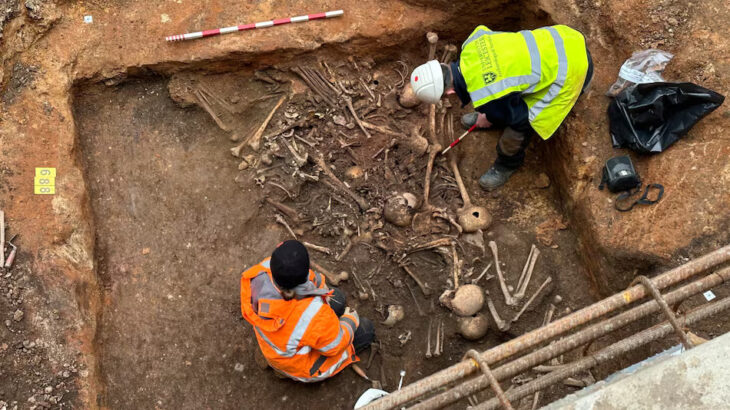
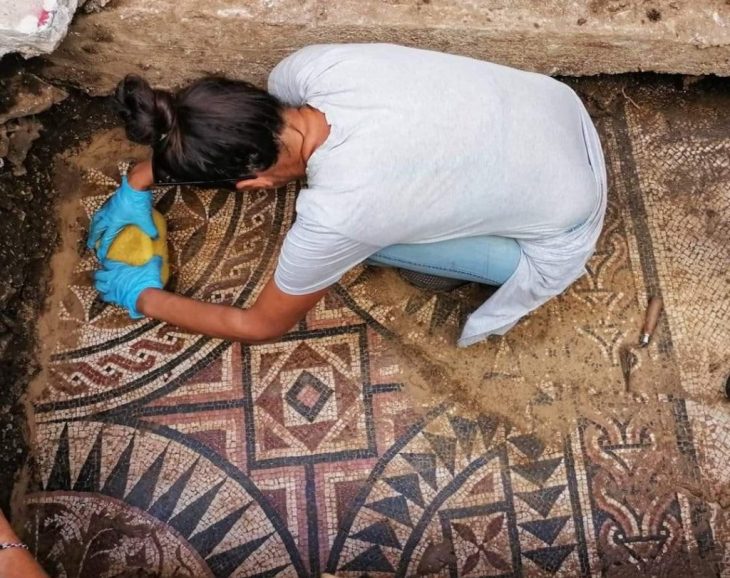
Göbeklitepe, Nevali Çori, Karahantepe, and Taştepeler, which will make us rethink what we know about human history, change the information about agriculture, belief, settled life, and question the history of religions, also sheds light on new information in terms of art history.
In the basins of the Euphrates, Tigris, and Jordan rivers, defined as the Fertile Crescent in the Near East, in all settlements since the beginning of the Neolithic Age, one encounters an extremely subtle, monumental, and sophisticated understanding of religious art and objects.
It would not be wrong for research to search for the factors that are effective in the formation and development of the social structures of the peoples of Southeastern Anatolia in these unique areas in the province of Urfa. This period is approximately the years 10200-7500 BC, the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A and B (PPNA-PPNB) periods.
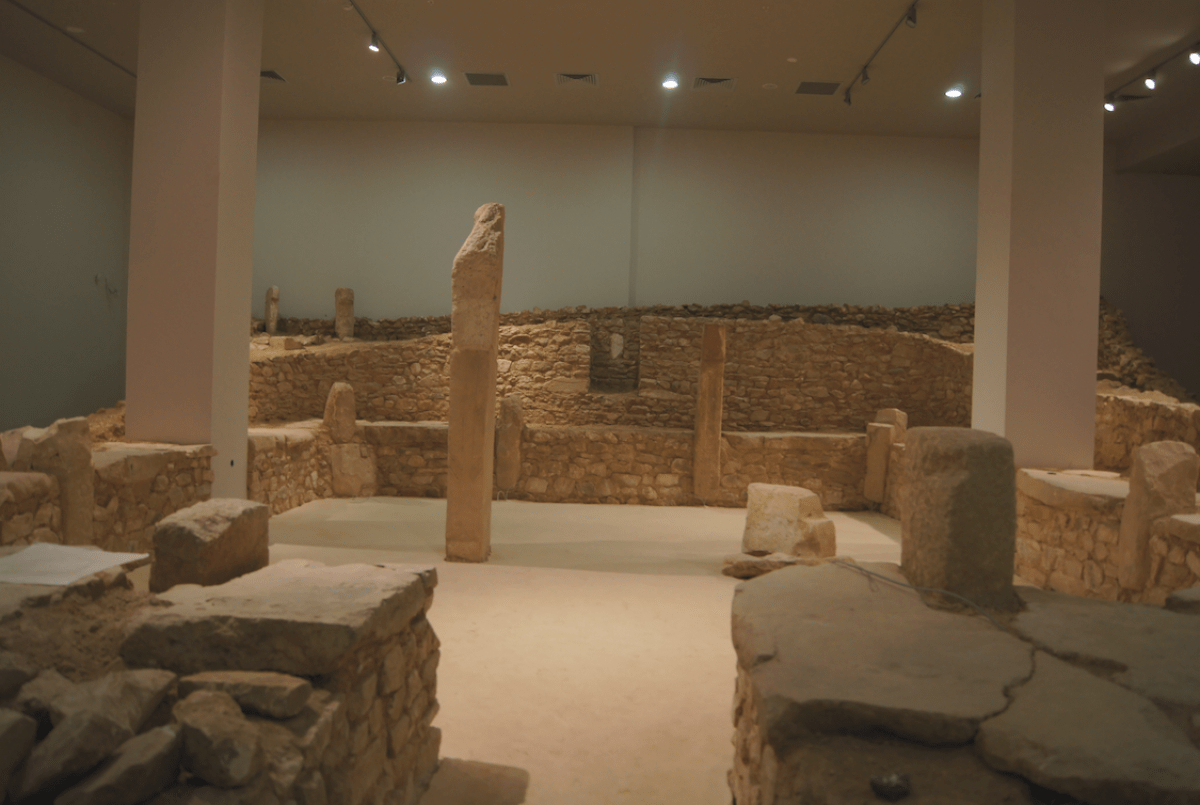
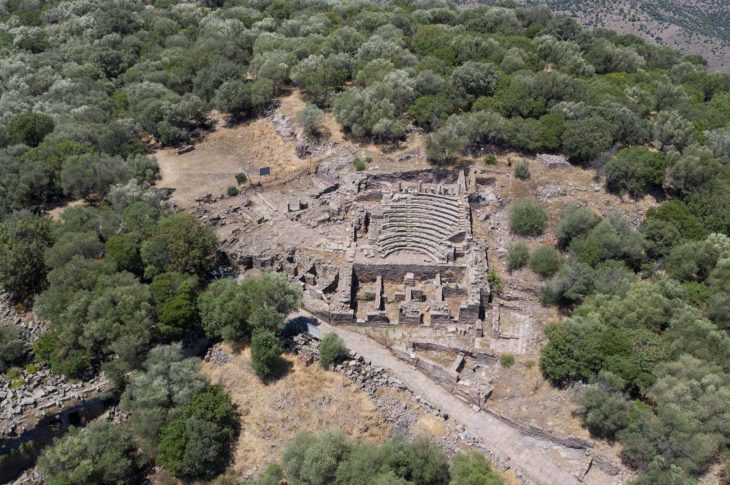
