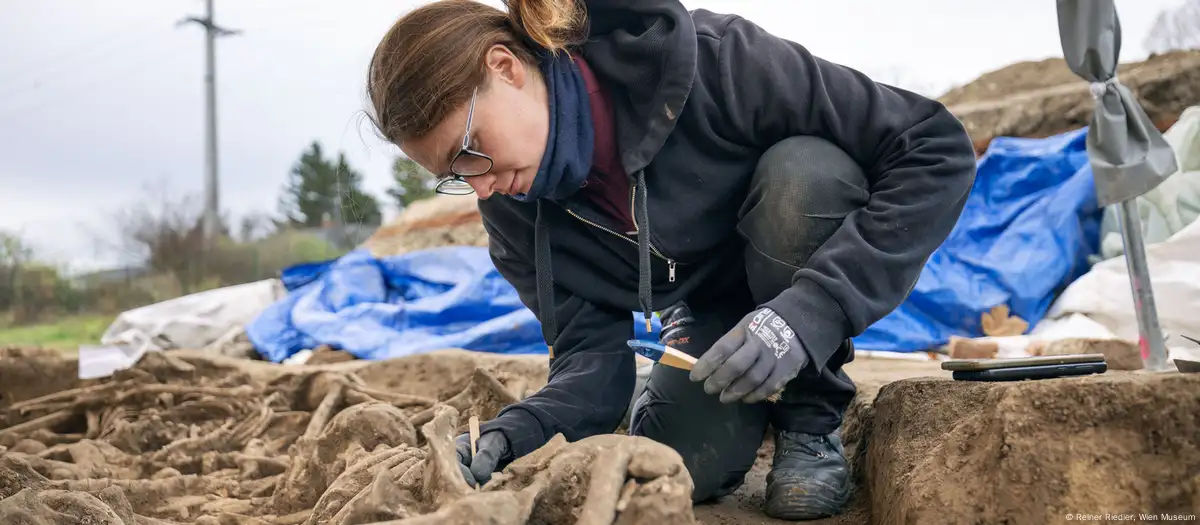
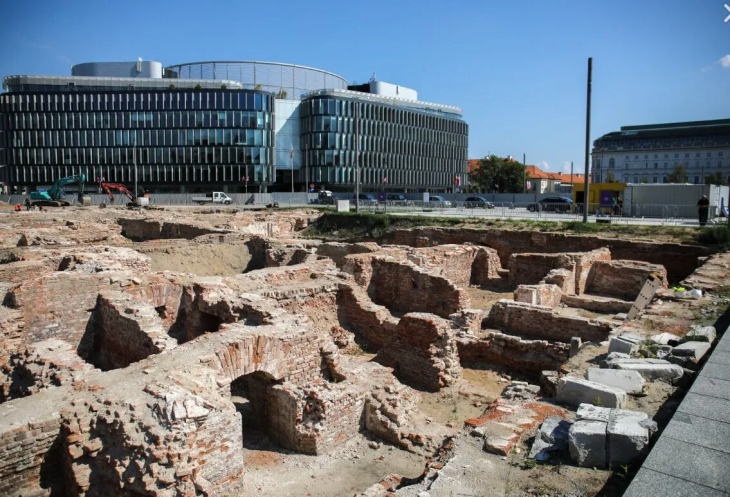
Archaeologists from the Vienna Museum have made a groundbreaking discovery on the outskirts of Vienna, unearthing the remains of approximately 150 soldiers in what has been described as an exceedingly rare find. The skeletal remains were uncovered during construction work to renovate a football pitch in the residential and industrial area of Simmering, with the initial discovery occurring in October.
Following expert analysis, it has been confirmed that the remains date back to the 1st century AD, during the height of the Roman Empire. The excavation revealed 129 individuals initially, but further analysis indicated that the total number of bodies could exceed 150. This mass grave is particularly significant as burials of this nature were uncommon in the European parts of the Roman Empire, where cremation was the prevalent funerary practice until the 3rd century AD.
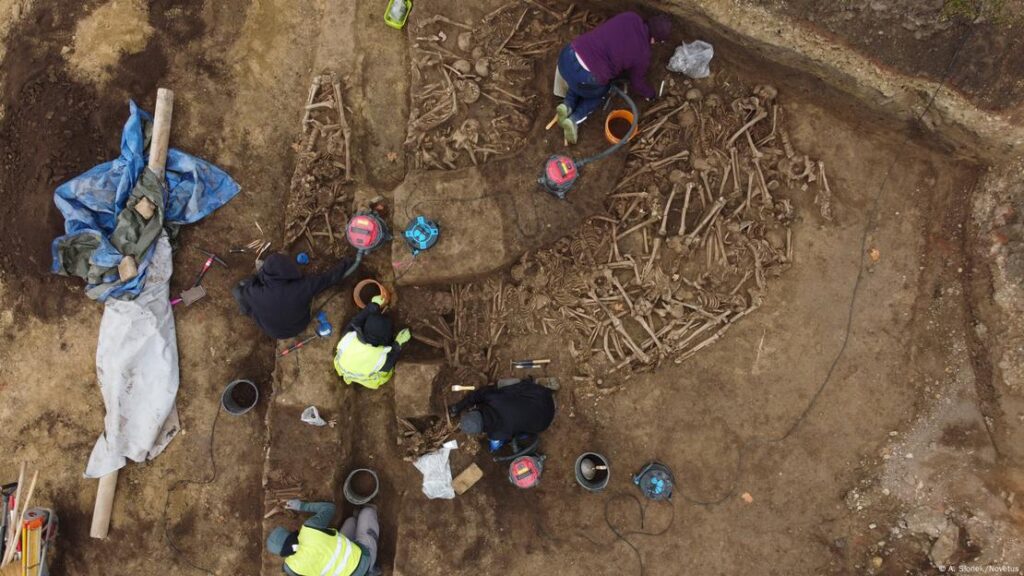
Kristina Adler-Wölfl, Head of City Archaeology, explained, “As cremation burials were common around 100 AD, body burials were an absolute exception. Finds of Roman skeletons from this period are therefore extremely rare.” The remains belong exclusively to young males aged between 20 and 30 years, who appear to have been killed in battle, as evidenced by injuries from swords, spears, daggers, and projectile bolts.
