According to archaeological research published in Science magazine on Wednesday, Homo sapiens ventured into the Neanderthal territory in Europe far earlier than previously thought.
The new discovery, by a team of archaeologists and palaeoanthropologists led by Ludovic Slimak of Toulouse University, pushes back the arrival of Homo sapiens in Western Europe to around 54,000 years ago.
Until now, archaeological discoveries had shown that Neanderthals vanished from the European peninsula around 40,000 years ago, just 5,000 years after their “cousin” Homo sapiens arrived, and there was no evidence of an encounter between these two groups
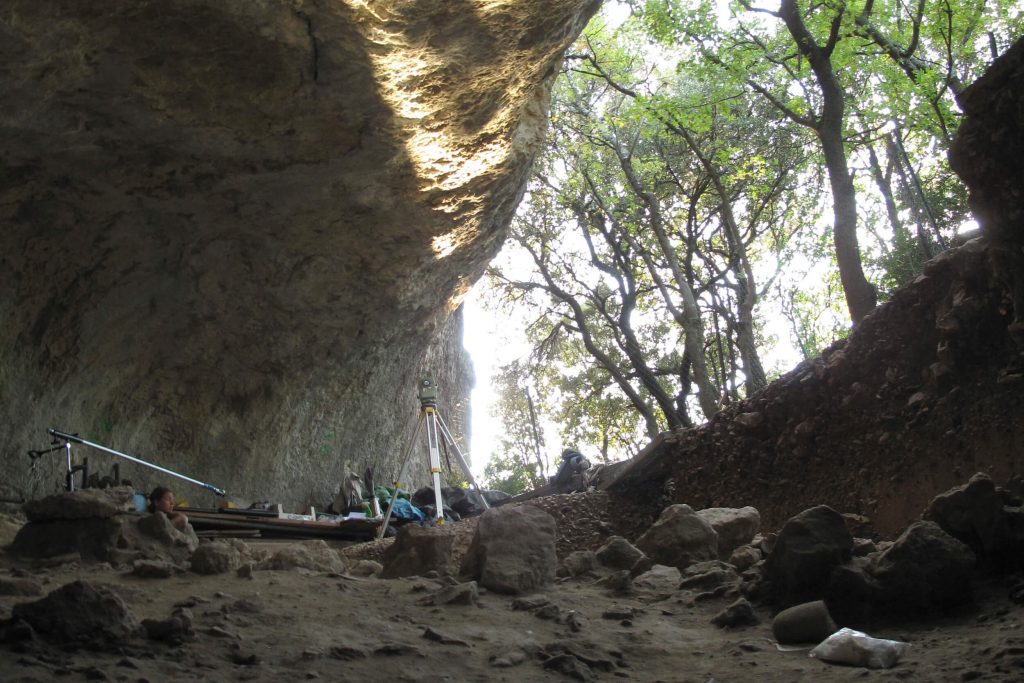

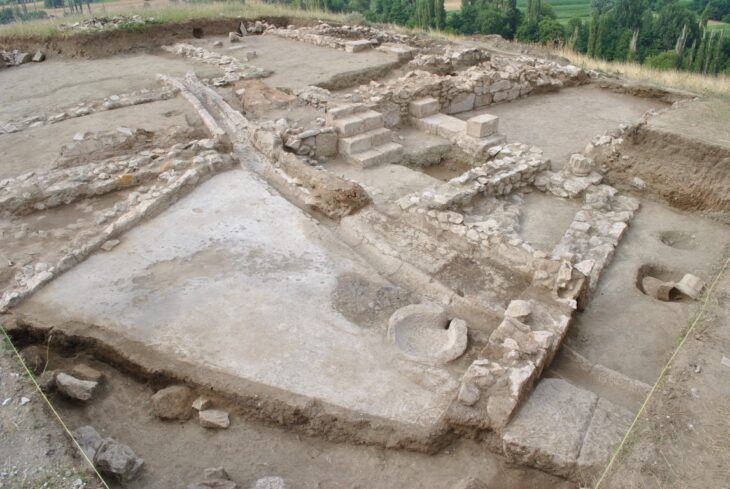
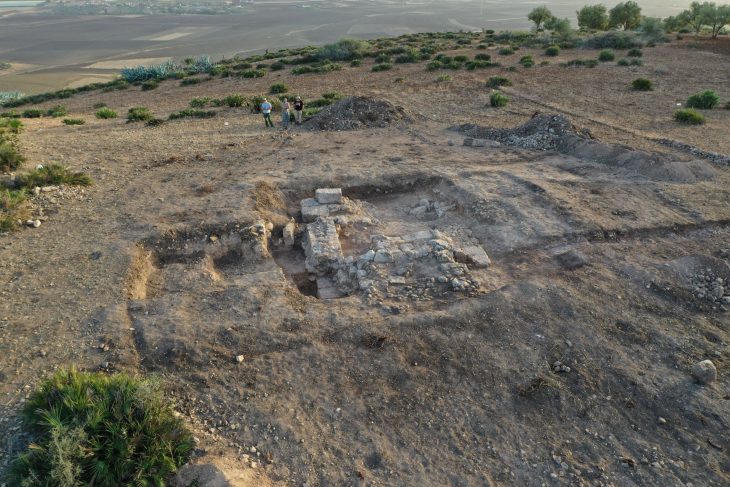
In a paper published Wednesday by the journal Science Advances, researchers from Europe and the United States described finding fossilized homo sapiens remains and tools sandwiched between those of Neanderthals in the Mandrin Grotto.