Although Göbeklitepe is known as the oldest and largest worship center in history, it is also a center that hosts the first examples of three-dimensional sculpture art in the world.

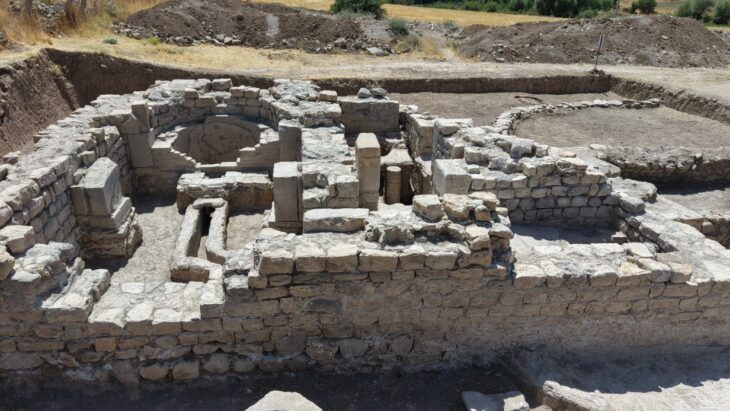
Four circular structures were unearthed at Göbeklitepe, and according to the layout, there are sixteen more similar structures waiting to be unearthed. The diameters of these round or oval structures vary between 10-30 meters The structures, each of which consists of concentric circles and narrow corridors between them, are equipped with stelae between 13 and 14, with an average of 12 adjacent to their walls and two more in the middle. Thus, in a ritual center like Göbeklitepe, we can talk about over 200 large stone columns in total. To date, about 50 of them have been excavated and unearthed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
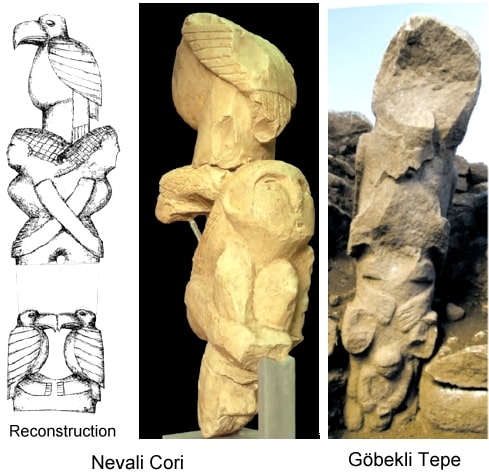
With their T-shaped obelisks at Karahantepe, Sefer Tepe, and Hamzan Tepe, all of which are also in Urfa, they seem to have a religious significance and serve a religious purpose. While 13 T-shaped stelae are seen in Nevali Çori, almost all of these styles are full of descriptions.
