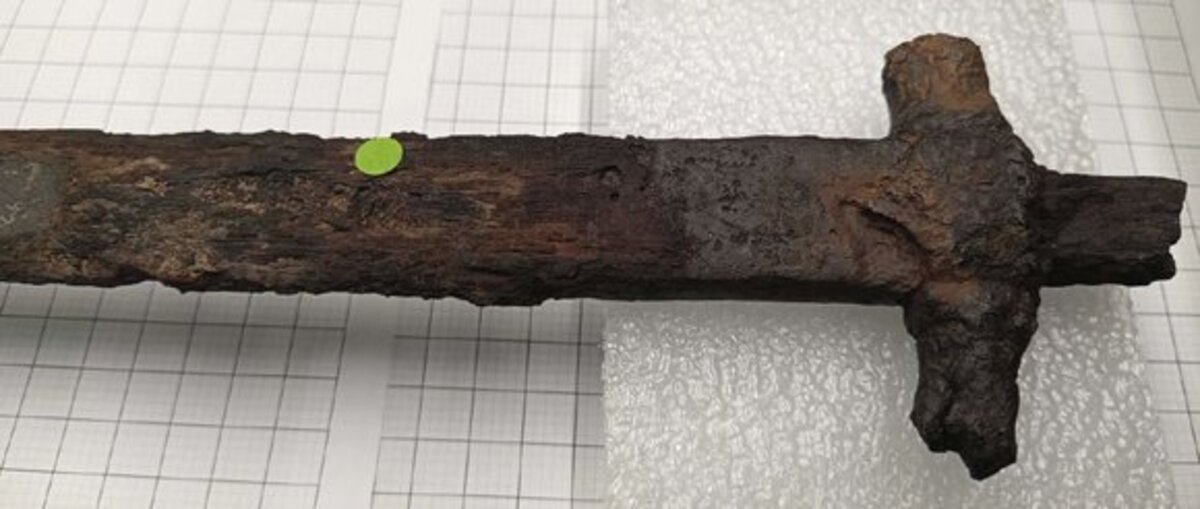
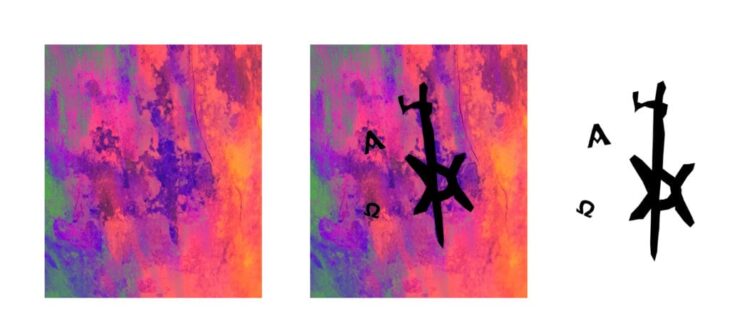In a remarkable fusion of history, archaeology, and cutting-edge technology, researchers from the Friedrich Schiller University Jena and INNOVENT e.V. have uncovered a hidden inscription inside a heavily corroded 16th-century sword. What lay concealed for centuries beneath layers of rust was finally revealed through modern computed tomography (CT) – the name of a Solingen swordsmith: Clemes Stam.
The Friedrich Schiller University Jena, located in the heart of Thuringia, Germany, has been a center of academic life since its founding in 1558. Within this historic context, the recent discovery of a hidden inscription on a 16th-century sword adds a remarkable new chapter to the university’s legacy.
This discovery not only breathes new life into Jena’s early university history but also demonstrates how non-destructive 3D analysis can illuminate forgotten stories etched in metal and time.
A Sword from the Collegium Jenense
The sword, or degen, was recovered from the ruins of the Collegium Jenense – the historic heart of Jena University. Before its destruction by bombing at the end of World War II, the Collegium Church had served as both the spiritual and academic center of the university since the 16th century. Between 1594 and 1814, it was also used as a burial site for professors, students, and their families.
Among the artifacts discovered in these crypts were four swords, each buried as part of funerary offerings. One of these swords, severely corroded and encrusted with centuries of decay, became the focus of an interdisciplinary research project: “Early Jena University History through the Collegium Quarter with a Special Focus on the Rectors’ Graves.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
From Rust to Revelation
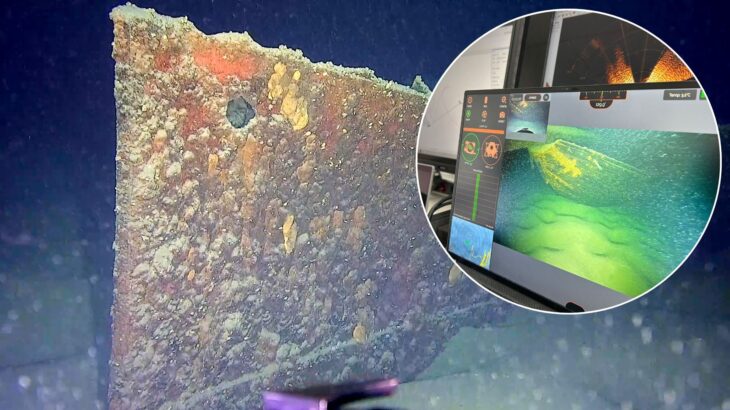
Restorer Ivonne Przemuß suspected that something might be hidden beneath the thick layer of corrosion. Instead of risking damage through conventional cleaning, the team turned to computed tomography — a technique usually reserved for medicine, materials science, and industrial inspection.
