights into the artistic and royal traditions of one of Iran’s most influential ancient dynasties — the Sasanian Empire.
Discovery in the Heart of Sasanian Heritage
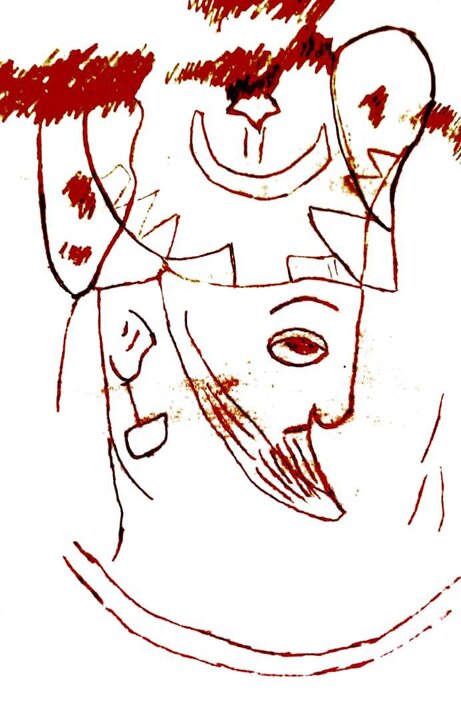
According to archaeologist and historian Abolhassan Atabaki, the newly identified carving portrays a regal figure wearing a distinctive crown, accompanied by celestial symbols such as a moon, a star, and a crenellated diadem. These motifs are hallmarks of Sasanian royal iconography, symbolizing divine legitimacy and cosmic authority.
Atabaki explained that the stylistic features of the carving — particularly the design of the crown and the fine needle engraving — resemble those found on Sasanian coins, metalwork, and rock reliefs from the later period of the dynasty, which ruled from 224 to 651 CE. This resemblance, he said, “suggests a close link between this newly discovered artwork and established Sasanian artistic traditions.”
Echoes of Ancient Royal Portraiture
Historian Najmeh Ebrahimi emphasized the importance of this find within the broader context of Sasanian royal portraiture. She cited the 10th-century historian Al-Masudi, who mentioned an illuminated manuscript discovered in Istakhr depicting Sasanian monarchs. Ebrahimi noted that the new carving “reflects the same artistic spirit — the glorification of kingship through refined, symbolic portraiture.”
Ebrahimi also pointed out that nearly 90 percent of known Sasanian royal reliefs have been discovered in the Marvdasht Plain, often carved into natural cliffs and mountain faces. These reliefs, she added, were not merely decorative but conveyed powerful political and religious messages, reinforcing the Sasanian belief in the divine nature of kingship.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Istakhr: The Birthplace of the Sasanian Dynasty
The ancient city of Istakhr, once a grand royal residence of the Sasanian kings, holds a significant place in Persian history. Situated near Persepolis, the ceremonial capital of the earlier Achaemenid Empire, Istakhr served as a bridge between two of Iran’s greatest civilizations.
The city rose to prominence around 224 CE, when Ardashir I, a Persian nobleman from the region, rebelled against Artabanus IV, the last king of the Parthian Empire. After defeating Artabanus, Ardashir established the Sasanian Empire, reviving Persian power and cultural identity. Choosing Istakhr as one of his main residences, Ardashir symbolically linked his new dynasty to the glory of the Achaemenids, whose palaces and tombs still dominated the nearby landscape.
The builders of Istakhr often reused architectural elements from Persepolis, blending ancient grandeur with contemporary Sasanian design. The nearby royal necropolis of Naqsh-e Rostam, featuring rock tombs of Achaemenid kings and later Sasanian reliefs, further underscores the area’s deep royal symbolism.

A Center of Art, Religion, and Power
During the Sasanian era, Istakhr was not only a political hub but also a center of Zoroastrian worship and scholarship. Temples, palaces, and fortifications adorned the city, reflecting the dynasty’s architectural sophistication and religious devotion. The Sasanian kings considered themselves guardians of Ahura Mazda’s divine order, and their artistic commissions often portrayed them receiving investiture from the supreme god.
According to a 10th-century account by geographer Istakhri, houses in the city were built from clay, stone, or plaster, depending on the wealth of their owners — an indication of the city’s diverse social fabric long after the fall of the Sasanian Empire.
A New Chapter in Iranian Archaeology
Experts believe the newly discovered needle-carved relief may date to the later Sasanian period, possibly between the reigns of Khosrow II (r. 590–628 CE) and his successors. Its craftsmanship and symbolism mirror the high artistic standards that characterized the empire’s final centuries before the Arab conquest of Persia.
Archaeologists plan to conduct further analysis, including 3D scanning and stylistic comparison, to determine the carving’s precise date and identify the ruler it represents. Preliminary studies suggest it could belong to a regional or lesser-known monarch who sought to align himself with the Sasanian imperial image.
Preserving the Legacy of the Sasanians
The discovery at Istakhr highlights the continuing richness of Iran’s archaeological heritage. Despite centuries of erosion and human activity, the Marvdasht region remains a treasure trove of ancient art and architecture. Scholars hope that renewed research and conservation will bring greater recognition to the Sasanian Empire, whose influence on Persian culture, religion, and art continues to shape Iran’s identity today.
Cover Image Credit: Tehran Times