T-shaped steles are thought to represent human beings (anthropomorphic), with the horizontal part the head and the vertical part the body. The stylized depictions of human arms and fingers on both some late examples at Göbeklitepe and the Nevali Çori obelisks support the idea that T-shaped columns symbolize humans.

Most of the 50 steles unearthed in Göbeklitepe have animal reliefs on them, and sometimes the column headings were engraved as animals. The most frequently depicted animals are the snake, wild boar, and fox, and there are also depictions of bears, cranes, vultures, wild donkeys, wild cattle, insects, centipedes, scorpions, leopards, and large reptiles.
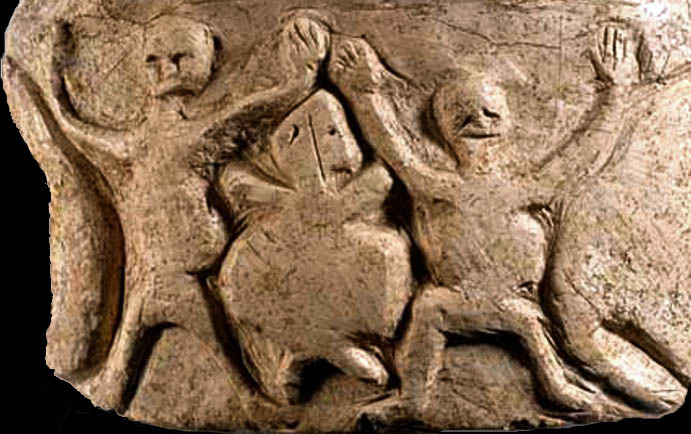
On the other hand, all the stelae in Nevali Çori are thought to represent a group of people dressed in a kind of special clothing similar to the cloaks of priests. In Göbeklitepe and Nevali Çori, apart from the animal reliefs and some symbols on the steles, some other monumental works of art are also encountered.

Especially in Nevali Çori, many monumental sculpture fragments were found. All but one of them were consciously embedded in the late stages of cult structure, that is, they were found in a secondary context. These finds are presentation objects left to cult structures.
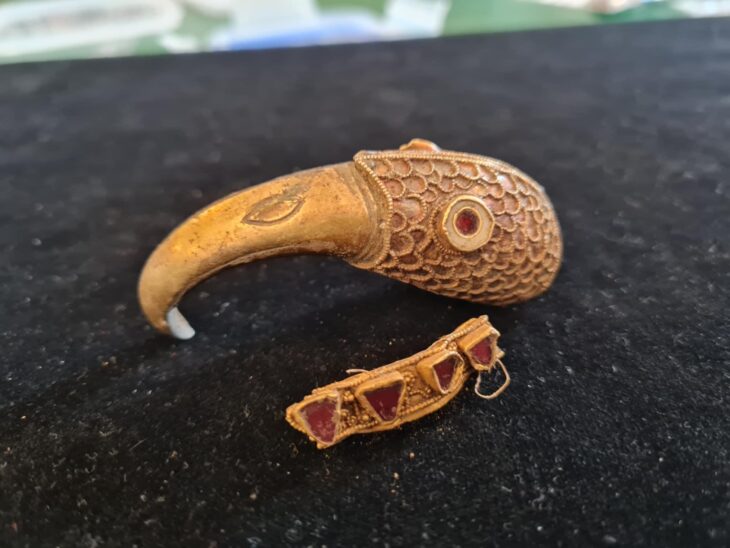
Among the statues in question, a bird, which is thought to be a stele head in a cult structure, caught the head of a woman with its claws is remarkable. The head of this bird, whose talons and torso have been preserved, is missing, but it probably belongs to a vulture, which should be related to the “cult of ancestors and skulls”.

