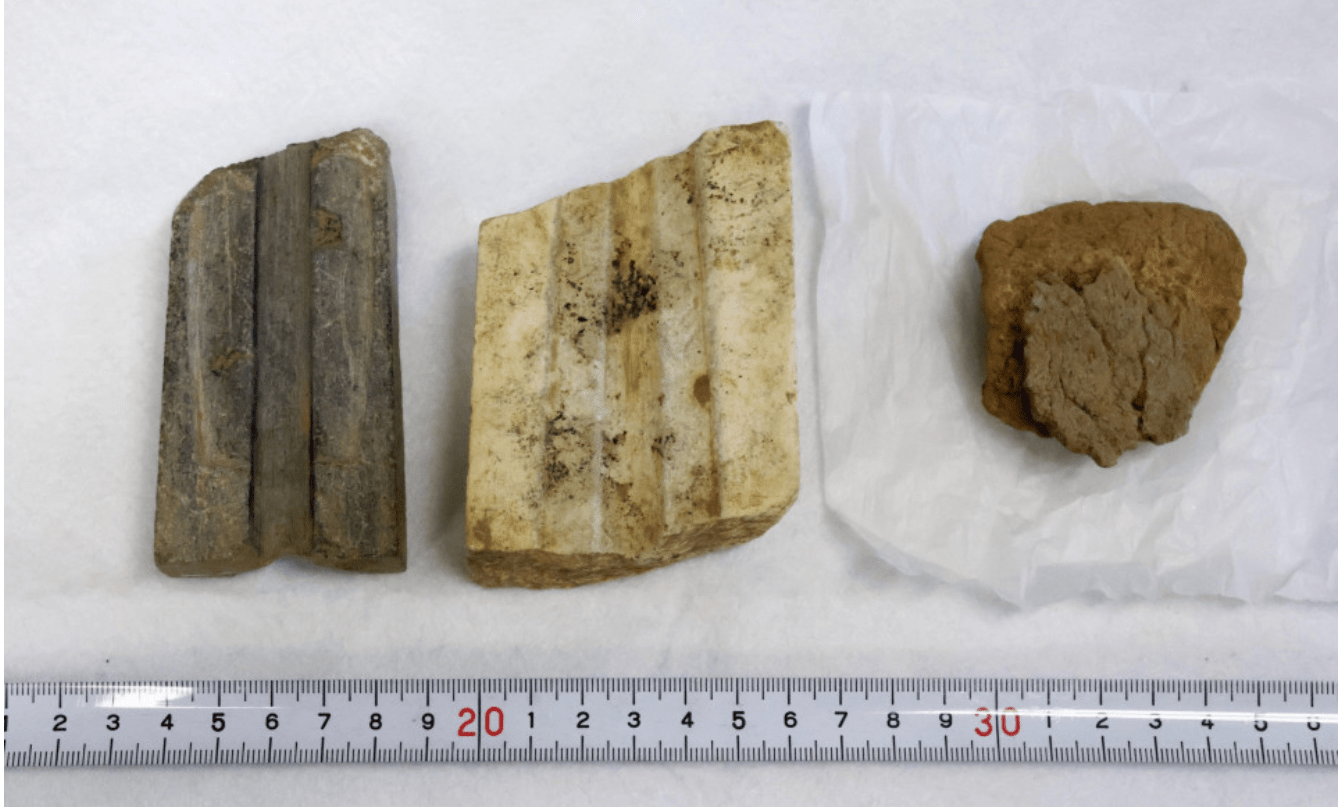
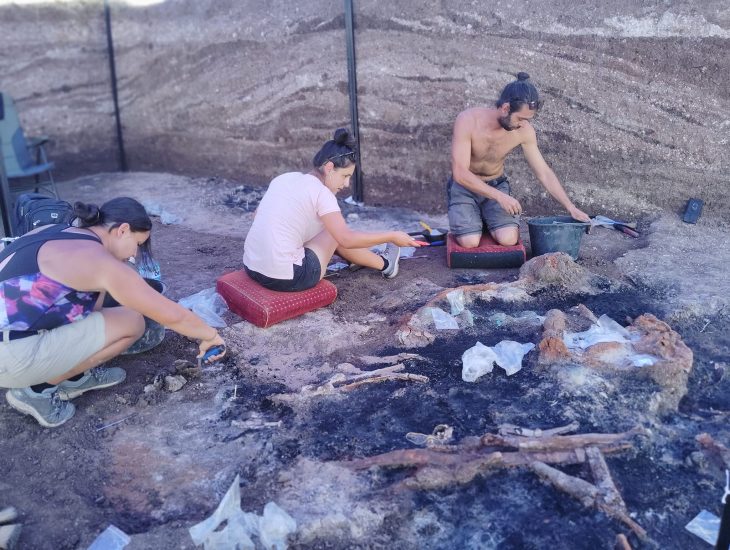
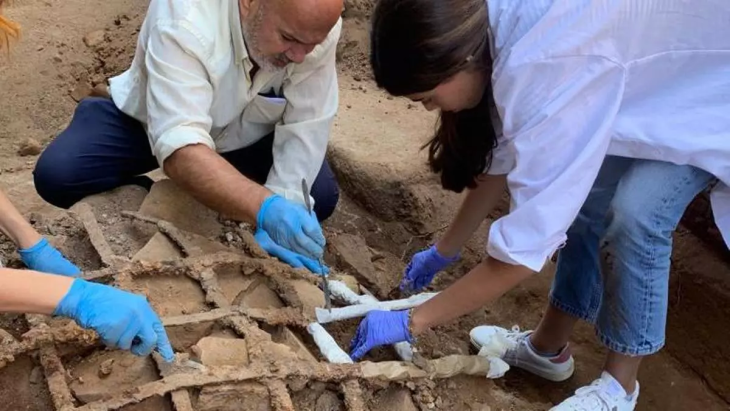
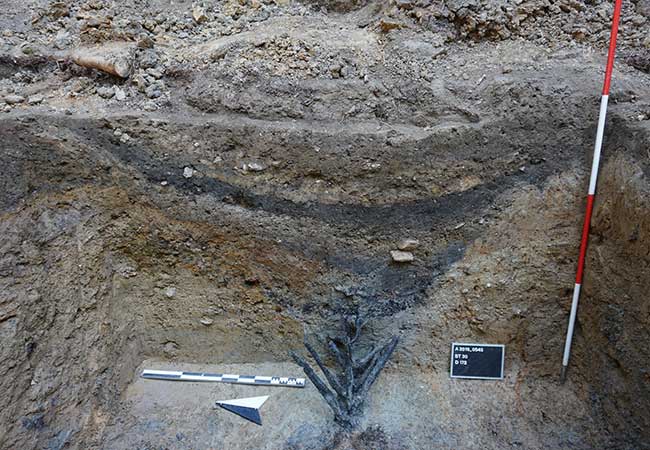
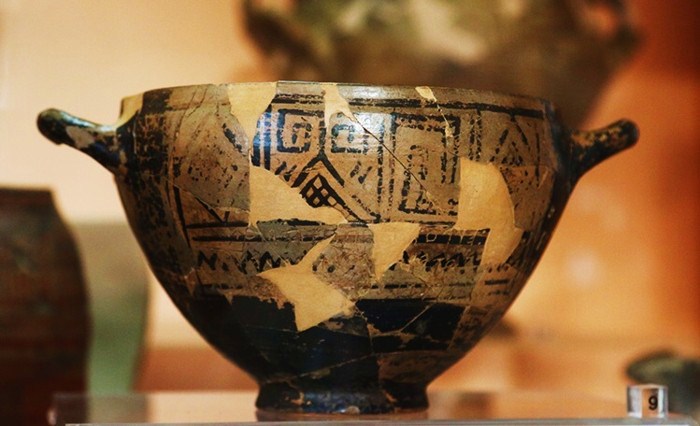
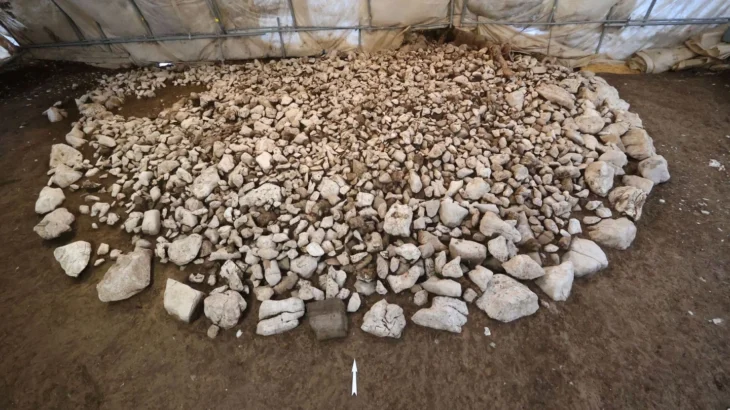
At the Yoshinogari Ruins in the western prefecture of Saga, relics including stone casting molds for bronze artifacts have been found. These molds may be the oldest of their kind in Japan, the Saga prefectural announced on Monday.
One of the molds could date back to around 200 BC, according to the local government. This date marks a unique time in Japanese history: Yayoi period. The period of Japanese history called the Yayoi Period spanned from 300 BC through 250 BC.
Culturally, the Yayoi represents a notable advance over the Jomon period and is believed to have lasted for some five or six centuries, from about the 3rd century BC to the 2nd or 3rd century CE.
