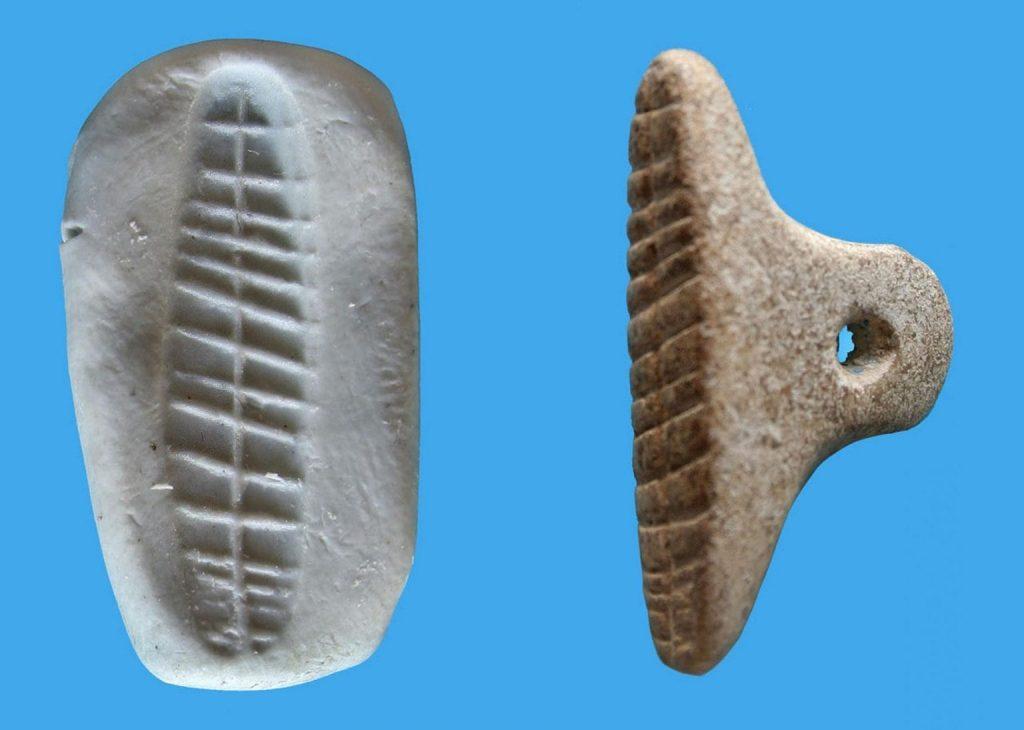
Israeli archaeologists unveiled a 7,000-year-old clay seal impression used for commerce and protection of property, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU) said.
A team of archaeologists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HU) made a rare discovery when they unearthed a small clay seal impression dating back some 7,000 years.
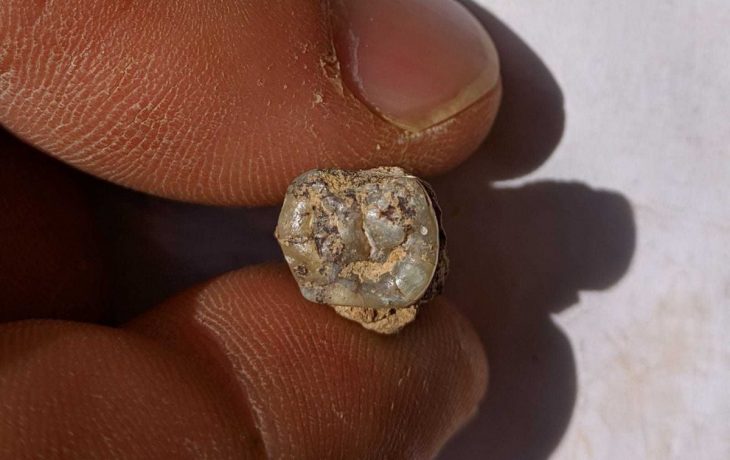
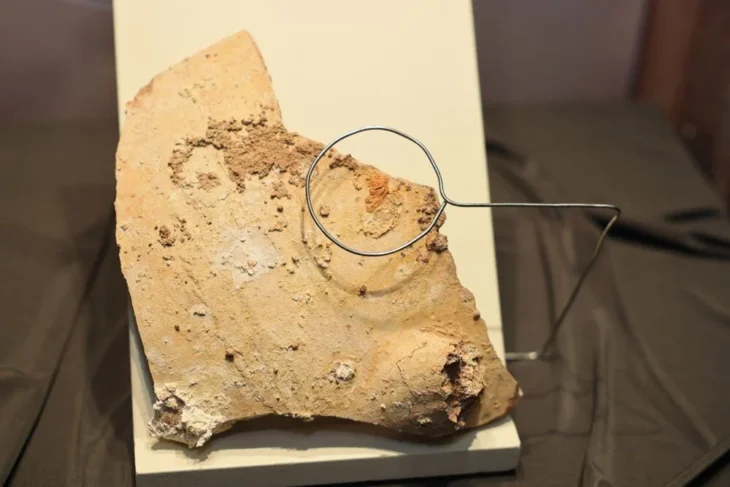
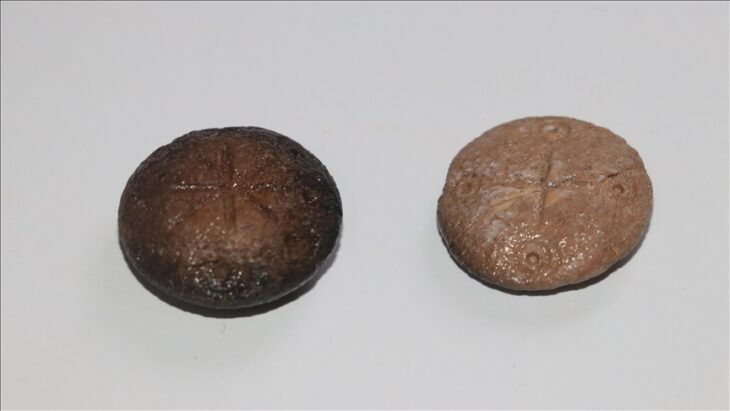
The impression, with two different geometric stamps imprinted on it, was discovered in Tel Tsaf, a prehistoric village located in Israel’s Beit She’an Valley in the country’s north.
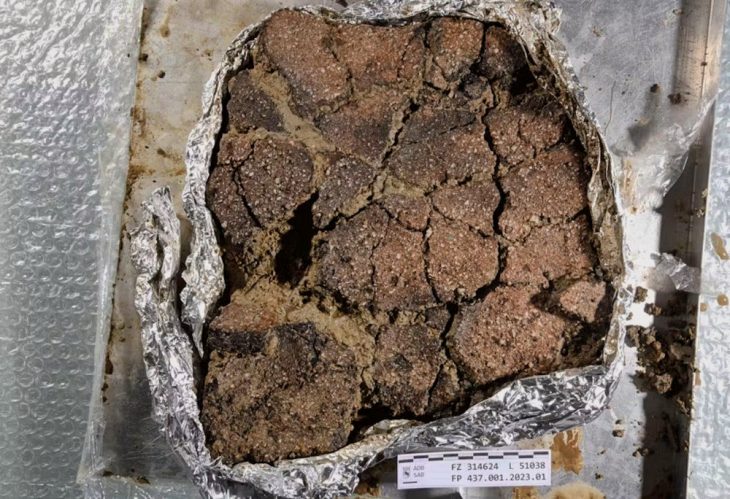
The finding was uncovered as part of an excavation headed by HU’s Professor Yosef Garfinkel and two of his students, Professor David Ben Shlomo and Dr Michael Freikman, both of whom are currently researchers at Ariel University, between 2004 and 2007. One hundred and fifty clay sealings were originally found at the site, with one being particularly rare and of distinct, historic importance. The object was published in the journal the Levant.
Sealings, also known as a bulla, are little pieces of clay that were used in ancient times to seal and sign texts, preventing others from reading their contents. The sealing discovered at Tel Tsaf is important because it is the first indication of the employment of seals to identify shipments or shutter silos or barns. When a barn door was opened, its seal impression would break – a telltale sign that someone had been there and that the contents inside had been touched or taken.

“Even today, similar types of sealing are used to prevent tampering and theft,” explained Garfinkel. “It turns out that this was already in use 7,000 years ago by land owners and local administrators to protect their property.”