The most striking finding of the study is that two human species live alternately in the Mandrin cave, now located in the Rhone region of southern France.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
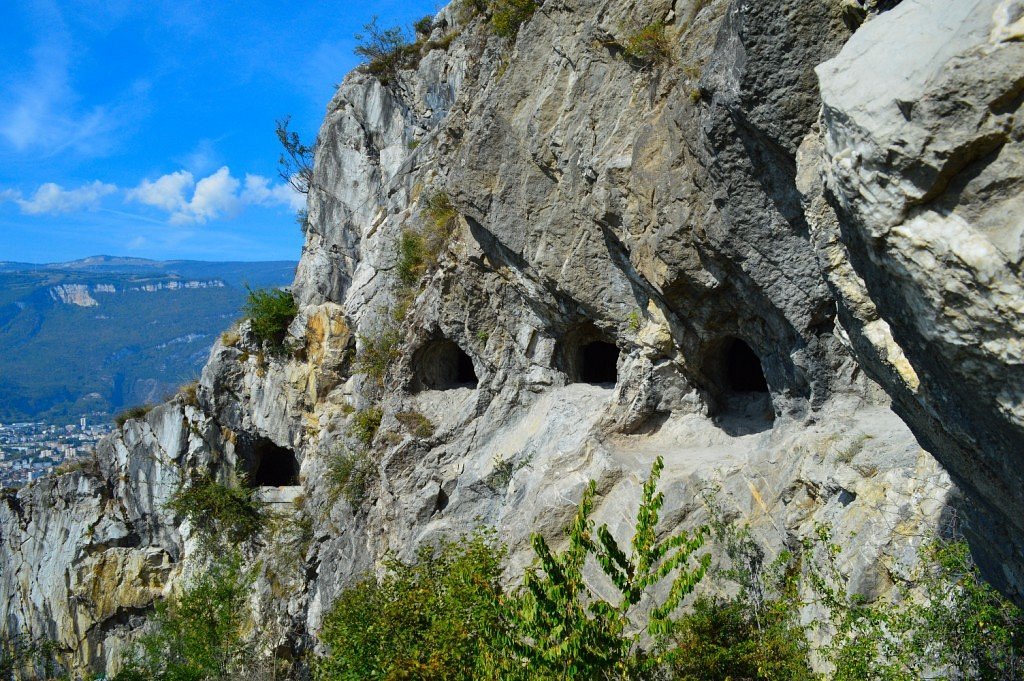
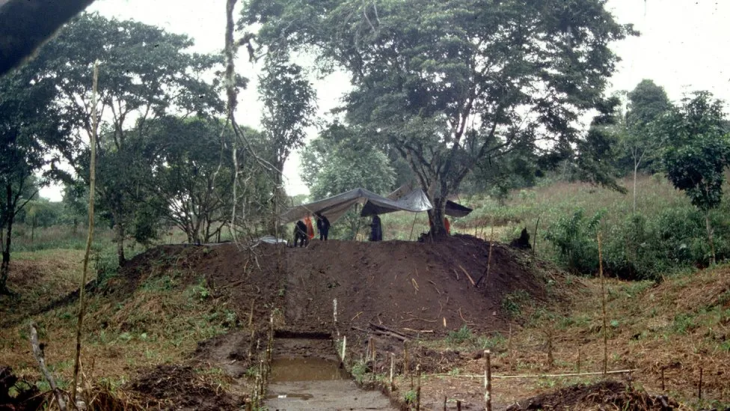
The Mandrin site, first excavated in 1990, includes layer upon layer of archaeological remains dating back over 80,000 years.