Michaela Binder, who led the archaeological dig, noted, “Within the context of Roman acts of war, there are no comparable finds of fighters. Finding the dead is unique for the entire Roman history.” The disorderly arrangement of the skeletons suggests that this was not a formal burial but rather an improvised grave following a violent event.

The discovery is linked to the military history of the region, as ancient Vindobona served as a significant military garrison of the Roman Empire. The presence of military artifacts, including a dagger with silver filigree inlays, fragments of scale armor, and spearheads, supports the hypothesis that these individuals were soldiers who fell in battle. This find represents the first direct archaeological evidence of a battle on the Danube Limes, the northern frontier of the Roman Empire.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Vienna’s Councilor for Culture and Science, Veronica Kaup-Hasler, emphasized the importance of this discovery, stating, “Each new archaeological discovery allows us to redefine the boundaries of our knowledge. This mass grave offers us a different perspective on Vienna’s early history and underscores the importance of preserving and studying our historical heritage.”
The ongoing research will include DNA and isotope analyses to determine the origins and living conditions of the individuals, potentially providing crucial insights into the composition of Roman troops along the Danube frontier. As archaeologist Michaela Kronberger noted, “We are facing research that could redefine our understanding of the Roman past in this region.”
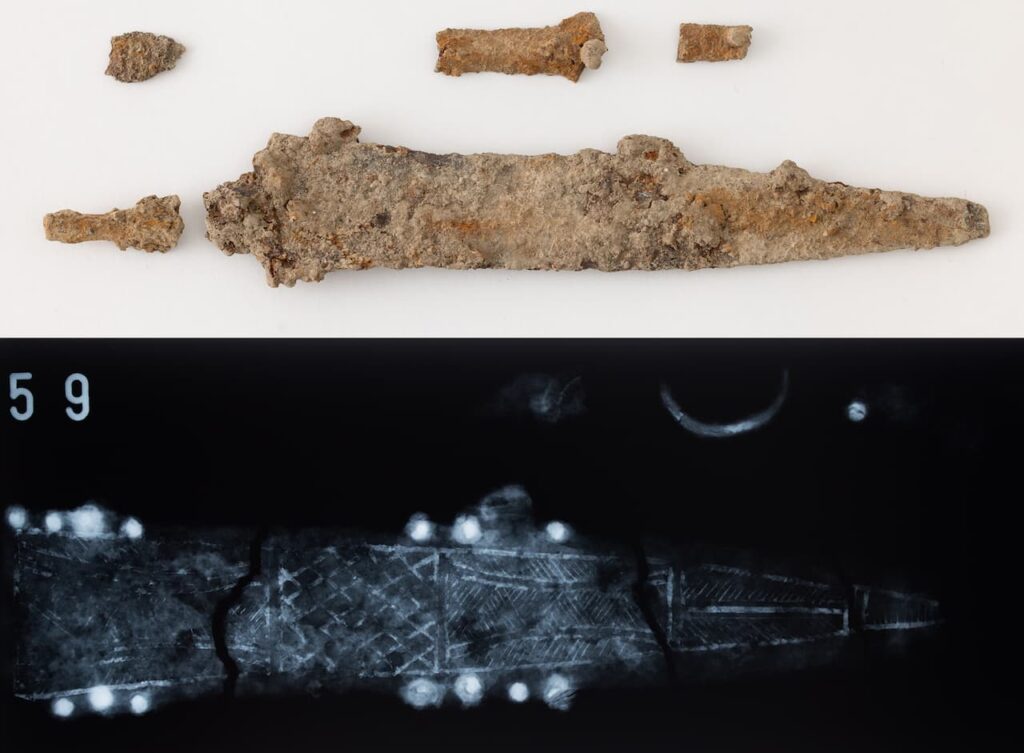
This unprecedented find not only sheds light on the military conflicts of the Roman Empire but also offers a unique opportunity to explore the early history of Vienna, paving the way for further investigations into the city’s ancient origins.
Cover Image Credit: Finding the buried bodies of early Roman soldiers is soldiers is extremely rare. Credit: Reiner Riedler, Wien Museum
















