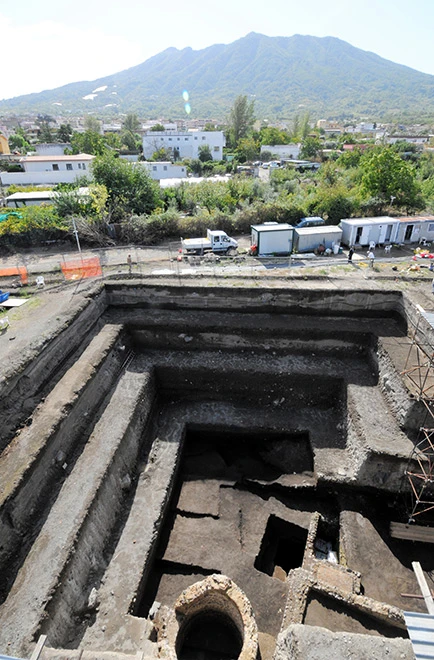
Researchers from the University of Tokyo have discovered a nearly 2,000-year-old building at a site with ancient Roman ruins buried in volcanic ash in southern Italy. The team believes it could have been a villa owned by the first Roman Emperor, Augustus (63 B.C.—A.D. 14).
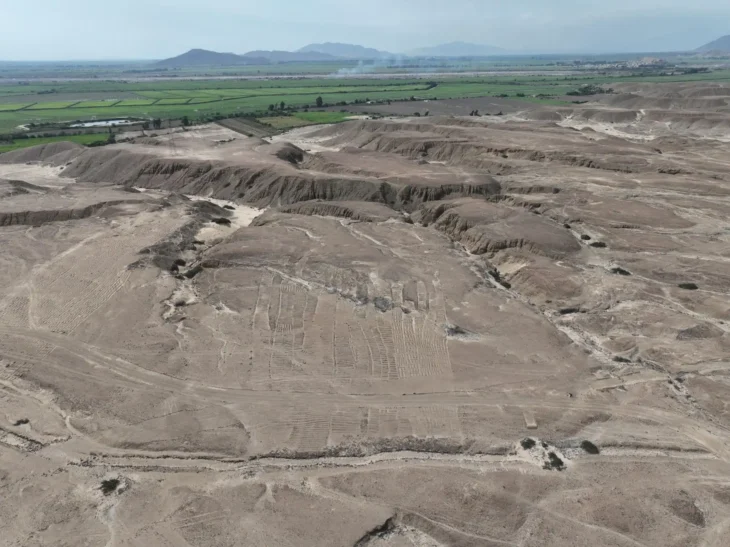
The team, led by Mariko Muramatsu, a professor of Italian studies, began excavating the Somma Vesuviana ruins on the northern side of Mount Vesuvius in the Campania Region in 2002.
According to accounts from antiquity, Augustus passed away at his villa northeast of Mount Vesuvius, and a memorial was subsequently built there in memory of his accomplishments. But the precise location of that villa remained a mystery.
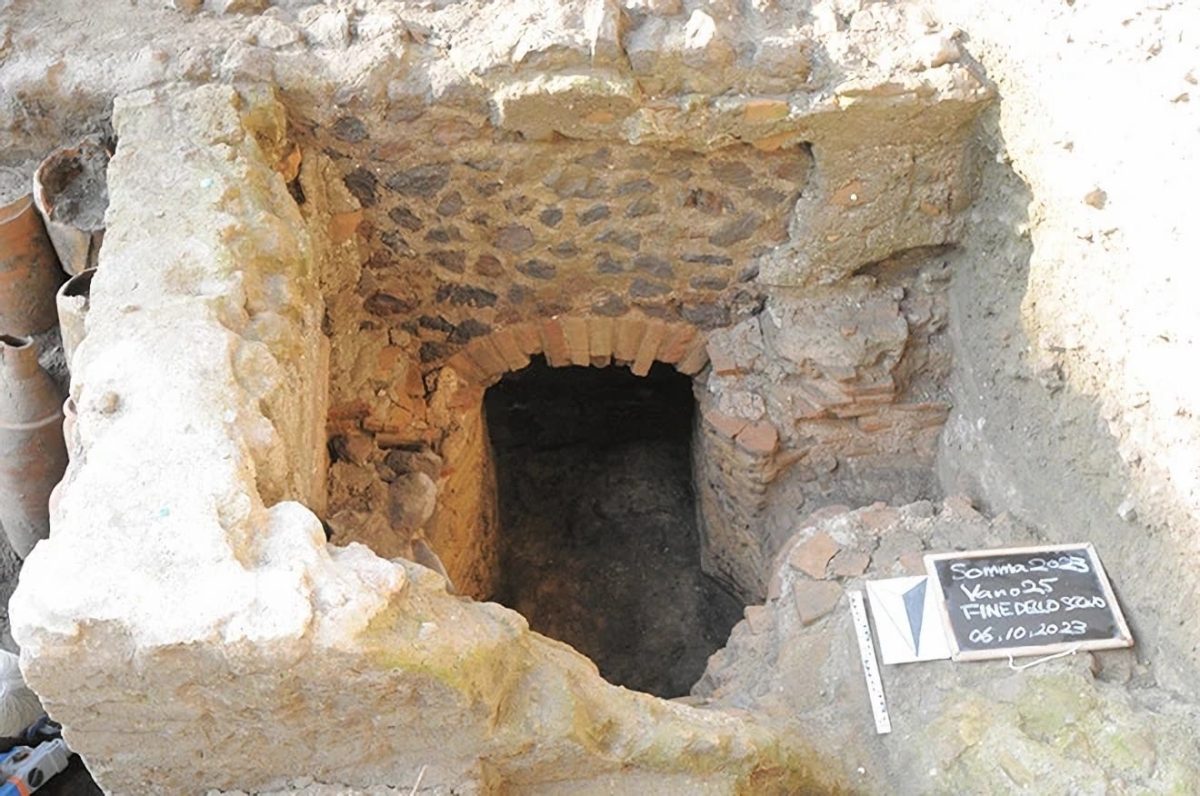
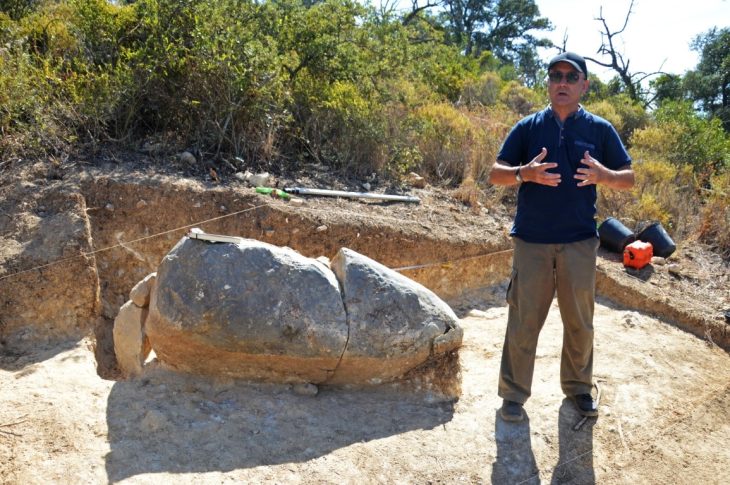
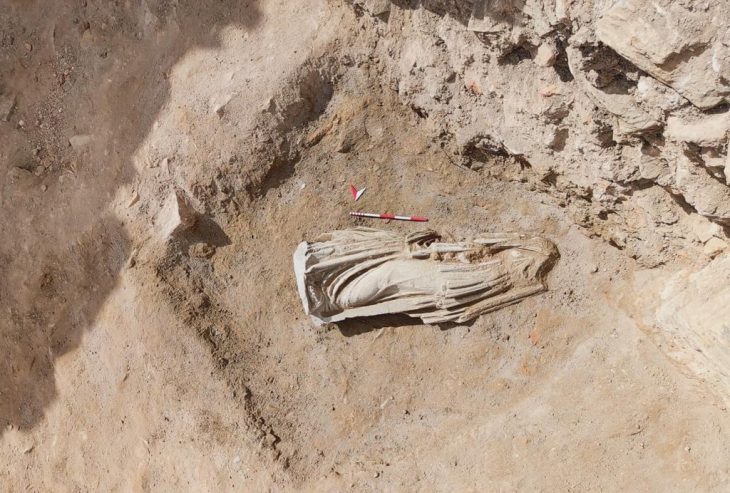
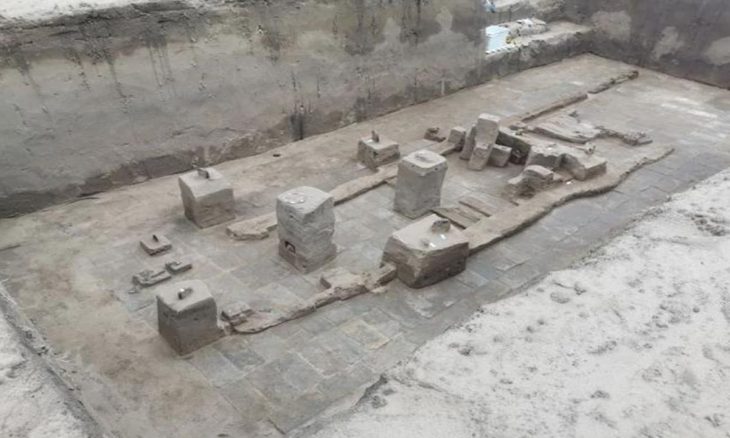
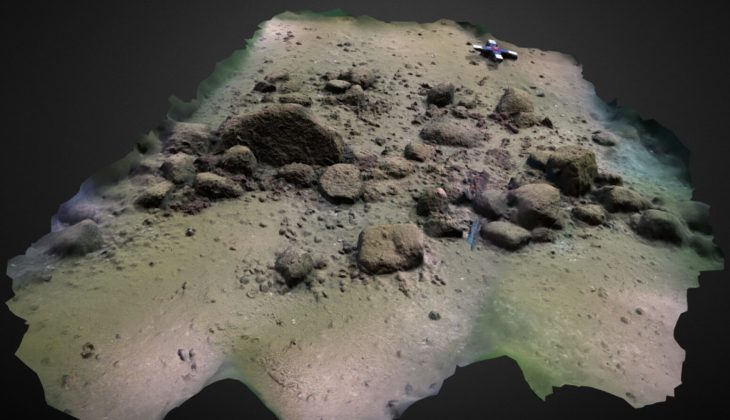