At INNOVENT’s technology center in Jena, the sword was examined using the EasyTom 150-160 X-Ray Micro & Nano-CT, developed by the French company RX Solutions. This powerful imaging system allows complete volumetric scans at an astonishing resolution of less than one micrometer. The sword fit entirely within the CT chamber, enabling a full 3D reconstruction without any physical intervention.
Using advanced analytical algorithms, researchers visualized the internal structure of the blade in false colors — identifying distinct materials, remnants of the scabbard, corrosion layers, and even tiny deformations caused by age or impact. And then, among the fine gradations of density, something extraordinary appeared: letters.
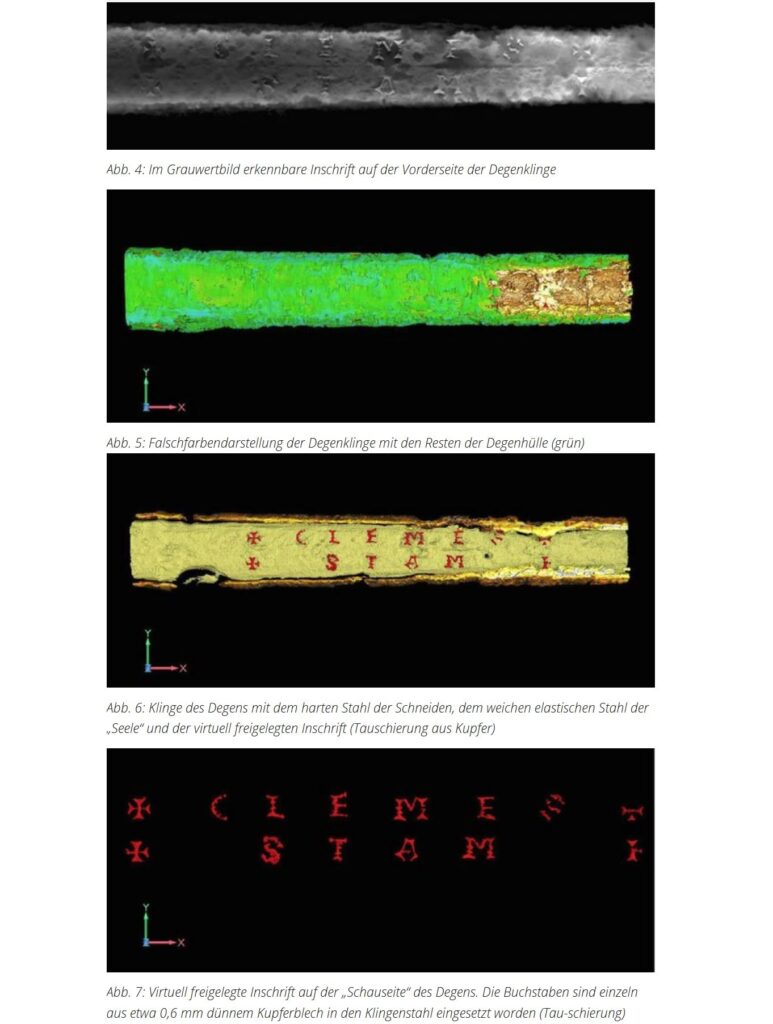
The Hidden Name: Clemes Stam of Solingen
The CT images revealed an engraved inscription reading “Clemes Stam”, the signature of a swordsmith documented in Solingen, Germany’s historic center of blade-making. Clemes Stam’s workshop operated at the end of the 16th century, a time when Solingen’s craftsmen produced weapons for the European nobility — even for the Spanish royal court.
Comparable swords dating from around 1580 to 1620 are preserved today in the German Blade Museum (Deutsches Klingenmuseum) in Solingen. The Jena sword, with its intricate inlay and masterful craftsmanship, would have been a symbol of high social status. Researchers suggest it may have belonged to a rector, professor, or a student of noble lineage.
Technology Meets Cultural Heritage
The project highlights how non-destructive CT analysis can revolutionize archaeological research. Unlike traditional excavation or cleaning methods, computed tomography allows scientists to look “inside” artifacts — to see what time has hidden — without touching or harming them.
As Dr. Enrico Paust, the project’s archaeologist, explains, “CT doesn’t just capture surface details; it reveals the object’s inner story. In this case, it literally uncovered a name that connects Jena to the European tradition of sword-making.”
The technique’s precision also provided material insights: CT imaging showed that different types of steel had been forge-welded together — evidence of sophisticated craftsmanship typical of Solingen masters. Even subtle blade deformations, possibly from combat or ceremonial use, became visible in the digital scans.
A Window into the Past — and the Future
The discovery of the hidden inscription within the Collegium Jenense sword offers more than a glimpse into Renaissance metallurgy; it symbolizes a bridge between past and present. Modern imaging tools such as computed tomography are giving archaeologists the power to revisit long-buried artifacts with fresh eyes — uncovering data invisible to the human hand or traditional restoration methods.
Moreover, the success of this project underlines the growing potential of CT in cultural heritage preservation, from artifact conservation to provenance studies. What once served to examine industrial components is now a window into Europe’s academic and artisanal history.
As the glowing 3D reconstruction of Clemes Stam’s name appeared on screen, centuries of silence were broken. The hidden inscription —once entombed beneath rust — now speaks again, reminding us how innovation can restore voices from the past.
Cover Image Credit: INNOVENT e.V.