“Mandrin is like a kind of neandertalian Pompeii, without catastrophic events, but with a continuous filling of sands in the cave deposited progressively by a strong wind, the Mistral,” Slimak told AFP.
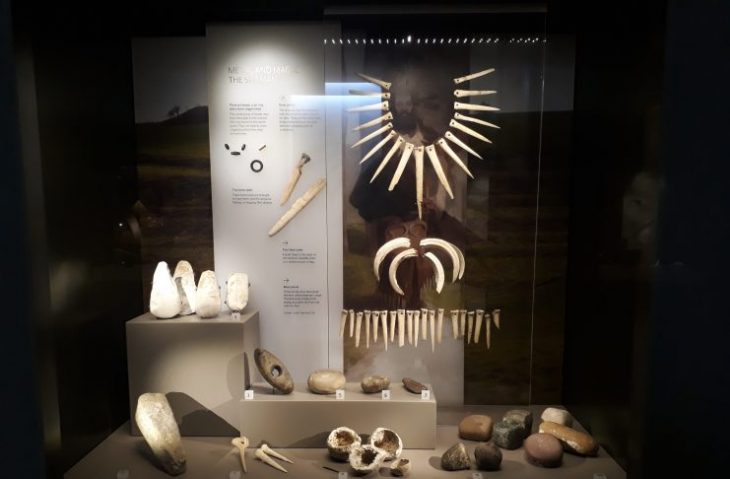
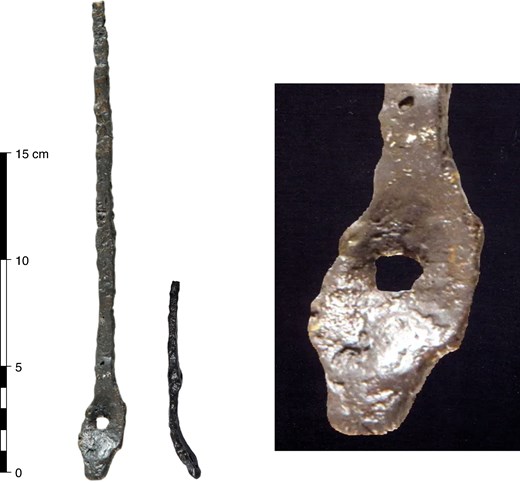
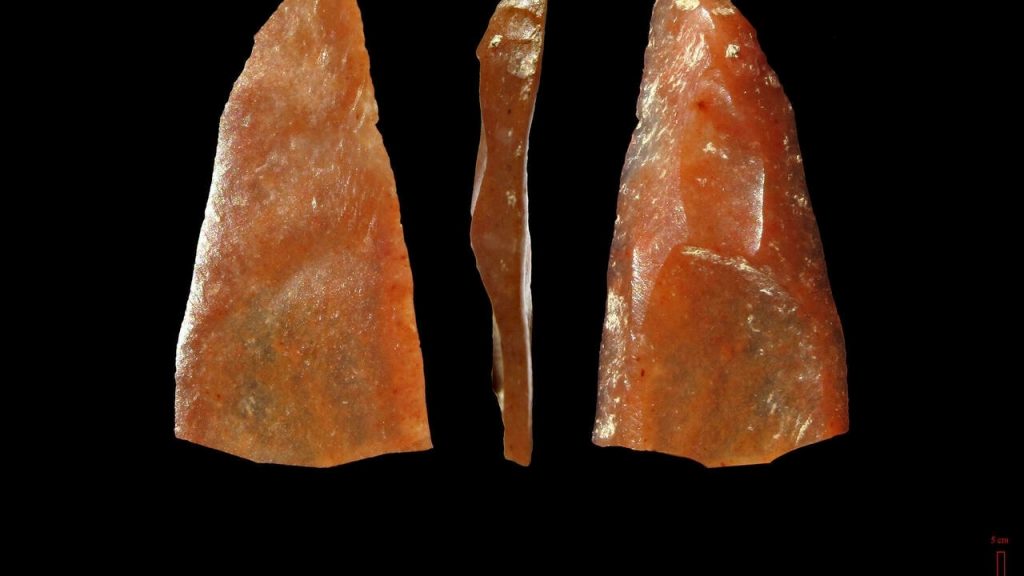
His team uncoevered a layer, known as the “E layer”, containing at least 1,500 cut flint points, more finely executed than the points and blades in the layers above and below.
