Excavating a hill considered to have played a critical part in the Battle of Bannockburn, archaeologists discovered a forgotten medieval road used by Robert the Bruce and his army.
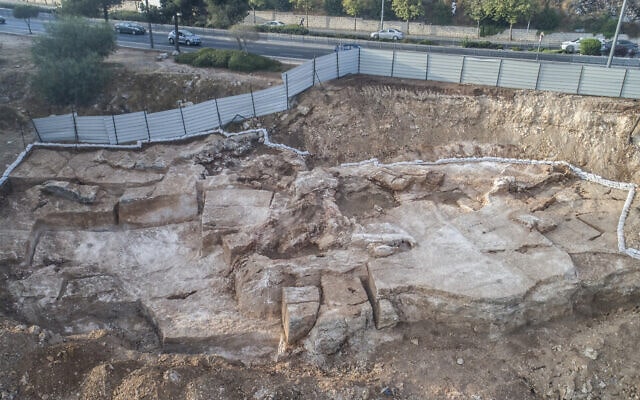
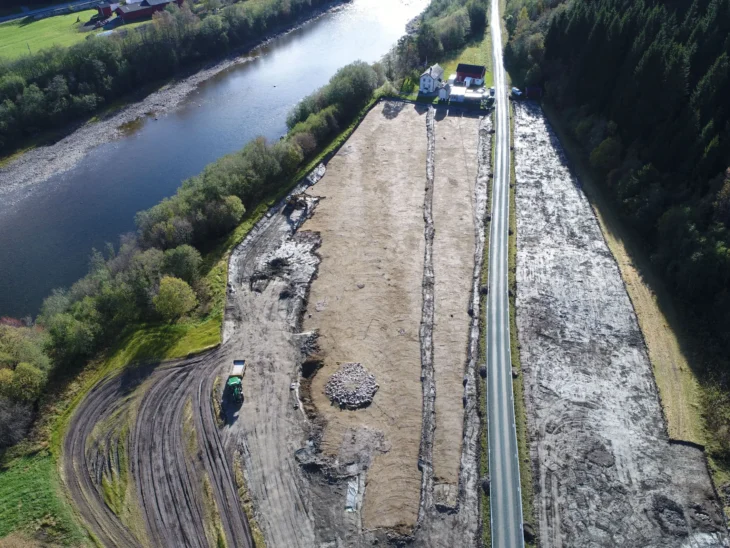
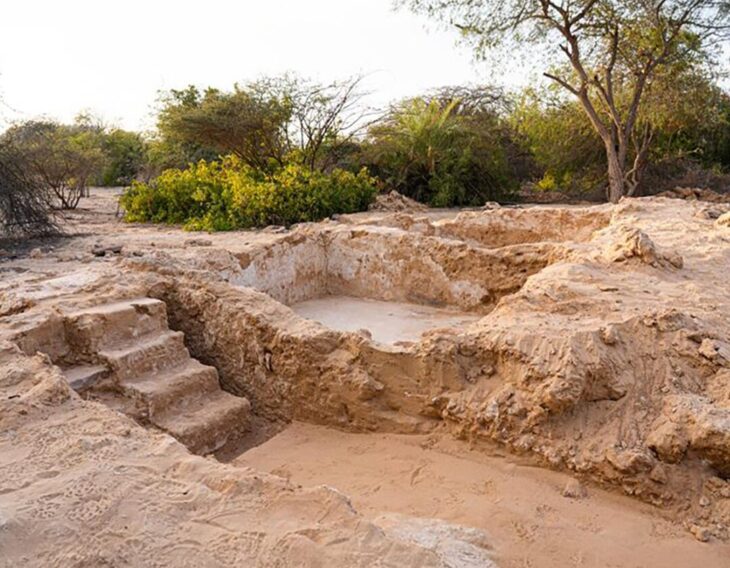
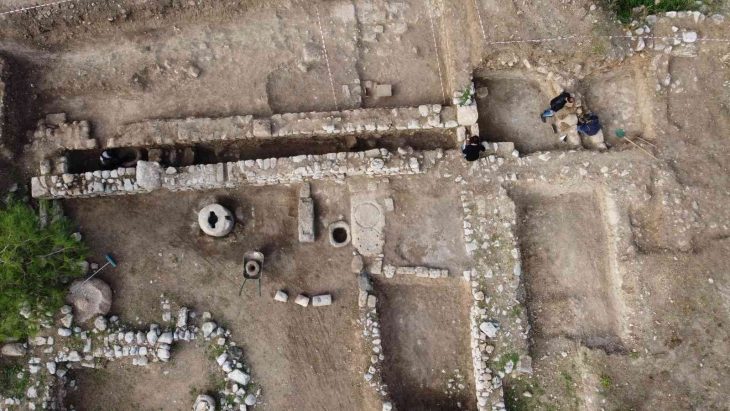
On Saturday, during the first excavation at Coxet Hill in Stirling, a long road was discovered. This hill is believed to be where Scots King Robert the Bruce set up his camp in preparation for the first day of warfare on June 23, 1314.
