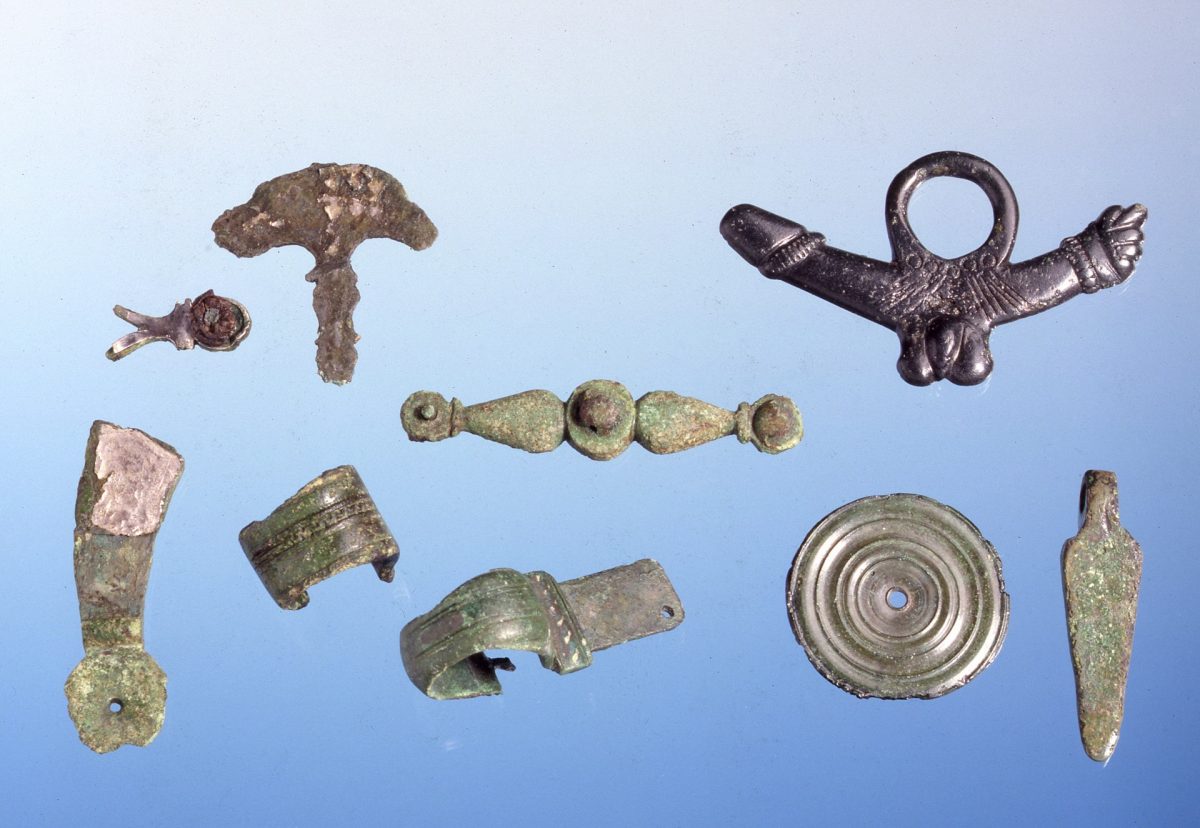
Researchers in Germany have identified the metallurgic signature of the Roman 19th Legion in artifacts recovered from the Battle of Teutoburg Forest in Kalkriese, Germany, using a new chemical analysis method.
The Roman defeat by Germanic tribes at the Battle of Teutoburg Forest in AD9 was such a disaster that it sent shockwaves throughout the empire. Three legions, totaling up to 20,000 men, were lost.
Now scientists used chemical analysis methods to track down the destroyed legions in Kalkriese and were able to identify the 19th Legion in Kalkriese.
