Researchers have discovered a find that could be a first for Norwegian archeology.
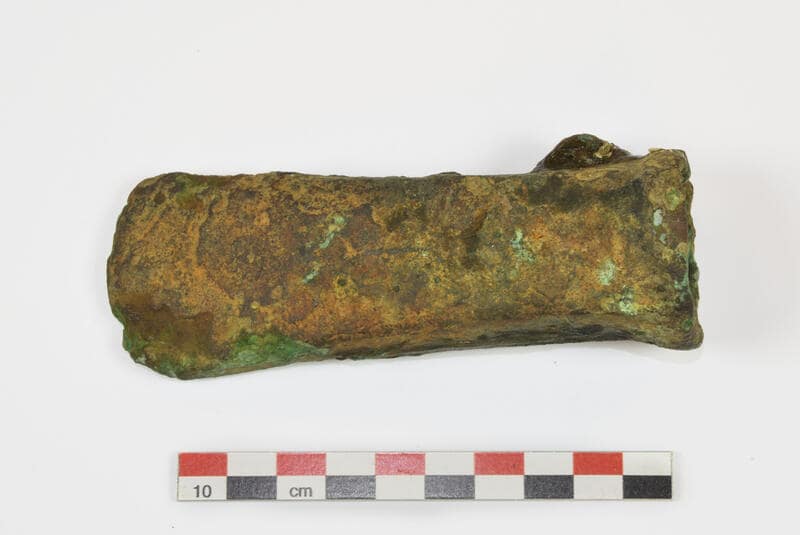
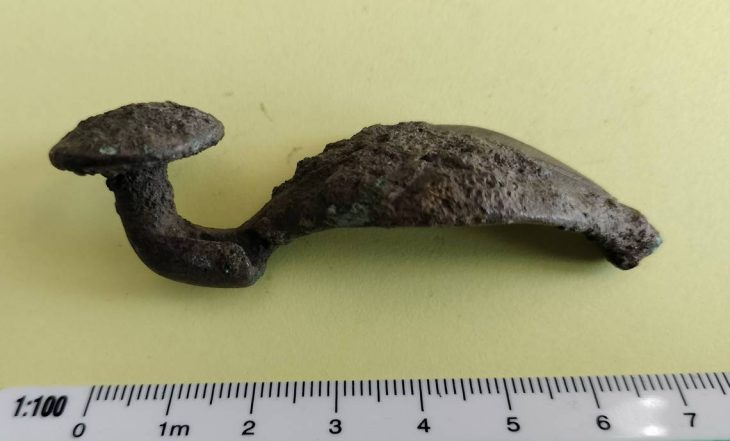
A hollow ax, which researchers believe dates from the Bronze Age, was discovered at a depth of 12 meters near Arendal.
The hollow ax, also known as the Celtic ax, was the main ax type of the Nordic Bronze Age (1800-500 BC). The hollow ax is attached to an angled wooden shaft, which is inserted into the opening at the end of the ax. This structure provides a functional ax and uses minimal precious metals.
“This is very exciting. We have no known shipwrecks from the Bronze Age, and if this find is dated to that time, it will be the first in the country,” archaeologist Frode Kvalø told Agderposten.
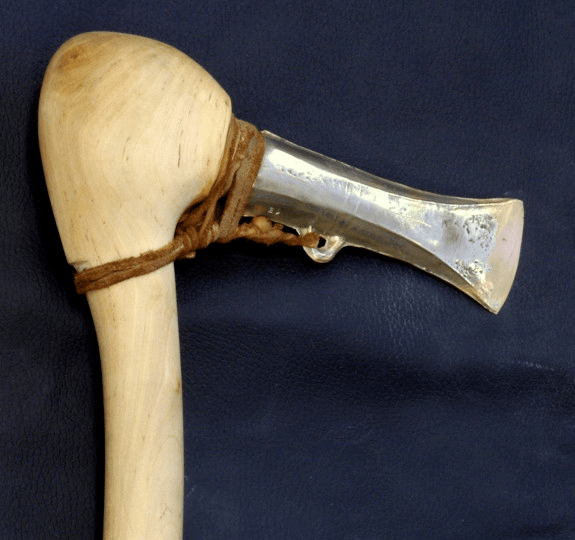
This heavy bronze ax weighing 327 grams is described as “well preserved” and maybe the first prehistoric metal object found in Norwegian waters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The ax was discovered during connection with cultural routine registration by the Norwegian Maritime Museum.
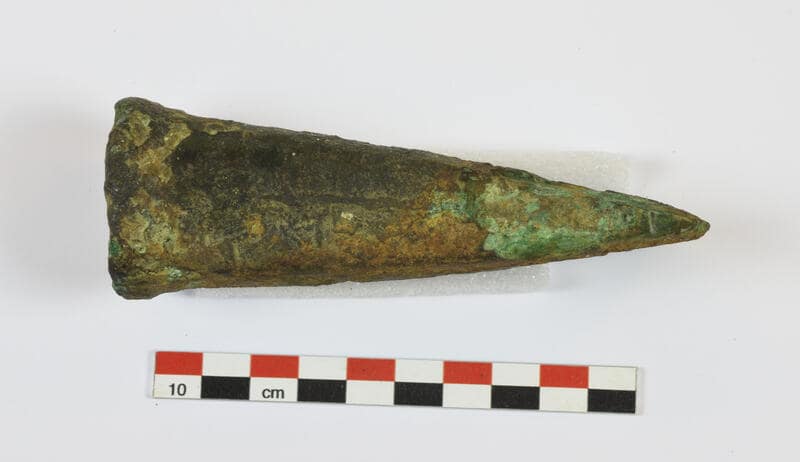

Now, researchers are working to determine when and how the ax landed on the seabed. A theory called the ballast hypothesis is that the ax is part of a ship that is only a few hundred years old, which will still make it an important discovery in the sailing ship age. However, the second and more exciting hypothesis is that the ax sank more than 3,000 years ago, and there was a ship passing through from southern Scandinavia, or a local ship sailing along the coast. vessel. If correct, this will make it the first known shipwreck site of the Norwegian Bronze Age.
“This could be front-page news, or it could be uninteresting, depending on what further research shows”, Sven Ahrens of the Norwegian Maritime Museum said.
