The shard, which was less than a millimeter across, was discovered in excellent condition due to the dry environment of the Beit She’an valley. Symmetrical lines denote the sealing. While many sealings discovered in the First Temple Jerusalem (about 2,600 years ago) incorporate a personal name and occasionally biblical figures, the sealing from Tel Tsaf dates from a time before writing was invented.
Instead of lettering, their seals were embellished with geometric designs. The presence of two separate stamps on the seal imprint may suggest a type of business operation in which two separate persons were participating.
The found fragment underwent extensive analysis before researchers could determine that it was indeed a seal impression. According to Garfinkel, this is the earliest evidence that seals were used in Israel approximately 7,000 years ago to sign deliveries and keep store rooms closed. While seals have been found in that region dating back to 8,500 years ago, seal impressions from that time have not been found.
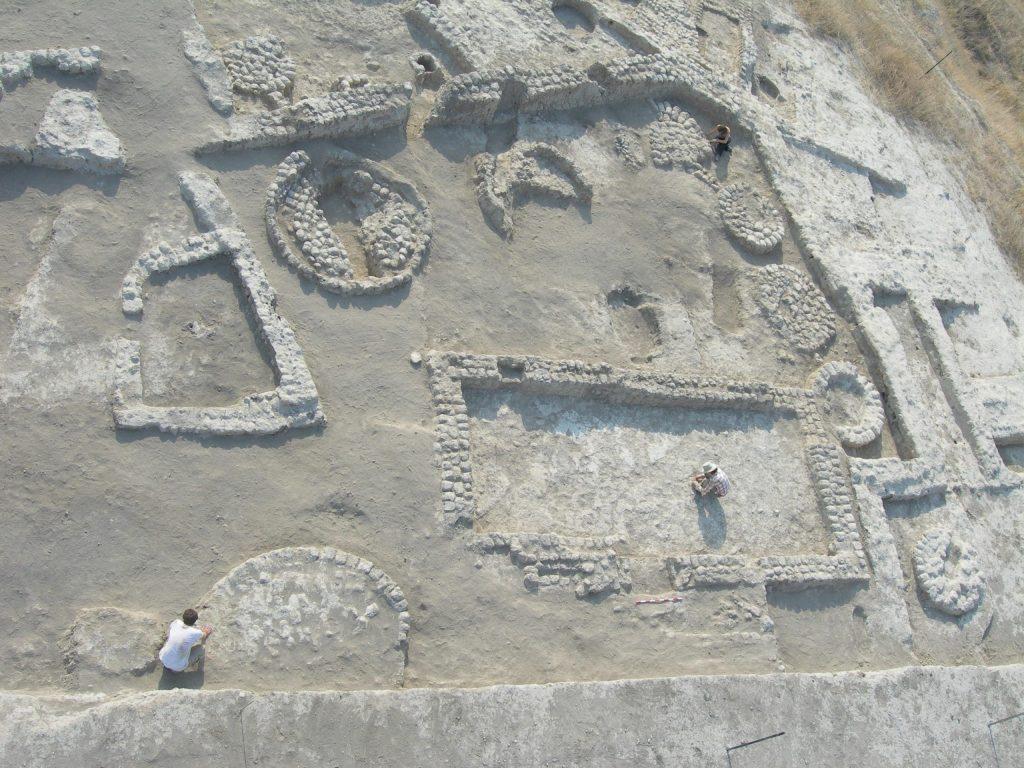

Based on a careful scientific analysis of the sealing’s clay, the researchers found it wasn’t locally sourced but came from a location at least ten kilometres away. Other archaeological finds at the site reveal evidence that the Tel Tsaf residents were in contact with populations far beyond ancient Israel.
“At this very site we have evidence of contact with peoples from Mesopotamia, Turkey, Egypt and Caucasia,” Garfinkel added. “There is no prehistoric site anywhere in the Middle East that reveals evidence of such long-distance trade in exotic items as what we found at this particular site.”
The site also yielded clues that the area was home to people of considerable wealth who built up large stores of ingredients and materials, indicating considerable social development. This evidence points to Tel Tsaf as having been a key position in the region that served both local communities and people passing through.
“We hope that continued excavations at Tel Tsaf and other places from the same time period will yield additional evidence to help us understand the impact of a regional authority in the southern Levant,” concluded Garfinkel.
Source: Israel National News