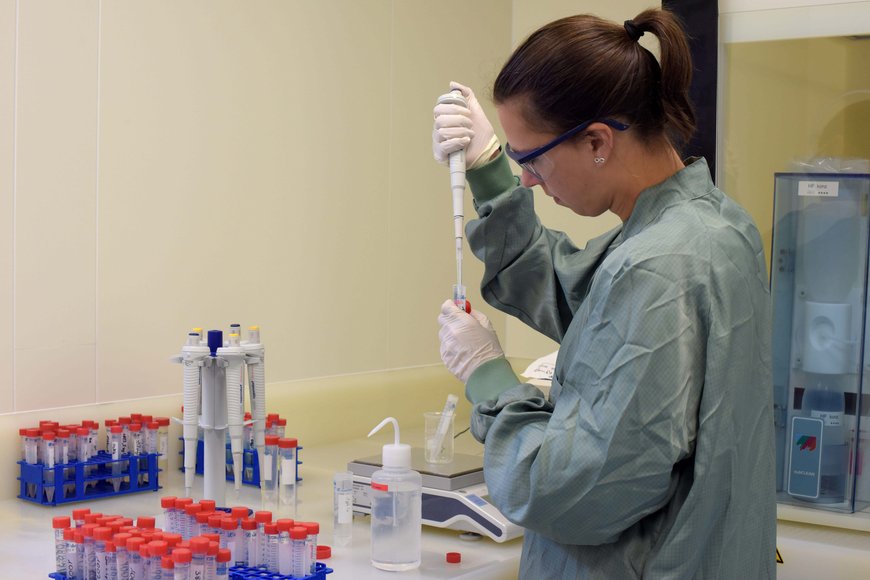

The characteristic composition of trace elements in an artifact can be identified by mass spectrometer analysis of non-ferrous metals like bronze and brass. Because each Roman legion had its own blacksmiths who worked constantly on the campaign to repair and replace weapons and equipment, even legions that fought together had a distinct chemical signature in their metals.
When dating and identifying complex battlefield remains like those at Kalkriese, the fact that this method can be used to conclusively link an object to a specific legion is a major archaeological breakthrough.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery of coins and slingshot ammunition in a field in northeastern Germany in 1987 by Tony Clunn, a British army officer and amateur archaeologist, fueled speculation that the battle site had been discovered. However, for decades it was only a plausible theory.
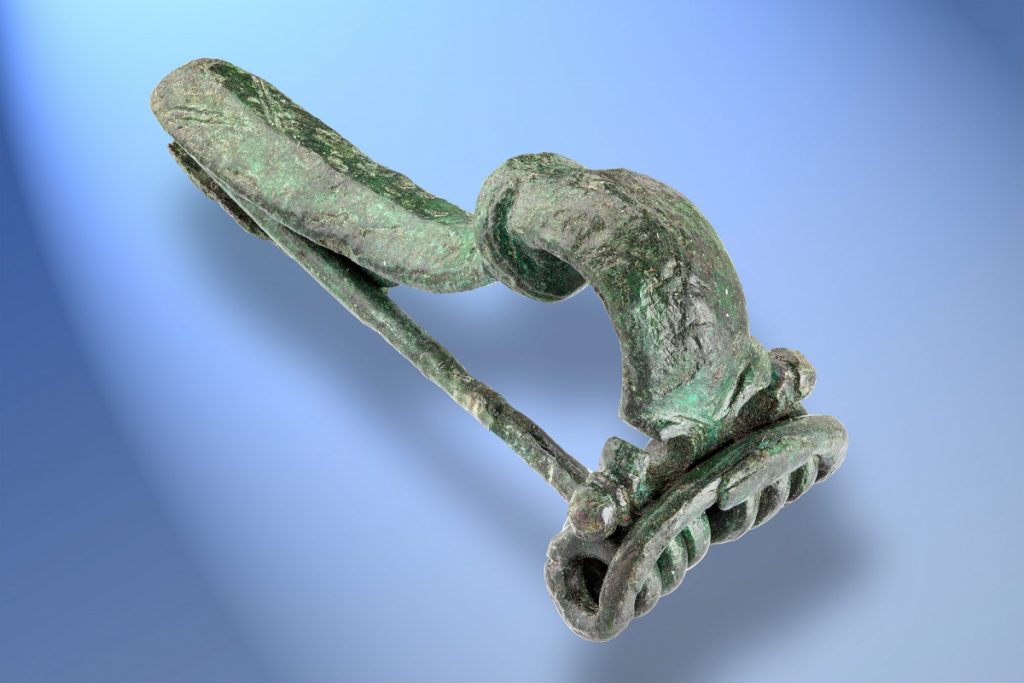

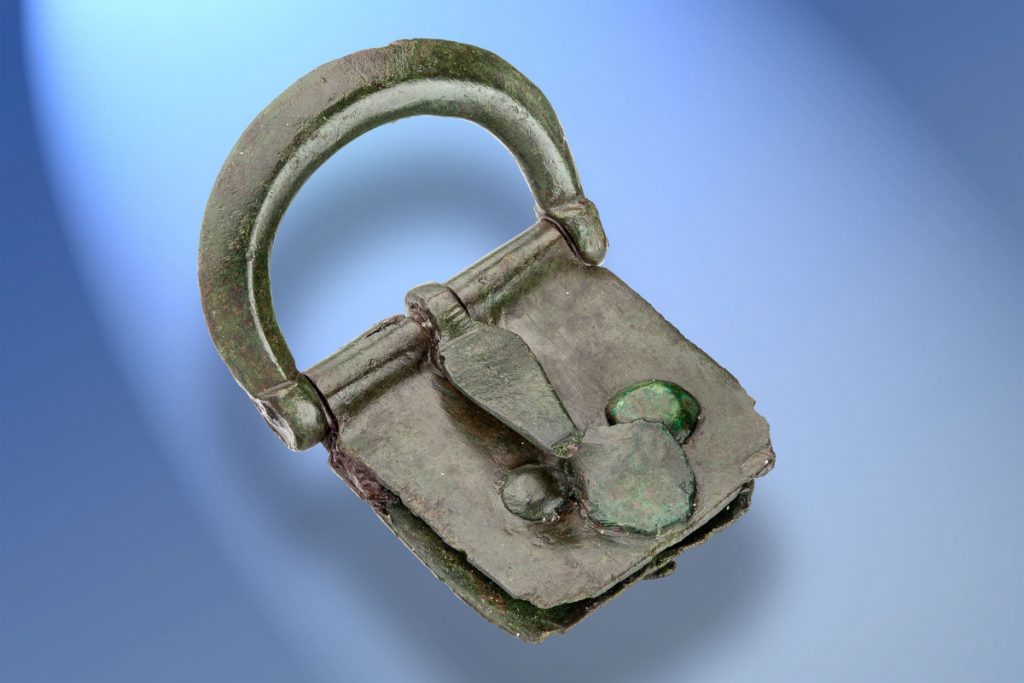
Since then, Kalkriese has unearthed more than 7,000 artifacts, ranging from complete horse bridle fittings to everyday items to the oldest set of Roman plate armor ever discovered in Germany. Undoubtedly, a significant Roman battle from the first century took place there, but it took decades for the Teutoburg battlefield to be identified, and there is still some scholarly disagreement on the matter. For instance, it might have been a battle that happened during Germanicus’ campaign six years later. The archaeological finds cannot be dated within a six-year range by any scientific dating method available to us.