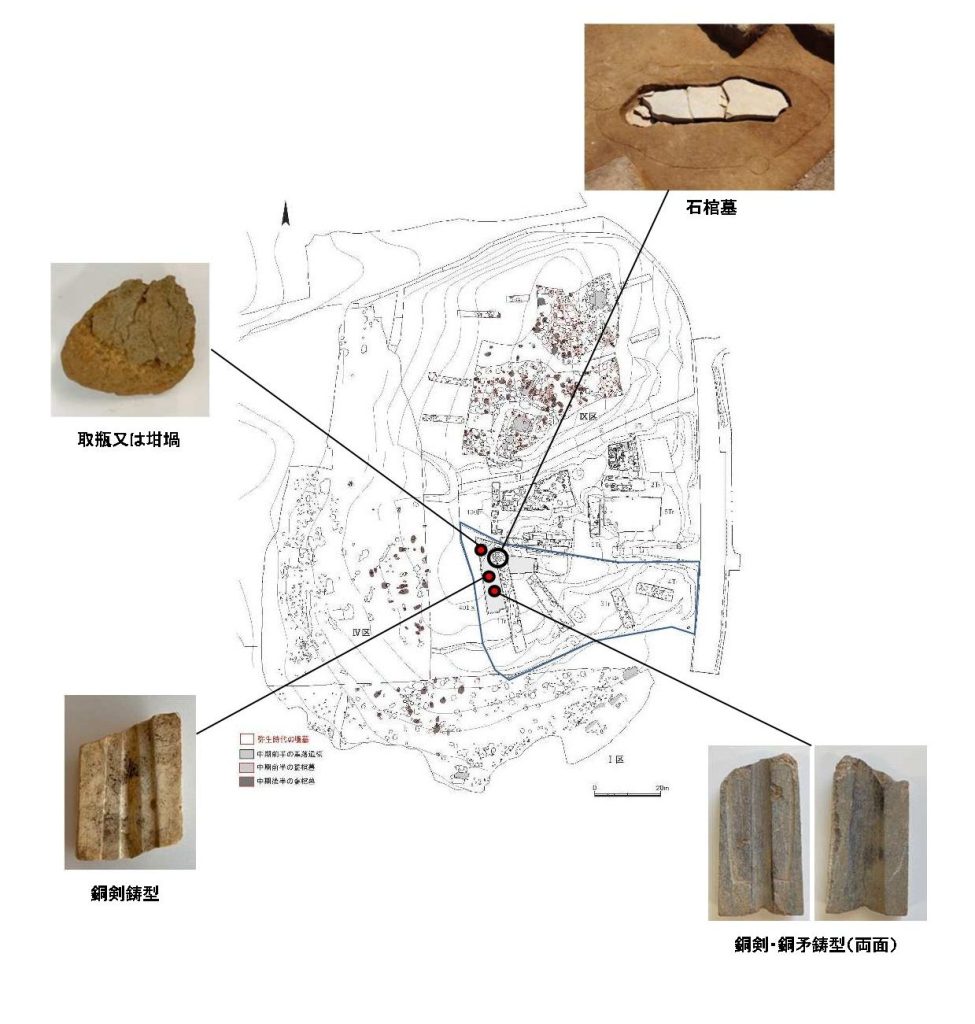
The discoveries between September and October at the Yoshinogari ruins followed the finding in April of a stone coffin tomb believed to have belonged to a person of high status in an area of the site.
The enigmatic coffin prompted experts and archaeology buffs to wonder whose burial site it is however it was announced in June that no human bones or burial accessories were found that could yield clues as to the individual’s identity or the exact burial period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The latest excavation of what is called the “mystery area,” which could not be surveyed because a shrine had been there, found three items — casting molds made of serpentinite and quartz-porphyry, as well as a clay vessel used as a container for molten metal.
The molds, possibly used for casting swords and spears, were found within a range of about 5 meters northwest to about 10 meters south-southwest from where the stone coffin was discovered, according to the prefecture.
Bronze Age metal tools were formed using moulds to shape the molten metal into the desired form. The technology for moulding bronze improved through the Bronze Age. Initially, items were cast by pouring the melted bronze into hollowed out stone moulds. By the Middle Bronze Age, people had invented two part moulds, where two hollowed stones were put together and metal was poured into a gap at the top. This allowed for sophisticated objects like axes and spearheads to be produced.
Have you ever heard of a civilization that completed the transition from the Stone Age through the Bronze and Iron Ages in 50 years? Well, the Yayoi People of Japan did all this and more.
“It is an extremely significant discovery in understanding distinct features of the structure (of ruins) and the changes,” a prefectural official said.
Serpentinite preceded quartz-porphyry as stone mold in general, said Chuhei Takashima, an archaeologist with expertise in the Yoshinogari ruins, adding that the technology could have directly derived from the Korean Peninsula.
The discoveries “added further meaning to Yoshinogari, which was a manufacturing site of bronze artifacts in Japan, introducing the most advanced technology back then,” Takashima said.
The bronze casting introduced during the middle of the Yayoi period can be considered an immensely significant discovery that builds upon earlier research findings at the Yoshinogari ruins, shedding light on the characteristics and transformations in the village structure.
Cover Photo: Photo taken on Dec. 4, 2023, shows relics — stone molds to cast bronze artifacts and a piece of clay vessel (R) — discovered at the Yoshinogari ruins in Saga Prefecture. (Kyodo). Photo: Saga Prefectural Government
















