Archaeologists investigating a megalithic monument in the Burabay district of the Akmola region of Kazakhstan have revealed that the monument may have been closely linked to gold mining activities in the region in the 2nd millennium BC and may possibly have been a place of worship for miners.
The results of the research were published by Dr. Sergey Yarygin and Dr. Sergazy Sakenov, researchers of the Margulan Archaeological Institute, and Zerrin Aydın Tavukçu, Associate Professor at Ataturk University in Türkiye.
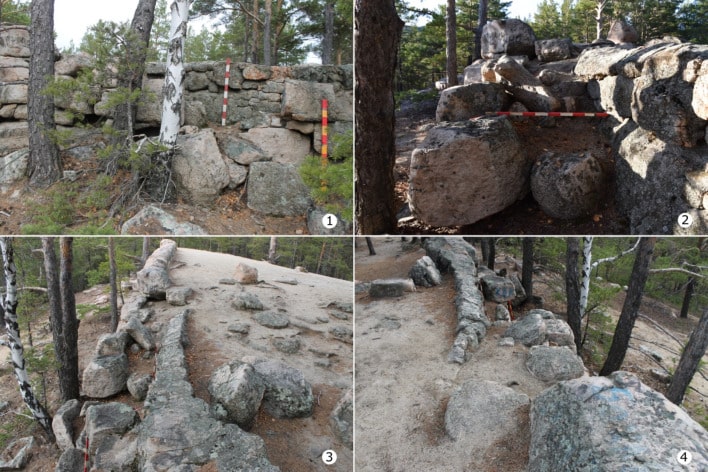
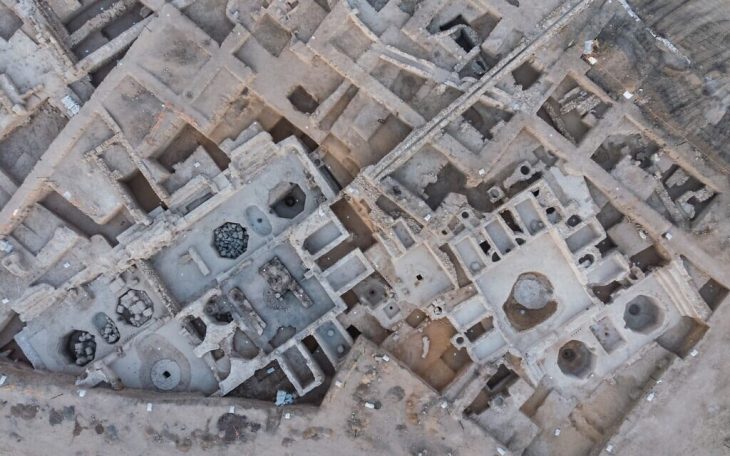
The monument received the name “Taskamal” (from the Kazakh language “Stone fortress”) from residents and tourists due to its monumentality and characteristic masonry of granite blocks.
The research focuses on recording the monument’s architecture and understanding its cultural and chronological context, but it also provides important insights into the understanding of gold mining activities in the Late Bronze Age.