It is also possible that the Scottish camp followers and troops who had not been schooled in Bruce’s tactics were stationed there on the critical second day when the English army was forced to escape. These “Sma’ Folk,” hidden behind the hill, are said to have appeared after victory was secured to obstruct King Edward II’s army’s withdrawal to Stirling Castle, thereby turning the Scottish triumph into a rout.
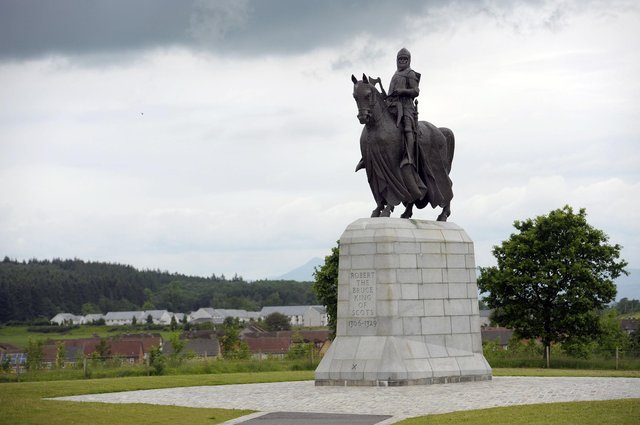

The archaeologist from Stirling, Dr. Murray Cook, who organized the excavations for the 707th anniversary of the battle, said the stone road would bypass the hill that was established in the 13th century as a hunting forest for game birds by King Alexander III. It would have been used by Bruce and his army in battle, and Dr. Cook believes that this may also have been the path taken by the People of Sma folk when they panicked the English ranks.
Dr Cook said: “Where we thought we had a boundary around Alexander III’s New Park, it now appears we have a road. We’ve got a 100 metre section of it, probably four metres wide.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
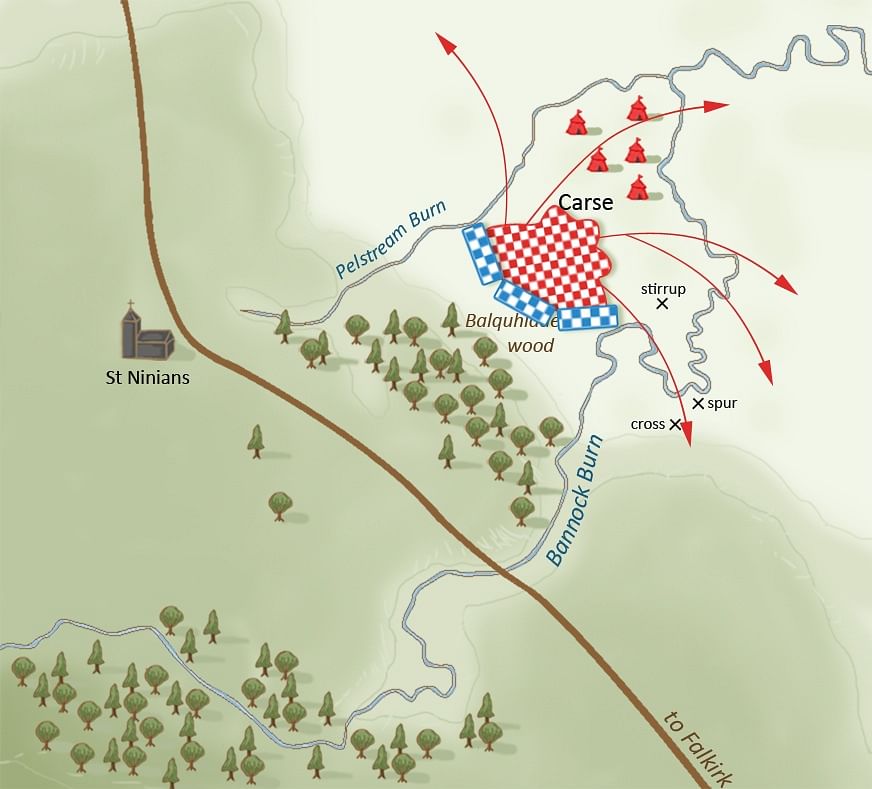
“This hard-packed stone road or track curves at the foot of Coxet Hill and is not found on any of the 200-year-old maps, suggesting a medieval origin. The fact that it is located around a medieval royal forest suggests that it was there before the Battle of Bannockburn and was in use at the time. It is logical that it was used by Robert the Bruce. This was also potentially the route used by the Sma people on their way to [the battle] of Bannockburn.” He said.
The Battle of Bannockburn was fought on June 23-24, 1314. King Edward II traveled to Scotland to find and destroy the Scottish army and to relieve Stirling Castle, which was under a Scottish siege.
Although Edward’s army of up to 25,000 men outnumbered Robert Bruce’s troops, the Scots prevailed. After a day of skirmishing, the Scots won a decisive victory on the second day of the fight.
If the English army had withdrawn to Stirling Castle, they could have reassembled to fight another day – and maybe even achieved a longer-term triumph – but their way was barred. When the tide turned in Bruce’s favor, the Sma’ Folk appeared from behind Coxet Hill, causing fear among the English ranks, who fled at the sight of a fresh army.
Cover Photo: Britannica
Source: The Scotsman