The story of modern man’s migration from Africa still remains unclear in many aspects. Why did people migrate? Is it because of population density or food shortages? Or what routes did people use to migrate? Although the origin of modern humans is well known, the timing and routes of the spread to Eurasia are still controversial due to the lack of suitable ancient DNA and the scarcity of fossils.
A study by Nature Communications shows that climate affects the time and route of Homo sapiens moving out of Africa. This study emphasizes the role of paleoclimate variation in the spread of modern humans and can help us understand the evolutionary story of Homo sapiens.
Robert M. Beyer, Mario Krapp, Anders Eriksson, and Andrea Manica used paleoclimatic reconstructions and estimates of the minimum rainfall required for hunter-gatherers to survive to assess when and where favorable conditions may have contributed to expanding weather conditions and Enter the wet corridors of Eurasia.
Their models’ predicted times and routes are consistent with archaeological and genetic data, suggesting that numerous migrations out of Africa may have happened during the previous 300,000 years.
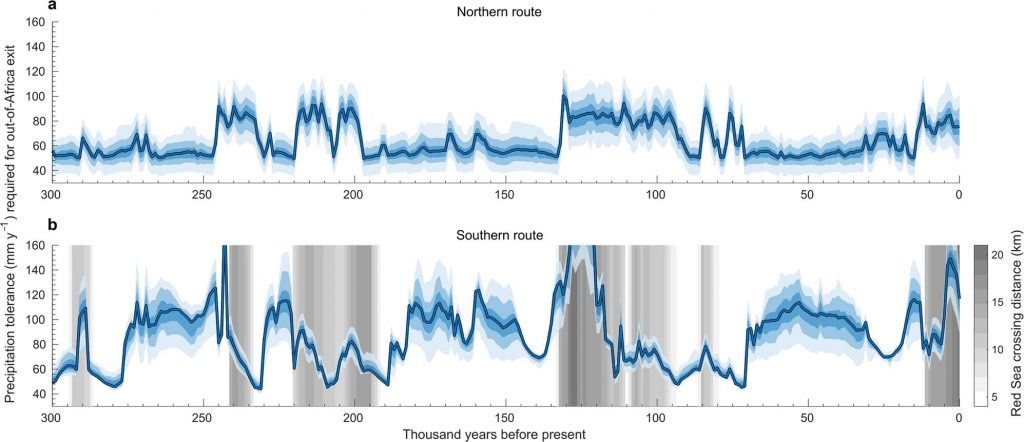
The authors propose that challenging environmental conditions in southwest Asia, the intermittent arrival of humans from Africa, and possible competition with other hominins may explain why early waves of Homo sapiens failed to settle permanently in Eurasia before a larger, highly successful wave of migration around 65,000 years ago.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to researchers, “Periods during which climatic conditions would have allowed Homo sapiens to leave Africa for Eurasia can now be estimated by combining the inferred tolerance requirements over time with actual tolerance thresholds of early humans.”
The authors conclude their research demonstrates when it would have been climatically feasible for Homo sapiens to migrate from Africa. However, further research is needed to explore whether these opportunities were seized.
doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24779-1
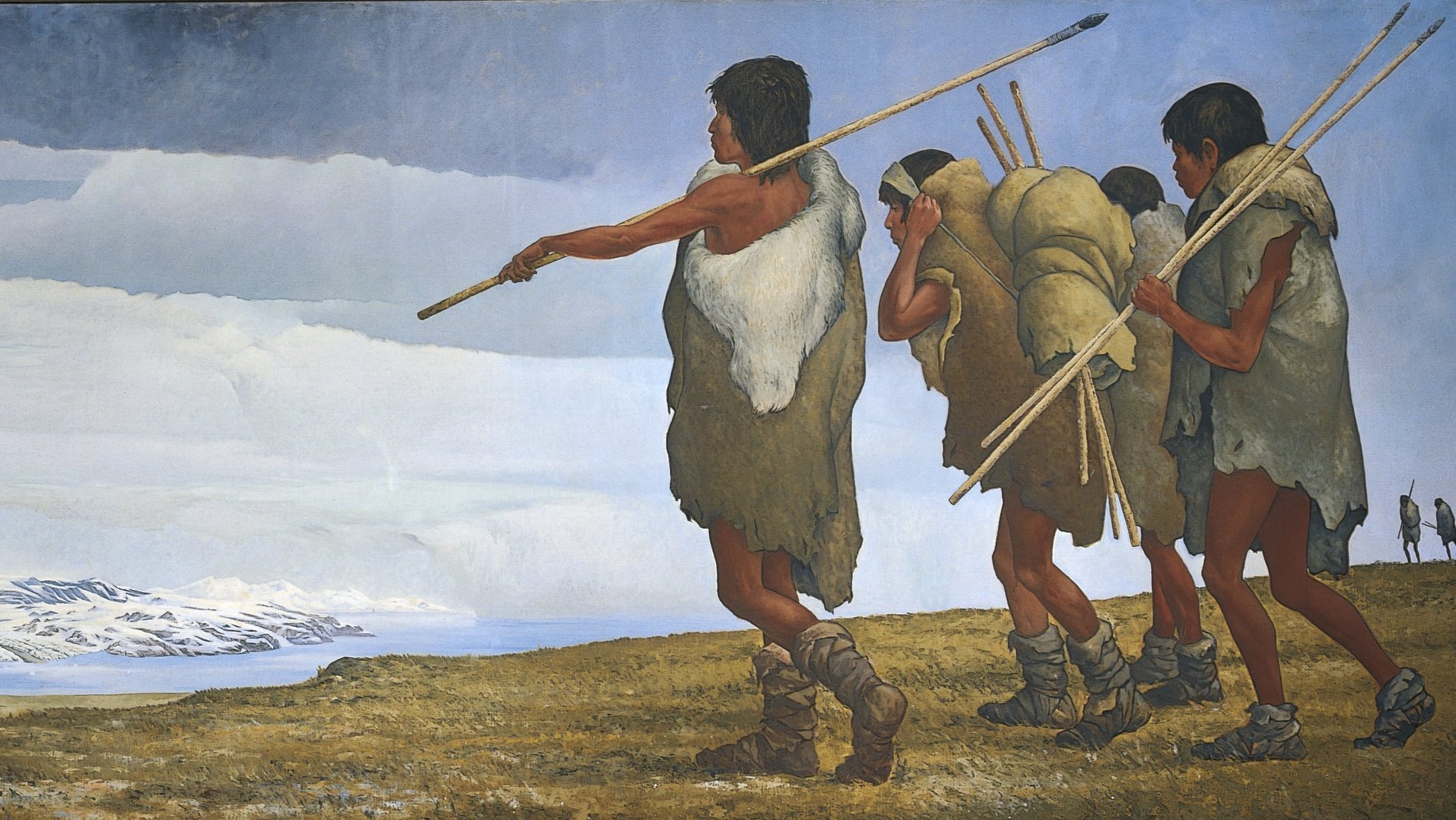
Over Photo: An artist’s re-creation of the first human migration to North America from across the Bering Sea.DEA Picture Library/De Agostini/Getty Images
