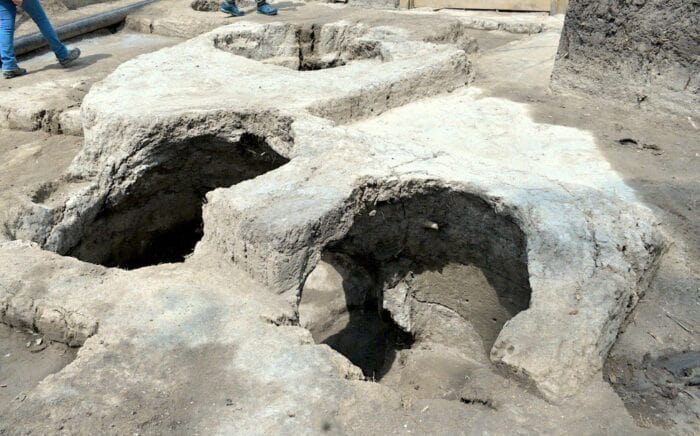
The Taskamal complex is home to some of the most remarkable architectural features, including a massive megalithic wall made of enormous granite blocks, an elevated platform in the center, two thoughtfully constructed access ramps, an external platform, several lithic stelae whose significance is yet to be unknown, and petroglyphs and reliefs that may hold important secrets about its purpose and cultural significance.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
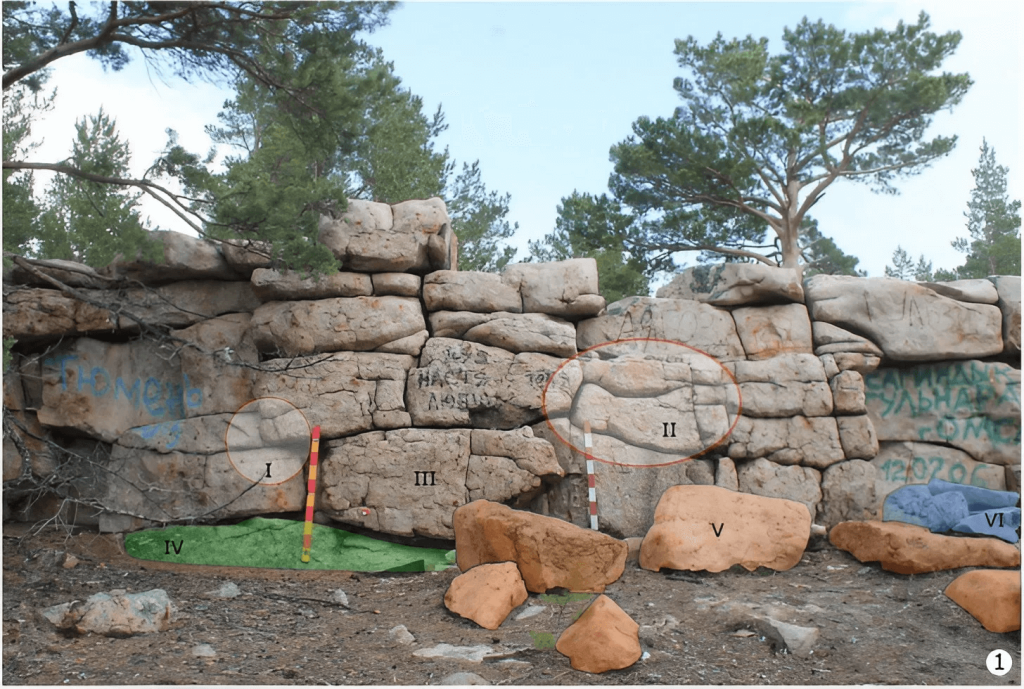

Based on comparisons of the complex’s individual components, building methods, and archaeological features—most notably, the image of a reclining bull—the monument’s preliminary dating to the second millennium BCE places Taskamal in the context of Central Asia’s Late Bronze Age, a time of significant social, technological, and economic transformation.
This proposed chronology assumes even more significance in light of the rich archaeological landscape that surrounds the Burabay region and environs. These areas include several cemeteries connected to the Fedorovo, Alakul, and Sargara-Alexeyev archaeological cultures, which flourished between 1800 and 900 BCE, as well as approximately 46 Late Bronze Age sites and 90 ancient gold mines that have been documented.
Archaeologists believe that the Megalithic object was constructed during the time of gold mining activities in Burabay and was likely associated with gold extraction.
Like other communities in Northern Kazakhstan, the populations that lived in the Burabay during the Late Bronze Age took part in the extraction, processing, and international trade of polymetals. The high number of gold mines around Burabay provided evidence of exploitation in ancient times, indicating that the local communities were primarily focused on gold mining.

In addition to the numerous gold deposits in the area and the evidence of ancient mining nearby, the monumentality of the Taskamal complex suggests that it served a purpose of great importance to the prehistoric communities who built it. These factors support the hypothesis that the Taskamal complex may have been connected to gold mining activities in the Mid-Bronze Age.
If confirmed, this hypothesis will shed light on the complex relationships between economic, ritual, and social practices in Bronze Age societies in Central Asia.
However, the researchers emphasize the need to obtain precise dates to improve the site’s chronology, to conduct geochemical analyses that can definitively confirm the complex’s link to gold mining, and to conduct broader regional studies to contextualize Taskamal within the vast and complex archaeological landscape of Central Asia.
The research was published in the journal Archaeological Research in Asia.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ara.2024.100536
Cover Image: Sergey Yarygin et al.