Very small in size, some of them less than a centimeter in length, these points “are standardized, to the nearest millimeter, something we haven’t seen at all with Neanderthals,” said Slimak, a specialist in Neanderthal societies.
These, he explained, were probably arrowheads, unknown in Europe at that time. He attributes this production to a culture called Neronian, linked to several sites in the Rhone area.

Milk tooth discovery
In 2016, Slimak and his team visited the Peabody Museum in Harvard to compare their discoveries with a collection of carved fossils from the Ksar Akil site at the foot of Mount Lebanon, one of the major sites of the expansion of Homo sapiens to the east of the Mediterranean.
The similarity between the techniques used convinced Slimak that the findings at the Mandrin site were the first traces of Home Sapiens found in Europe.
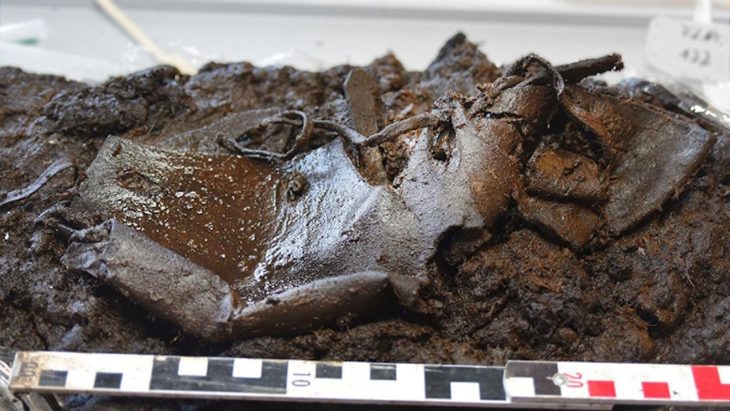
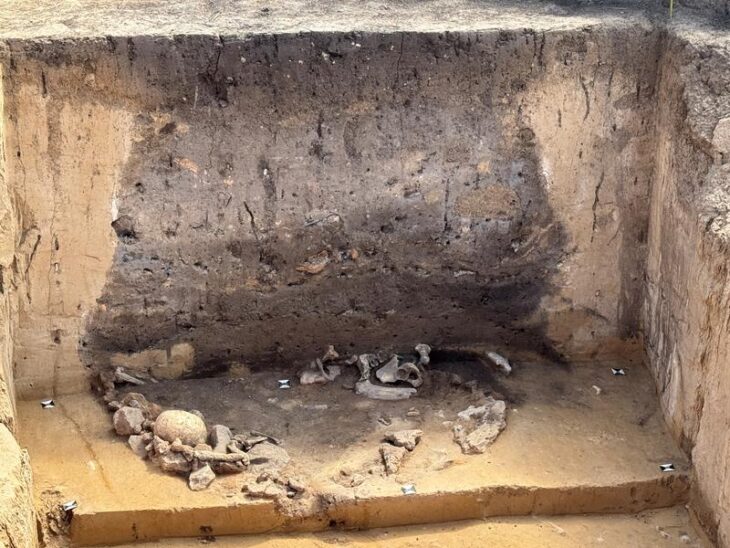
A milk tooth found in the “E layer” confirmed his suspicions.
In all researchers found nine teeth at the Mandrin cave site, belonging to six individuals. These ancient teeth were entrusted to Clement Zanolli, a palaeoanthropologist at the University of Bordeaux.
Using microtomography, similar to medical scanning technology, the verdict was clear. The milk tooth from the “E” layer” was the only modern human tooth found at the site.
That “fossil molar from a modern human child provides the earliest known evidence of modern humans in western Europe”, the Natural History Museum in London said in a statement.
While the researchers found no evidence of cultural exchanges between the Neanderthals and modern humans who alternated in the cave, the rapid succession of occupants is in itself significant, they said. In one case, the cave changed hands in the space of about a year, said Slimak.