Love and hate are universal emotions that have persisted throughout human history. Ancient civilizations developed their own distinct methods of expressing and comprehending these emotions, which were frequently intertwined with religious and magical beliefs.
The new study brings together a diverse range of texts from various ancient cultures, including Egyptian, Mesopotamian, Greek, and Roman. These texts provide valuable insights into the beliefs, rituals, and practices surrounding love and hate in ancient times.
A team of scholars spent five years studying them: “magical” Egyptian texts written on papyrus, parchment, paper, and clay shards – known as ostraca – between the fourth and twelfth centuries AD.
The effect of these papyri was magical. Worn in an amulet around the neck or secretly hidden in the house of an adversary, they were supposed to heal illnesses, curse enemies, evoke love or hatred or allow a glimpse into the future, among other things.
What these texts also have in common is that they were all written in Coptic script and language. Coptic is the last stage in the development of the Egyptian language. It replaced Demotic around the second century A.D. and was itself gradually replaced with the Arab conquest of Egypt in the 7th century.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Through examining these texts, researchers have acquired a more profound comprehension of the societal and cultural workings of historical communities. They reveal the complexities of relationships, the power dynamics between individuals, and the role of magic in shaping human emotions.
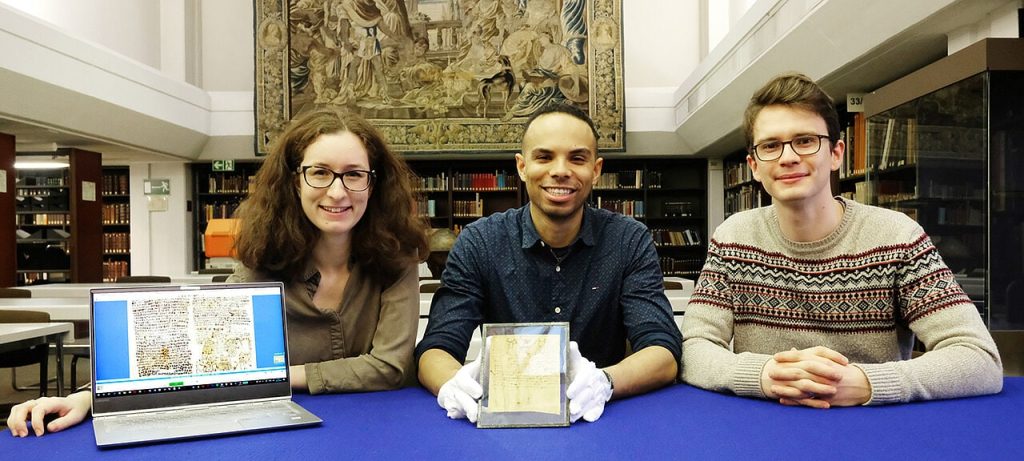
Magical texts from Egypt in Coptic script and language are the focus of a research project at the University of Würzburg. They are now being presented for the first time in a 600-page book.

Five Years of Research
“Papyri Copticae Magicae” is the title of the recently published work, published as volume 48 of the series “Archiv für Papyrusforschung und verwandte Gebiete – Beihefte”. The scholars of antiquity Dr. Korshi Dosoo and Markéta Preininger are responsible for the publication. At the Chair of Egyptology at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU), the two have led the research project of the same name for the past five years, which was funded by the JMU’s “Excellent Ideas” program.
“Around 600 of these texts have survived, but the largest published collection to date only contains around 100 of them. The rest were previously scattered in numerous books and articles and were therefore only accessible and known to a few specialists,” says Korshi Dosoo, describing the initial situation of the project.
Love Spells and Separation Wishes
The content of these texts can be categorised into a handful of categories. For example, they deal with protection from death or demons, the appeasement of enemies or the fulfilment of very specific wishes. Love spells are a frequently found genre; they were mainly used by men. In some cases, the spell was intended to ensure that married couples separated again. Magic played an important role in medicine, for example to prevent fever, headaches and insomnia. It was not uncommon for the papyrus to help its wearer become pregnant.
“These documents serve as an important source of information about popular religion – the reality, rather than the ideal, of religious practices and beliefs as they were lived and practiced in everyday life,” explains Markéta Preininger Svobodova. They thus provide today’s readers with information about the experiences of people on the threshold of the transition from traditional Egyptian religion to Christianity and Islam, about their ideas of the human and divine world and about how human experiences such as happiness and success, suffering and illness, love and conflict were understood and negotiated. “These texts give us a direct insight into people’s private lives at the time; they convey their true emotions,” says the researcher.