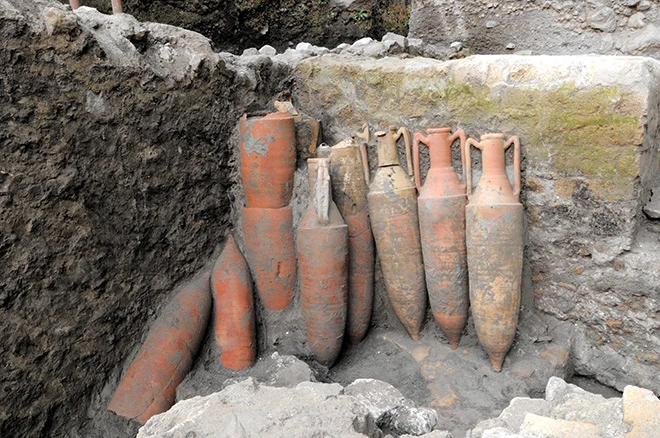
Researchers from the University of Tokyo have uncovered part of a structure that was used as a warehouse. A wall of the building had dozens of amphora ceramic containers arranged in a row. Additionally, they discovered the ruins of what was probably a furnace that was used to heat the bath. Part of the wall had collapsed, scattering ancient roof tiles along the floor.

Carbon dating of carbon from the furnace found that most samples were from around the first century. Researchers say nothing was dating back to the following period and they believe the kiln was no longer used afterward.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The researchers say there is a possibility that the building was the emperor’s villa because it had a private bath, which was installed in the residence of an influential figure. They also say the bath was out of use around the same time when Augustus died and what appeared to be a large temple was later constructed on the site.
The volcanic pumice covering the ruins was found to have originated from the pyroclastic flow of lava, rocks, and hot gases from Mount Vesuvius’ eruption in 79, according to a chemical composition analysis carried out by the team. Pompeii on the mountain’s southern slope was completely destroyed by that same eruption.

“We have finally reached this stage after 20 years,” said Masanori Aoyagi, professor emeritus of Western classical archaeology at the University of Tokyo, who was the first head of the research team that started excavating the site in 2002. “This is a major development that will help us determine the damage caused to the northern side of Vesuvius and get a better overall idea of the eruption in 79.”
Cover Photo: The remains of what is believed to be a furnace used to heat a bath at the Somma Vesuviana site (Photo: Research Division for the Mediterranean Areas, Institute for Advanced Global Studies, University of Tokyo, Komaba)