A composite sculpture group with a half-meter-long flying bird, possibly a vulture, a hybrid creature with a bird body and a stylized human head, and two back-to-back female sculptures, possibly depicted with a vulture on their heads, which should also be a column capital. Other important and form symbolic cult objects.
When the scraping tools used in sculptures of this period are examined, it is understood that they consist of bone and flint. For this reason, it is understood that ceramics and sculptures made with clay are more understandable and detailed, while stone sculptures are in silhouette, without details. The biggest feature of the stone sculptures in Nevali Çori is their small size. Similar statues of these statues appear in Göbeklitepe in larger sizes. It can be said that the gigantic works to be built were designed in Nevali Çori and built-in Göbeklitepe.

German archaeologist Hauptmann Harald, who participated in the Nevali Çori excavations carried out before the Göbeklitepe excavations, wrote in an article, The fact that the sculptures made of stone are individual works suggests that they are models of large-scale sculptures,” he wrote.
Based on this, it is understood that it was designed in Nevali Çori before Göbeklitepe was built, and it was built in a period right after it. As Hauptmann stated, “They probably migrated to another place due to the effect of environmental conditions (flooding or excessive precipitation as a result of melting glaciers). Maybe the animal species decreased and they starved.”
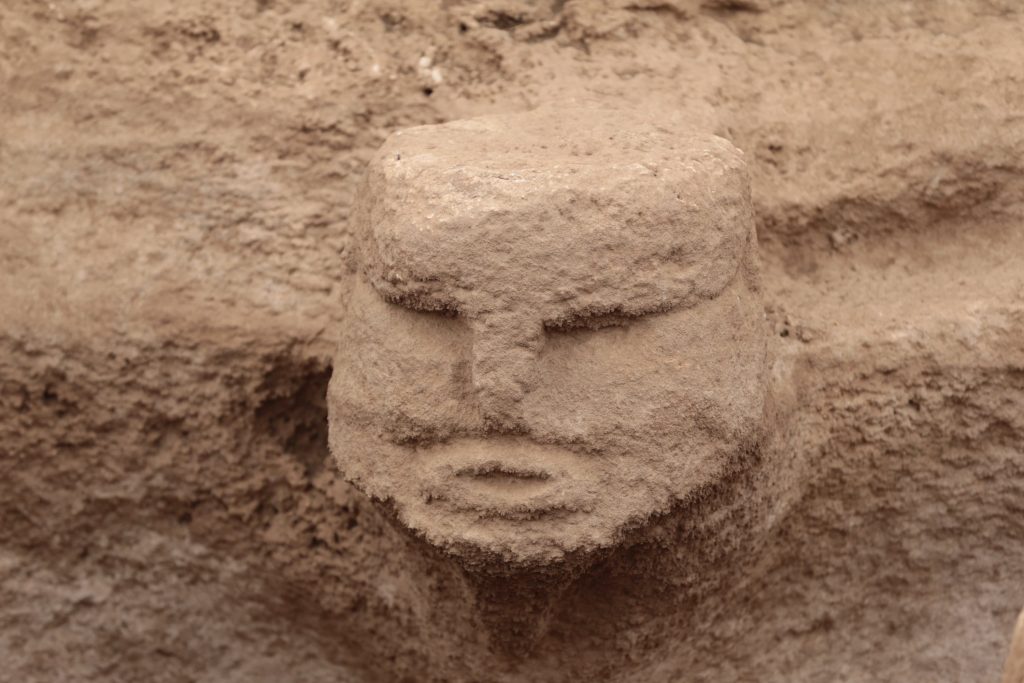

In this context, it can be thought that the Nevoli Çori civilization settled in Göbeklitepe, which is a higher place in the changing conditions, lived here for a long time, and completed its main development here.
However, why a region or area was considered sacred for the Prehistoric hunter-gatherers of the Near East is certainly not a question that can be answered with certainty. This question is actually valid for the selection of all sanctuaries that exist in every period and culture. Sometimes a water source, sometimes a location dominating the Harran Plain like Göbeklitepe and the environment, and sometimes proximity to a raw material source may have played a role in these choices.
In this article, excerpts are taken from Serap Özdol’s article “The Religion and Social Structure in Southeastern Anatolia in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Period”.
Cover Photo: Şanlıurfa Archeology Museum
