The Transition to Christianity Leaves its Mark
In fact, this transition to Christianity also left its mark on the magical texts. “The Christianization of Egypt ended the cults of the numerous gods of the Pharaonic period, but it did not end the belief in a world full of superhuman powers,” explains Korshi Dosoo. Instead, people transformed their former gods into angels and saints who served the almighty God and into evil beings who wanted to harm his creation.
Accordingly, these manuscripts are “rich sources of information about daily life and religion in Egypt in the last centuries of Roman rule and the first centuries after the Arab conquest”, as the publisher writes.
Closing a Gap in the Research Landscape
The publication of this new anthology on ‘magical’ texts is a significant contribution to the field of ancient studies. It sheds light on the intricate relationship between love, hate, and magic in ancient times, offering valuable insights into the human experience across cultures and centuries.
With their interest in magical texts from Egypt, the Würzburg research team is following in a long tradition. As early as 1928, the papyrologist Karl Preisendanz published the collection of texts Papyri Graecae Magicae (PGM), which, despite its name, essentially contained papyri from Egypt and was later supplemented by the Papyri Demoticae Magicae. However, a comprehensive collection of magical texts in Coptic script and language had been lacking until now. “Thanks to JMU funding, Korshi Dosoo and Markéta Preininger have been able to begin to close this gap with the volume that has now been published,” explains Professor Martin Andreas Stadler, Chair of Egyptology at JMU.
Exploring these ancient texts allows us to gain a better understanding of our own emotions and how our ancestors shaped them. Love and hatred are timeless, and this anthology serves as a reminder of their continued importance.
https://doi.org/10.1515/9783111080109
The research project’s Website https://www.coptic-magic.phil.uni-wuerzburg.de/
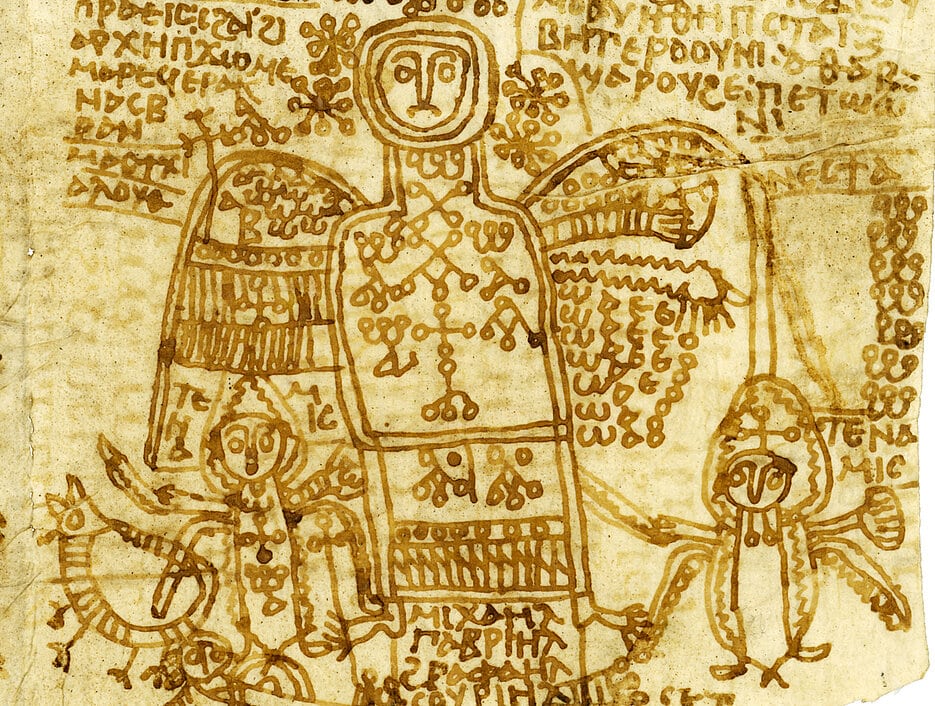
Cover Photo: The part of a papyrus shows the archangel Michael, who is accompanied by two angelic powers. Such images were used for many ritual purposes, for example, to heal illnesses, drive out evil demons, protect against robbers, or curse other people. Photo: Elke Fuchs / Institut für Papyrologie, Universität Heidelberg