Let’s introduce the metallurgic signature. 550 samples were taken for the project from non-ferrous metal artifacts found at Kalkriese.
The metals used for repairs in the camp forges contain trace elements in such small amounts that the Roman forges did not notice them, and they were not intentionally manipulated. These elements entered the metals through the original ores, various additives used during processing, and tool adhesions. On-site processing has caused the legions to develop a distinct pattern in the composition of trace elements over time.

“In this way, we can allocate a legion-specific metallurgical fingerprint to the legions, for which we know the camp locations at which they were stationed,” German Mining Museum Bochum researcher Annika Diekmann continues. Based on this, all Roman non-ferrous metals from Kalkriese were sampled and compared with non-ferrous metals from numerous Roman locations where it is known from written records which legions were stationed here.
After the analysis is complete, it is evident that the 19th Legion in particular, which perished with Varus and was stationed in Dangstetten in southern Germany years earlier, stands out from the other legions, which were only deployed later in Germany in the Roman vengeance campaigns. This is based on the composition of the trace elements.
“When comparing the finds from Kalkriese with the finds from the other sites, we find that the finds from Dangstetten and Kalkriese show significant similarities. The finds that come from legion sites whose legions did not perish in the Varus Battle, on the other hand, differ significantly from the finds from Kalkriese and thus show significant differences to the finds from Kalkriese.